See also: blood test and high bilirubin
Bilirubin is a waste product deriving from the metabolism of hemoglobin (a protein present in red blood cells mainly responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the various tissues of the body).

As anticipated, most of the circulating bilirubin is produced during the catabolism of hemoglobin, which in turn results from the destruction of aged or damaged red blood cells. Only 10-20% of the circulating share (normal serum bilirubin levels: 0.3 - 1 mg / dl) derives from the catabolism of other hemoproteins (myoglobin, cytochromes, peroxidase, catalase) and abnormal erythroblasts (precursors of red blood cells produced in the bone marrow).
The bilirubin produced by these catabolic processes is known as free bilirubin, unconjugated bilirubin, or indirect bilirubin. By virtue of its fat solubility, indirect bilirubin is transported in the bloodstream by albumin, to which it binds with a "weak" bond. Also for this characteristic it cannot be filtered by the kidney, so it is not found in the urine.
Indirect bilirubin metabolism occurs in the liver.
The liver cells, called hepatocytes, sequester indirect bilirubin dissociated from albumin, incorporate it by diffusion or active transport across the plasma membrane, and prevent its reflux into the blood by binding to a protein, called ligandin. At this point, bilirubin is conjugated with two molecules of glucuronic acid, this reaction occurs inside the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocyte and is mediated by the enzyme bilirubin-glucuronyltransferase.
The substance resulting from the conjugation process (which occurs in two stages: bilirubin monoglicuronide → bilirubin biglicuronide) is known as conjugated or direct bilirubin. Being water-soluble, it is excreted with the bile.
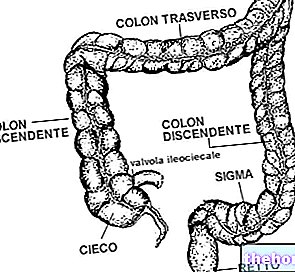
Through the bile flow, the direct bilirubin is poured into the intestine and precisely into the duodenum, where it flows through the choledochus. Most of it is then eliminated with the faeces, while a small percentage is transformed by the ileum and colon bacteria into " Urobilinogen ". This colorless substance undergoes a particular metabolism, which is easier to understand by looking at the image at the bottom of the article.
- In the terminal ileum and colon direct bilirubin is transformed into urobilinogen by bacterial beta-glucuronidase, which splits it to glucuronic acid and bilirubin; the latter is further processed and converted into urobilinogen, mesobilinogen and stercobilinogen, all colorless substances.
- The urobilinogen is mostly excreted with the faeces, in the form of colored pigments (stercobilin). A 20% is instead reabsorbed by the blood and conveyed to the liver, where it is again excreted with the bile.
- A small amount of the reabsorbed urobilinogen escapes the hepatic filter and is excreted in the urine, where it is oxidized to urobilin, the substance responsible for their characteristic color.
As anticipated, in the kidney the indirect bilirubin (unconjugated, bound to albumin) is not filtered by the glomeruli; as such, it is not found in the urine. On the contrary, conjugated or direct bilirubin does not need to bind to albumin, and being water-soluble it passes the glomerular filter; therefore, it can be found in the urine.
The amount of urobilinogen that has escaped the hepatic filter is also present in the urine, either as such or in the form of urobilin.

Select Blood Tests Blood Tests Uric acid - uricaemia ACTH: adrenocortitotropic hormone Alanine amino transferase, ALT, SGPT Albumin Alcoholism Alphafetoprotein Alphafetoprotein in pregnancy Aldolase Amylase Ammonemia, ammonia in the blood Androstenedione Antibody-endomysial antibodies Anti-gliadicides Nucleus Helicobacter pylori antibodies Embryo carcinoal antigen - CEA Prostate specific antigen PSA Antithrombin III Haptoglobin AST - GOT or aspartate aminotransferase Azotemia Bilirubin (physiology) Direct, indirect and total bilirubin CA 125: tumor antigen 125 CA 15-3: tumor antigen 19-9 as tumor marker Calcemia Ceruloplasmin Cystatin C CK-MB - Creatine kinase MB Cholesterolemia Cholinesterase (pseudcholinesterase) Plasma concentration Creatine kinase Creatinine Creatinine Creatinine clearance Chromogranin A D-dimer Hematocrit Blood culture Hemocrome Hemoglobin Glycated hemoglobin a Blood tests Blood tests, Down syndrome screening Ferritin Rheumatoid factor Fibrin and its degradation products Fibrinogen Leukocyte formula Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin GGT - Gamma-gt Gastrinemia GCT Glycemia Red blood cells Granulocytes HE4 and Cancer at "Ova" Immunoglobulins INR Insulinemia Lactate dehydrogenase LDH Leukocytes - white blood cells Lymphocytes Lipases Tissue damage markers MCH MCHC MCV Metanephrines MPO - Myeloperoxidase Myoglobin Monocytes MPV - average platelet volume Natremia Neutrophils Homocysteine Thyroid hormones OGTT Osmocyte Plasma protein A associated with pregnancy Peptide C Pepsin and pepsinogen PCT - platelet or platelet hematocrit PDW - distribution width of platelet volumes Platelets Plateletpenia PLT - number of platelets in blood Preparation for blood tests Prist Test Total IgEk Protein C (PC) - Protein C Activated (PCA) C Reactive Protein Rast Protein Test Specific IgE Reticulocytes Renin Reuma-Test Oxygen Saturation Sideremia BAC, BAC TBG - Thyroxine Binding Globulin Prothrombin Time Partial Thromblopastin Time (PTT) Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) Testosterone Testosterone: free and bioavailable fraction Thyroglobulin Thyroxine in the blood - Total T4, free T4 Transaminases High transaminases Transglutaminase Transferrin - TIBC - TIBC - UIBC - saturation of transferrin Transtyretin Triglyceridemia Triiodothyronine in the blood - Total T3, free T3 Troponin TRH and Troponins of s thymol to TRH TSH - Thyrotropin Uremia Liver values ESR VDRL and TPHA: serological tests for syphlis Volemia Conversion of bilirubin from mg / dL to µmol / L Conversion of cholesterol and triglyceridemia from mg / dL to mmol / L Conversion of creatinine from mg / dL to µmol / L Conversion of blood glucose from mg / dL to mmol / L Conversion of testosteronemia from ng / dL - nmol / L Conversion of uricemia from mg / dL to mmol / L





.jpg)


















