Generality
Breast needle aspiration is an examination aimed at taking a sample of breast tissue, in order to study it under a microscope.
Typically, this test is performed to analyze the cells that make up a lump or "area of breast tissue suspected at radiological (ultrasound and mammography) and clinical (breast examination) diagnosis.

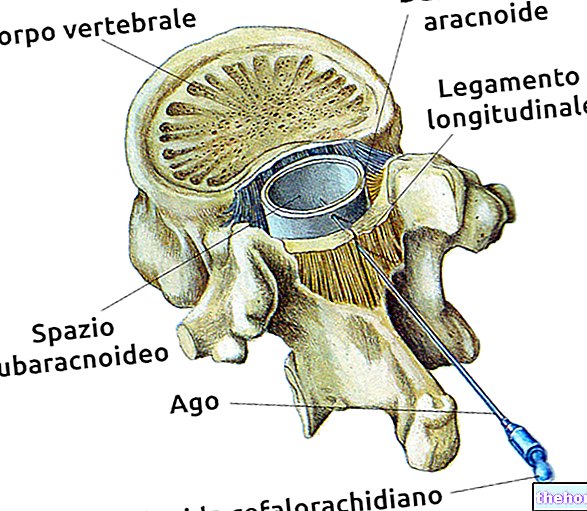
The technique is minimally invasive and involves the collection of a sample of cells or liquid to be subjected to cytological examination. The sampling is performed under ultrasound guidance, by introducing a very thin needle into the breast, until the suspicious formation is reached, from which part of the content is collected to be subjected to subsequent laboratory analyzes.
What is the Breast Needle Aspirate?
Breast needle aspiration is a procedure for integrating the radiological and clinical diagnosis of mammary gland pathologies, which allows to evaluate the presence or absence of cellular anomalies.
On the basis of the "outcome of the cytological examination", the specialist doctor will decide whether to proceed with further investigations and / or will establish the most appropriate therapeutic path for the case.
The method is performed with a fine needle (similar to that of a normal injection) and consists in taking a sample of cells or liquid from an area or a lump considered suspicious. Subsequently, the collected material is sent to the pathologist for the cytological study (ie of the cells) in the laboratory.
The procedure is complementary to the ultrasound examination of the breast and mammography: in case of suspected neoplastic formations, the cytological sampling allows to establish their nature and characteristics, excluding or confirming the diagnosis of malignant breast cancer.
The mammary fine needle aspiration therefore allows a more in-depth diagnostic classification: the cytological examination evaluates all the possible pathological aspects of the single cells present in the collected sample.
In most cases, the cytological sampling is carried out under ultrasound guidance (ie with the use of ultrasound) or radiography (in the case of mammography), to better locate the suspected lesion and reach the target exactly.
What does it mean to discover?
The fine needle aspiration allows to discriminate a benign alteration of the breast (as in the case of cysts and fibroadenomas) from a breast lesion of a malignant nature (carcinoma or other tumors).
Usually, the cytological sampling is performed following breast ultrasound and / or mammography, in the event that these investigations have highlighted suspicious lesions and a more in-depth diagnostic classification is required.
How is it done?
The fine needle aspiration consists in taking samples of breast tissue with a hollow needle, of similar caliber to that of a normal syringe.
During the examination, the needle is inserted into the breast through the skin, until it reaches the nodular changes or suspicious areas to be examined.
The fine needle aspiration can be performed with the help of the ultrasound guide or, if the mammary lumps are palpable, without the aid of imaging tools.
Withdrawal takes a few minutes. The patient is made to lie supine on a bed, with the arms turned up and the breast uncovered, in a relaxed and easy position for the doctor to perform the procedure. An ultrasound probe identifies the lesion and the point d is chosen. entrance of the needle.
The skin is disinfected and the collection begins: when the area is reached, suction begins, which allows a small fraction of cells to be collected. During this maneuver, the needle is moved repeatedly inside the lesion (back and forth, in multiple directions) to sample the most suspicious areas.
The cellular material collected in this way is placed on two or more slides, which will then be treated and studied under the microscope by the specialist in pathological anatomy, who will define the nature of the lesion.
The result is generally available within a few days.
When is it indicated?
- In case of a lump, a cyst, a mass or an area of suspicious and not better defined breast tissue, the fine needle aspiration can be indicated to study the cells that compose it and better understand their nature. This outpatient procedure therefore integrates the breast examination, breast ultrasound and / or mammography, in order to exclude any diagnostic doubts and have the most accurate response possible.
- The fine needle aspiration is also performed on known tumors, to monitor the effect of the treatment or to obtain samples to be subjected to diagnostic investigations.
- The method can also be used for the needle aspiration of suspicious lymph nodes both in the axillary area and in other locations.
- Breast needle aspiration can also be used for therapeutic purposes, for example to drain abscesses or to empty the fluid contained inside breast cysts, when these cause discomfort in the patient.
- This procedure may also be indicated for preoperative centering.This involves the introduction of a thin needle, through which a metal wire can be positioned (which will then be removed during surgery) or a few drops of a radioactive tracer are injected, in order to mark the site of the lesion that must be be removed by the surgeon.
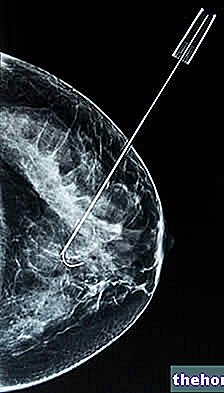
Difference between fine needle aspiration and needle biopsy
Breast needle biopsy and fine needle aspiration are procedures that have the same purpose: to take a small sample of tissue or cells for examination under a microscope and evaluate its nature.
The choice of the technique to be used is made by the specialist doctor on the basis of various factors, such as the characteristics, size or location of the formation to be analyzed.
Breast needle biopsy allows you to take a small portion of tissue from an area deemed suspicious. Compared to fine needle aspiration, this technique uses a larger gauge needle to remove a greater amount of material from the lump (called a frustule) and is generally performed under local anesthesia.
The substantial difference between the two techniques is, therefore, the greater invasiveness of the needle biopsy, which, however, in some situations is necessary to obtain greater diagnostic reliability.