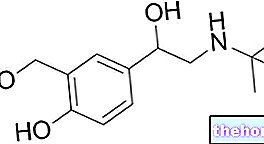
MAXAQUIN ® is a drug based on Lomefloxacin Hydrochloride
THERAPEUTIC GROUP: Antimicrobials - antibiotics for systemic use

Indications MAXAQUIN ® Lomefloxacin
MAXAQUIN ® is an antibiotic used in the clinic in the treatment of urinary tract and lower respiratory tract infections sustained by microorganisms sensitive to Fluoroquinolones and in particular to Lomefloxacin.
Mechanism of action MAXAQUIN ® Lomefloxacin
Lomefloxacin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic belonging to the category of second generation Fluoroquinolones, active against both Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, and characterized by the marked bacteriostatic activity exerted by the inhibitory capacity against some bacterial enzymes, such as DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerases, normally involved in bacterial DNA replication.
The bacteriostatic activity, effective even at minimal concentrations, also extends to the lower urinary tract thanks to some pharmacokinetic characteristics that allow the active principle to reach the urinary environment unaltered.
In fact, from a pharmacokinetic point of view, Lomefloxacin, taken orally, is rapidly absorbed in the intestine, reaching the maximum plasma concentration in just 90 minutes.
Distributed among the various tissues, with the exception of the nervous system, given the inability to cross the blood brain barrier with intact meninges, it carries out its therapeutic action, being metabolized only minimally by liver enzymes and therefore being excreted unchanged through the urine. .
These characteristics make the administration of Lomefloxacin effective and highly reproducible with the exception of patients with impaired renal function, for whom, unfortunately, continuous dosage adjustments are required.
Studies carried out and clinical efficacy
LOMEFLOXACIN vs CIRPFLOXACIN
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002 Jul; 20: 18-27.
Lomefloxacin versus ciprofloxacin in the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Naber KG; European Lomefloxacin Prostatitis Study Group.
Study comparing the therapeutic efficacy of Lomefloxacin to that of Ciprofloxacin in the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis, demonstrating similar results both in terms of side effects and therapeutic
LOMEFLOXACIN AND BACTERIAL CONJUNCTIVITIS
Clin Drug Investig. 1998; 15: 263-9.
Topical Lomefloxacin versus Topical Chloramphenicol in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Conjunctivitis.
Agius-Fernandez A, Patterson A, Fsadni M, Jauch A, Raj PS.
Work that demonstrates the efficacy of topical use of Lomefloxacin in reducing clinical complications associated with bacterial conjunctivitis, thus demonstrating antibiotic efficacy even when used topically.
DIFFUSION OF MULTI-RESISTANT STRAINS
Andrology. 2005 Jun; 37 (2-3): 61-4.
Chlamydia trachomatis survival in the presence of two fluoroquinolones (lomefloxacinversus levofloxacin) in patients with chronic prostatitis syndrome.
Smelov V, Perekalina T, Artemenko N, Smelova N, Ukleeva G, Gorelov A.
Interesting study demonstrating for the first time the onset of resistance mechanisms to fluoroquinolones and in particular to Lomefloxacin in Chlamydia Trachomatis, thus describing multidrug-resistant strains.
Method of use and dosage
MAXAQUIN ®
Lomefloxacin 400 mg tablets.
Generally the recommended dosage is one tablet a day for 7-14 days depending on the type of infection and its clinical severity, taking care to continue the therapy for at least 2-3 days despite the remission of symptoms.
In any case, the therapeutic scheme should be set by the competent doctor also based on the patient's physiopathological conditions.
MAXAQUIN ® Lomefloxacin warnings
In order to minimize the onset of clinically relevant side effects, thus safeguarding the efficacy and safety of the therapy, it is recommended to:
- Avoid exposure to ultraviolet radiation, given the photosensitivity induced by Lomefloxacin;
- Seek medical advice and supervision when suffering from kidney disease;
- Use MAXAQUIN ® with caution in case of enzyme deficiency of glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase.
PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
Known the pharmacokinetic characteristics of Lomefloxacin and given the absence of studies capable of evaluating the safety profile of the drug on the exposed fetus, the use of MAXAQUIN ® during pregnancy and in the subsequent breastfeeding period is not recommended.
Interactions
In light of the various pharmacokinetic studies in the literature, it would be advisable for the patient receiving MAXAQUIN ® to avoid the simultaneous use of:
- Foods, supplements and drugs containing divalent metals, given the ability to form chelating complexes, responsible for reducing the therapeutic efficacy of the antibiotic;
- Thiazanidine, methotrexate, theophylline, xanthines and phenytoin for the altered tubular secretion induced by Fluoroquinolone;
- Oral anticoagulants, due to the increased anticoagulant activity induced by Lomefloxacin.
Contraindications MAXAQUIN ® Lomefloxacin
The use of MAXAQUIN ® is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the active substance or to one of its excipients, during pregnancy and in the subsequent period of breastfeeding.
Undesirable Effects - Side Effects
The use of MAXAQUIN ®, especially when prolonged over time, could lead to the onset of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and in the most severe cases pseudomembranous colitis, headache, irritability, asthenia and sleep disturbances, photosensitivity, alterations in renal and hepatic function and osteoarticular disorders.
Note
MAXAQUIN ® is a drug subject to mandatory medical prescription.
The information on MAXAQUIN ® Lomefloxacin published on this page may be out of date or incomplete. For a correct use of this information, see the Disclaimer and useful information page.