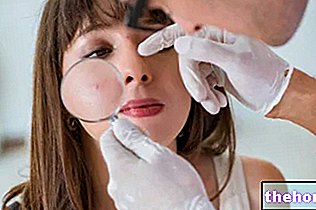
Angular or ring-shaped cheilitis is a small cut, sometimes resembling an abrasion, which occurs at the level of the labial commissures.
The main cause of cuts in the corners of the mouth is infectious, but malnutrition also plays a very important role.
Symptoms are typical of inflammation:

- Redness.
- Pain (especially in the opening of the mouth).
- Sometimes swelling.
- Wear of the skin.
Angular cheilitis occurs mainly in children, the elderly, and people who show predisposing factors.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of angular cheilitis; such indications must in no way substitute the opinion of the attending physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient. (candidiasis). It's possible to use:
- Medicines.
- In association, also natural remedies (phytotherapeutic).
- It is important to follow the celiac diet especially in the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms, generalized malabsorption and other symptoms of celiac disease.
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency.
- Iron deficiency.
- It is important to compensate for the iron and cobalamin deficiency, especially in the presence of anemia (iron deficiency, pernicious or both).
- Vitamin PP (niacin) deficiency.
- It is important to compensate for niacin deficiency, especially in the presence of dermatitis of the arms and neck, gastrointestinal disorders, anxiety and depression.
- Sweet and sour fruit: lemon, grapefruit, orange, mandarin, clementine, kiwi, cherries, strawberries etc.
- Vegetables and tubers: parsley, pepper, lettuce, spinach, radicchio, broccoli, tomato, potato, etc.
NB. Vitamin C or ascorbic acid is a thermolabile molecule and degrades with cooking. This means that to ensure its intake it becomes necessary to consume many raw foods. Furthermore, being involved in the absorption of the little available iron, it is important that it is taken with specific foods.
- To ensure the supply of vitamin B12 (cobalamin) it is necessary to eat:
- The same foods as a source of heme iron;
- Remember that certain foods may contain anti-nutritional principles that reduce the absorption of iron. To reduce its content, it is necessary to practice:
- Soaking.
- Fermentation (yeasts or bacteria).
- Cooking.
NB. Since cooking inhibits the nutritional principles but limits the availability of thermolabile vitamins, it is advisable that raw and cooked foods are equally present in the diet. It is advisable to reserve the heat treatment especially for legumes and cereals, while most fruits and some vegetables could be eaten raw.
- To ensure the intake of vitamin PP (niacin) it is sufficient to respect a varied but balanced diet. It is contained in: cereals, legumes, meats, eggs, fishery products and offal.
- In addition to the above, to help the immune system it is advisable to also consume:
- Probiotic foods.
- Foods rich in vitamin D and E.
- Foods rich in magnesium, zinc and selenium.
- Lysine and glycine amino acid foods.
- Foods rich in omega 3.
- Foods rich in polyphenolic antioxidants.
- Single-issue diets.
- Vegan diet.
- Diet free of vegetables and greens.
- Diets based solely on:
- Cooked foods.
- Preserved foods.
- Tormentosa Uncaria (Uncaria tomentosa)
- Echinacea (Echinacea purpurea)
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
- Antibacterial drugs:
- Especially Propolis.
- Itraconazole (eg Sporanox, tablets).
- Amphotericin B (e.g. Abelcet).
- Nystatin (for example Mycostatin).
- Cancidas (e.g. Caspofungin).
- Mycamine (for example Micafungin).