What is gastritis?
The term "gastritis" identifies a disorder characterized by a complex and heterogeneous set of symptoms triggered by inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the cause of origin, gastritis can take an acute or chronic course.

The diagnosis of gastritis is essential to trace the cause of the inflammatory process and remedy it through appropriate therapy.Acute gastritis - especially if dependent on an incorrect diet - are easily resolved through appropriate dietary measures (see: diet and gastritis) and possibly pharmacological. The chronic forms, on the other hand, require more in-depth diagnostic investigations and also the therapy is generally more complex and articulated.
Diagnosis
Any suspicion of gastritis must be investigated by means of appropriate diagnostic-investigative tests; among these, the diagnosis makes use of:
- Patient history: often sufficient for the doctor to hypothesize an ongoing gastritis and formulate hypotheses about its origin
- Test for " Helicobacter pylori:
- Blood test (Complete blood count)
- Analysis of faeces (search for faecal antigens of the "Helicobacter pylori)
- Breath test (urea breath test)
- Gastric endoscopy, diagnostic test useful for viewing the internal walls of the stomach looking for any signs of inflammation that can confirm the diagnosis of gastritis
- Biopsy: involves taking a tissue sample from the stomach for a subsequent cytological laboratory investigation
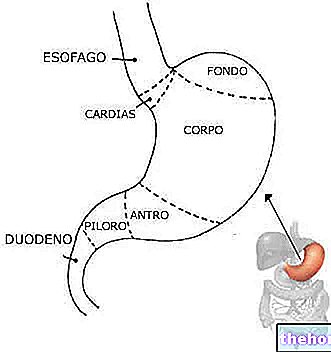
- X-ray of the upper digestive system, useful for obtaining an image of the esophagus, stomach and small intestine. It is sometimes performed to search for any abnormalities of the gastro-intestinal system.
Remedies, treatment and prevention
For further information: Medicines for the Treatment of Gastritis
Before embarking on any therapy for the treatment of gastritis, it is essential to go back to the triggering cause and understand if you are facing an acute or chronic form. The therapeutic approach for the treatment of acute gastritis is in fact different from the one undertaken for its chronic variant.
CARE FOR ACUTE GASTRITIS
- When acute gastritis is caused by alcohol abuse, it is necessary to stop taking it as soon as possible. In fact, alcohol irritates the gastric mucosa, making it more sensitive to the damaging action of gastric juices. We also remind you that alcohol - taken in high doses - favors the onset of gastritis because it reduces the amount of bicarbonate in the mucus. (For further information: read the article on alcohol and gastritis)
- Gastritis dependent on the abuse of NSAIDs requires the suspension of use of these drugs, naturally supervised by the doctor who will indicate the appropriate replacement therapy. If it is not possible to suspend a drug therapy that has proved to be gastrically damaging, it is suggested to associate it with gastroprotective drugs, capable of buffering gastric acidity. For further information, read the article "Gastro-damaging drugs that cause gastritis"
- Acute gastritis can be caused by an unbalanced diet characterized by spicy, fatty and irritating foods of the gastric mucosa. The phenomenon is accentuated if, in addition to taking foods that are contraindicated in the case of gastritis, meals are eaten quickly and without chewing properly. Incorrect food associations can also fuel the heartburn that accompanies gastritis. For further information: read diet and gastritis
- Nerve substances can accentuate heartburn. Coffee, for example, being an eupeptic substance (it stimulates the secretion of gastric juices to aid digestion) is included in the list of prohibited foods in case of gastritis. (For further information: read coffee and gastritis). Patients with or predisposed to gastritis should also limit their intake of cola, cocoa, guarana, tea and mate.
- Heavy smokers are also at risk for gastritis. Smoking, by dilating gastric emptying times, promotes gastro-duodenal reflux while reducing the secretion of bicarbonates. For this reason, smoking cessation is an effective remedy for gastritis, both to prevent it and to treat it.
- Although taken for granted, stress relief can help alleviate the symptoms of acute gastritis. For this purpose, it is advisable to engage in sports regularly, and to attend yoga or pilates courses.
In all the circumstances described above, the administration of antacids (e.g. aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide), gastric mucosal protectors or proton pump inhibitors can relieve heartburn, abdominal cramps and dyspepsia, speeding up recovery from gastritis.
Examples of the most used drugs in therapy for the treatment of gastritis
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs):
- Pantoprazole
- Lansoprazole
- Antacids:
- Aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide
- calcium carbonate
- sodium bicarbonate
- Protectors of the gastric mucosa:
- Sucralfate
- Compounds of bismuth
Nature can also help to alleviate the symptoms of gastritis. In this case, it is advisable to take mucilaginous and gastroprotective drugs (eg mallow, chamomile, aloe GEL, marshmallow, etc.), in the form of herbal teas or infusions. insights: read the article on natural remedies for gastritis.
CURE FOR CHRONIC GASTRITIS
For the treatment of chronic gastritis the therapeutic approach is more complex. This involves, on the one hand, minimizing the symptoms and, on the other, removing the responsible cause. In most chronic forms of gastritis, the main culprit is the "Helicobacter pylori. The infection requires a rather aggressive pharmacological approach which consists of a combined therapy (triple or quadruple therapy) which involves the association of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors and / or protectors of the gastric mucosa:
- Combination of two antibiotics: amoxicillin and metronidazole +
- PPI (eg Pantoprazole or Lansoprazole) +
- Gastroprotective drugs (eg Sucralfate)
We remind you, however, that alcohol can also cause chronic gastritis; therefore, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol or to follow a specific therapy for alcoholism.
The therapy for chronic gastritis always requires compliance with the dietary precautions described for acute gastritis.
Untreated gastritis can seriously affect the patient's health. Remember, in fact, that chronic gastritis - especially caused by "H. pylori - considerably increases the risk of stomach cancer.
Other articles on "Gastritis: Diagnosis and Cure"
- Gastritis: Symptoms and Complications
- Gastritis
- Atrophic gastritis
- Gastritis - Medicines to cure Gastritis
- Diet and gastritis
- Gastritis: natural remedies
- Gastritis: nutrition and natural remedies
- Remedies For Gastritis