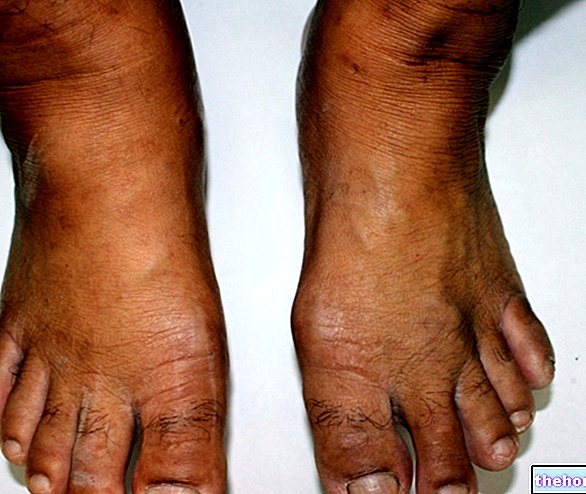
Venous insufficiency can be related to pathological changes in the veins (stasis dermatitis, deep vein thrombosis, varices) or to functional overloads to which they are subjected (eg lymphedema, postural alterations, etc.).
on the skin;Did you know that ...
Some symptoms - such as, for example, heaviness, swelling / tension in the legs and pain along a varicose vein - can be accentuated in certain specific circumstances: pregnancy, prolonged standing (standing position), menstrual cycle.
intracapillary that characterizes venous insufficiency can cause:
- Increased risk of bacterial cellulite;
- Skin dystrophies: this is a degenerative skin disorder that appears dry (xerosis cutaneous), wrinkled and inelastic;
- Ischemia;
- Skin ulcerations;
- Varicophlebitis: formation of a secondary thrombus arising on varices.
Differential diagnosis with other diseases that could cause similar symptoms is important, such as:
- Contact allergy;
- Basal cell carcinoma;
- Bacterial cellulitis;
- Stasis dermatitis;
- Erysipelas;
- Skin manifestations of heart / kidney diseases;
- Telangiectasias;
- Trauma ulcers;
- Varicose veins.
Classification of venous insufficiency
The clinical classification of venous insufficiency will be reported below, which provides for the subdivision into different classes:
- Class 0: absence of visible or palpable clinical signs of venous disease.
- Class 1: presence of telangiectasias or reticular veins.
- Class 2: presence of varicose veins.
- Class 3: presence of edema.
- Class 4: trophic disorders of venous origin (pigmentation, eczema, hypodermatitis).
- Class 5: as class 4 with healed ulcers.
- Class 6: as class 4 with active ulcers.
Among other useful measures to manage venous insufficiency, we remember:
- Use of elastic stockings / compression bandages, indicated to relieve swelling in the legs and reduce pain;
- Avoid remaining in static positions for long periods: subjects who, for work reasons, are forced to remain seated for many hours, should move their limbs from time to time, in order to favor the return of blood to the heart;
- Avoid staying upright, almost motionless, for a long time;
- Avoid staying in hot environments, with high humidity, for long periods: this behavior favors vasodilation;
- Application of creams or ointments with capillary-protective, anti-edema and decongestant action: preparations formulated with extracts of sweet clover, red vine, horsetail, anise, marjoram, witch hazel and ginkgo biloba are particularly suitable.
The implementation of these simple measures reduces the risk of venous insufficiency in predisposed patients and speeds up healing in affected subjects.
For further information: Remedies for Venous Insufficiency
Medicines for the Treatment of Veosa Insufficiency
If he deems it necessary, the doctor may decide to resort to the administration of some drugs that can help in relieving the symptoms but which are not able to cure the disease itself.
Among the drugs that can be used we find:
- Phlebotonic drugs: increase the tone of the venous wall, consequently reduce the feeling of fatigue and heaviness in the legs;
- Anticoagulant drugs (useful, for example, in the presence of deep vein thrombosis);
- Fibrinolytic drugs.
Surgical Treatments
When venous insufficiency is associated with severe skin ulcers, pathological thickening of the skin (lipodermatosclerosis) and disabling pain in the legs, the specialist could consider resorting to surgical treatment:
- Valvuloplasty: involves the repair of one or more valves of the circulatory system altered by pathological conditions, without however resorting to their replacement with a prosthesis.
- Removal of the diseased venous portion with subsequent reconnection of the tracts upstream and downstream of the excision: indicated in case of venous insufficiency dependent on varicose veins.
- Radiofrequency ablation: surgery which, thanks to radiofrequency energy, allows to heat the wall of the varicose veins involved in venous insufficiency. The vein can be accessed through a small cut usually above the knee. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to insert a catheter into the vein involved in the pathology. Inside this catheter radiofrequency energy is transmitted (thanks to a special probe or source): the energy subjects the vein to heating, which damages its walls by closing and blocking it. At this point the blood will naturally be redirected to a collateral circulation, flowing into one of the healthy veins.
- Laser therapy: similar to the previous intervention, laser therapy also makes use of the help of an ultrasound guide and involves the insertion of a catheter into a vein. A laser beam, which is passed through the catheter, releases the energy necessary to heat the wall of the varicose vein responsible for the venous insufficiency to the point of occluding it. Subsequently, the blood will naturally be redirected to one of the healthy veins through a collateral circulation.
PLEASE NOTE
It is up to the doctor and specialist to choose which treatment is best suited to each patient; treatment that can vary according to the severity of the venous insufficiency, the triggering cause and the presence of other associated disorders or diseases.