Definition
Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory disease affecting the bronchioles.
This disease is typical of childhood and affects, in particular, children under the age of two. However, there is the possibility that bronchiolitis may also arise in adults, although - in this last category of patients - very often disease is asymptomatic.
Causes
The underlying cause of most cases of bronchiolitis is a "viral infection sustained by the respiratory syncytial virus (or RSV).
Transmission of the virus occurs by air, through the saliva and / or nasal secretions of infected individuals.
Symptoms
Symptoms that may occur in patients with bronchiolitis are: dyspnoea, wheezing, respiratory distress, irritated and panting cough, tachycardia, irritability, tachypnea, cyanosis, insomnia, nausea and vomiting.
The information on Bronchiolitis - Bronchiolitis Cure Drugs is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Bronchiolitis - Bronchiolitis Cure Medicines.
Medicines
In many cases, bronchiolitis tends to regress spontaneously within a few days, without resorting to the use of drugs.
When, on the other hand, bronchiolitis does not regress by itself, but requires treatment, the main therapeutic strategies that are undertaken consist in rehydration and oxygenation of the patient.
Sometimes, the doctor may also decide to resort to the use of bronchodilator drugs to help the patient breathe better, even if, in reality, the occlusion of the airways is not caused by a bronchospasm, but by the thickening of the bronchial walls and from the accumulation of mucus.
Finally, in pediatric patients in whom bronchiolitis is associated with other pathologies, such as congenital or pulmonary heart diseases, cystic fibrosis or hypertension, treatment with inhaled antiviral drugs can be undertaken.

The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against bronchiolitis and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the active ingredient and dosage most suitable for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment.
Bronchodilators
In some cases, for the treatment of bronchiolitis - or rather, to counteract the breathing difficulties it causes - the doctor may decide to resort to the administration of bronchodilator drugs.
Among the different types of bronchodilators, we find:
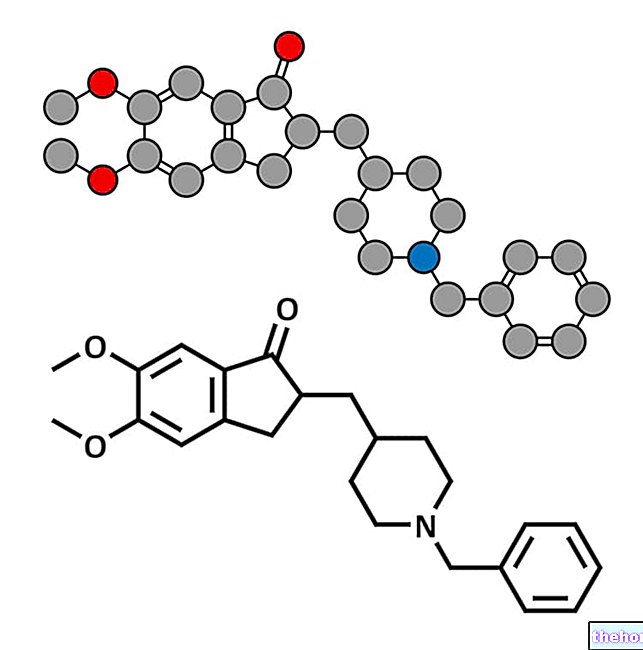
- Formoterol (Symbicort ®): Formoterol is an active ingredient belonging to the class of selective long-acting β2-adrenergic receptor agonists and is administered by inhalation.
In adults and adolescents over 18 years of age, the usual dose of formoterol is 12-24 micrograms, to be taken twice daily.
In children from six years of age onwards, however, the dose of drug usually administered is 12 micrograms twice a day. - Ipratropium bromide (Atem ®, Breva ®, Naos ®): ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic drug with bronchodilator activity. In adults and adolescents from 14 years of age onwards, ipratropium bromide is administered by inhalation at the dose 0.5 mg, two to four times a day, according to the doctor's prescription.
- Theophylline (Theolair ®, Theo-Dur ®, Aminomal ®): theophylline is a methylxanthine with bronchodilator activity and is available in pharmaceutical formulations suitable for oral administration.
In adults, the usual dose of theophylline is 200-350 mg twice a day. In children, on the other hand, the quantity of active ingredient usually used is 100-200 mg, to be taken twice a day.
Antivirals
As mentioned, in pediatric patients in whom bronchiolitis is associated with congenital heart disease, lung disease, cystic fibrosis or hypertension, the doctor may decide to intervene by instituting antiviral therapy.
More precisely, the active ingredient used in these cases is ribavirin (Virazole ®) administered by inhalation in the form of an aerosol.
The dose of drug usually used is 6 g per day which must be dissolved in 300 ml of water for injections. The solution obtained must then be administered by inhalation, only and exclusively, through the special dispenser. In any case, when starting treatment with inhaled ribavirin, it is essential to strictly follow the instructions provided by the doctor.
Finally, it is very important to remember that the use of ribavirin is contraindicated in patients requiring assisted ventilation.
Other articles on "Bronchiolitis - Bronchiolitis Cure Drugs"
- Bronchiolitis in brief: summary on bronchiolitis
- Bronchiolitis
- Bronchiolitis: symptoms, diagnosis, therapy