Four types of prostatitis can be distinguished:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis;
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- Chronic Prostatitis Syndrome / Chronic Pelvic Pain;
- Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
Among the hypothesized risk factors we find: cystitis, compression of the prostate by other tissues, immune deficiencies, stress, localized trauma, urethritis.
diffuse, difficulty urinating, dyspareunia, pain during ejaculation and defecation, localized pain in the prostate, slow and painful passing of urine, bleeding with urine and rectal tenesmus.
Among the most frightening complications, we remember: epididymitis, orchitis, bacteremia (in case of bacterial prostatitis).
For further information: Prostatitis Symptoms and the most suitable dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment.
If in doubt, consult your doctor.
Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones are antibiotics that are generally used orally in the treatment of both acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis.
The treatment of prostatitis with this type of drug can last several weeks (even in chronic prostatitis it can be up to six weeks of therapy).
However, it should be noted that treatment with antibiotics should be guided by the results of the cultures carried out.
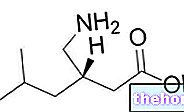
Among the active principles belonging to the family of fluoroquinolones that can be used orally in the treatment of prostatitis we mention ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin.
For further information: Fluoroquinolones: What Are They? What are they for? Side Effects and ContraindicationsBroad spectrum antibiotics
In some cases, it is possible to resort to the use of broad spectrum antibiotics, such as penicillins or cephalosporins.
The use of intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics can be done in hospitalized patients with suspected sepsis. At this juncture, the use of antibiotics such as ampicillin (a penicillin) or gentamicin (an aminoglycoside antibiotic) could be used. However, even in these cases, antibiotic therapy is usually adjusted according to the results of the culture tests.
PLEASE NOTE
Of course, the use of antibiotics in the treatment of prostatitis is useful and should only be carried out in cases where the pathology is of bacterial origin.
NSAIDs
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) may be prescribed by the doctor in case of prostatitis to treat the pain that the disease can cause. In fact, these are drugs with both anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving activities.
Although many NSAID-based medicines are freely available without a prescription, you should always consult your doctor before taking them.
Alpha-blocking drugs
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe the use of alpha-blocking drugs. The use of similar drugs - whose activity consists in relaxing the smooth muscles of the bladder and prostate - could be useful in solving some urinary problems that occur. they can manifest in the context of prostatitis.
Among the active ingredients that can be used we mention terazosin, tamsulosin and doxazosin.
PLEASE NOTE
We remind you once again that the choice of the active ingredient to be used in the treatment of prostatitis is up to the attending physician or specialist; therefore, it is advisable to follow the instructions provided by them. If you have any doubts, please contact these health professionals.