What is it for?
Toothpaste is used to keep teeth clean, but also healthy and aesthetically pleasing, while refreshing the oral cavity. It is therefore not surprising that in supermarkets there is a huge selection of toothpastes available, with various formulations according to the intended use: normal, for sensitive teeth and gums, anti-tartar, whiteners, anticaries, enamel protectors, etc. The risk is, sometimes, that of letting oneself be influenced too much by messages or advertising images, when that of toothpaste should first of all be a conscious choice, which we want to support with this article.

First of all, it is important to remember that the fundamental basis for correct oral hygiene consists in the mechanical removal of food residues that feed the bacteria, and in the disintegration of the plaque adhering to the dental surfaces. Brushing is therefore the essential prerequisite for "adequate cleaning, while the toothpaste merely facilitates and assists its action, making it even more pleasant thanks to the flavorings it contains, which help to leave the breath fresh. Inside" however, some chemical substances with particular properties may be present in toothpastes (anti-plaque, mineralizing, anti-tartar, etc.).
To learn more: Children's Toothpaste: the 5 Best according to Amazon Reviews toothpaste, which however cannot replace it. In practice, the bacterial plaque is lifted by the toothbrush and the toothpaste completes the removal process by keeping it in suspension, enclosed in the bubbles of the foam. On the other hand, it is important to note that the use of toothpaste tends to reduce the effort and time necessary for carrying out an adequate brushing; the foam it produces also prevents visual control of the position and movement of the brush bristles during cleaning operations. Also for this reason the toothpaste should be used in limited quantities, to avoid that the too strong taste and the consequent need to spit lead to stop the brushing action earlier than expected. Another reason why it is good not to overdo the quantities of toothpaste consists of the risk of absorbing excessive amounts of fluoride; this mineral, in order to fix itself on the teeth, however, needs to be kept in place for an adequate time..
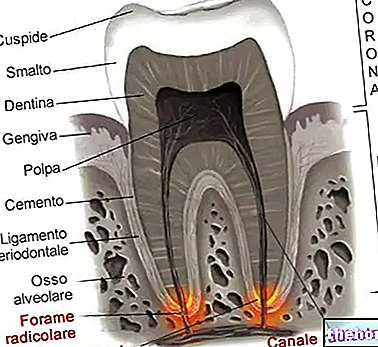
Especially in the so-called whitening toothpastes there is the risk of scratching or excessively abrading the enamel and dentin, increasing the risk of cariogenic phenomena and dental sensitivity, especially in the case of uncovered collars.
The abrasive power of toothpaste is related to the ingredients, but above all to the size of the particles and the shape of the microgranules.
According to the American Dental Association (ADA), in order not to cause damage to the enamel, the abrasiveness index of a toothpaste must vary, on the RDA scale (acronym for Relative Dentin Abrasivity), from 50 to 200.
According to the abrasiveness, toothpastes are divided into four bands:
- Low abrasion toothpastes (60 to 70)
- Medium abrasive toothpastes (70 to 100)
- Moderately abrasive toothpastes (100 to 120)
- High abrasion toothpastes (120 to 200)
An excessively high RDA value (greater than 200) can cause damage to the enamel over time. The American Dental Association recommends not using toothpastes with abrasiveness greater than 30 RDA in the case of sensitive exposed dentin; in the presence of healthy teeth and gums, the ideal abrasiveness coefficient should however not exceed 75 RDA.
PLEASE NOTE: Liquid or gel toothpastes are generally less abrasive than pasty ones.
No less important than the degree of abrasiveness of the toothpaste are the brushing technique and the type of toothbrush; it is therefore important to avoid too vigorous brushing and to prefer toothbrushes with soft bristles.
/ desensitizer and the refreshing component of the breath. If in doubt about the choice and use of toothpaste, consult your dentist or dental hygienist.What to pay attention to
Toothpaste should be kept away from younger children, as the pleasant taste may lead them to ingest it in large quantities.
For further information: Guide to choosing toothpaste