Definition
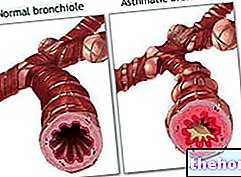
By bronchiolitis we mean an acute inflammatory process, characterized by the obstruction of the bronchioles (last bronchial branches): a typical early childhood disease, bronchiolitis causes breathing difficulties, serous nasal discharge, sneezing and loss of appetite.
Incidence
The target of bronchiolitis is represented by early childhood, in particular by children under the age of 2 years: infants, up to the age of six months, represent by far the category most at risk.

The degree of severity of the disease is inversely proportional to the age of the child: in other words, a few months old child suffering from bronchiolitis tends to present a much more severe symptomatological picture than an infected child of older age.
Medical statistics show that, for the same age, males are more at risk of bronchiolitis than females. Although bronchiolitis cannot be properly defined as a seasonal disease, in the winter period there are generally more affected children.
Globally, 150 million new cases of bronchiolitis are reported each year, of which almost all (95%) are observed in developing countries.
Bronchiolitis and colds
In the previous paragraph we have explored bronchiolitis in children: this does not mean, however, that this disease can also affect adults. In fact, bronchiolitis does not only affect infants: often times, however, bronchiolitis in adults is erroneously diagnosed as a simple cold or, in other cases, it is asymptomatic or in any case not very problematic.
Infection
Bronchiolitis is an infection that is transmitted by air, through saliva / nasal secretions of infected patients, or by means of micro-droplets of saliva that are dispersed in the environment following sneezing or coughing. After the infection, it is estimated that the incubation time of the microorganism is around 4 days: infected children can transmit bronchiolitis even after a week / 10 days from the infection.
Causes
The main etiopathological element responsible for bronchiolitis is a virus: in particular, it is the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Respiratory Syncytial Virus, or RSV).
The VRS is highly resistant to common antiseptic substances (disinfectants), as well as to the classic techniques of sterilization of the environment.
However, other possible microorganisms directly or indirectly related to the manifestation of bronchiolitis have been isolated:
- Influenza virus type B
- Parainfluenza viruses of types 1, 2 and 3
- Adenovirus types 1, 2 and 5: in this case, bronchiolitis is more precisely defined obliterating, as it destroys the small bronchial branches
- Rhinoviruses
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae: microorganism responsible for a particular form of bronchiolitis that affects school-age children.
- Chlamydia: unlike the microorganisms listed above, chlamydia is a bacterium: it is responsible for a particularly ferocious type of bronchiolitis, especially for newborns and infants up to 3 months.
[adapted from Handbook of Infectious Diseases, by Mauro Moroni, Spinello Antinori, Vincenzo Vullo]
Risk factors
Although the Respiratory Syncytial Virus constitutes the main causative element, bronchiolitis is also correlated to other risk factors, which affect in a more or less serious way according to the sensitivity of the subject and the age of onset of the disease.
Among the most alarming risk factors, the primacy certainly belongs to cigarette smoking: it has been shown that children born to smoking mothers are more exposed to bronchiolitis in the first months of life, since their lung parenchyma is strongly altered - especially in terms of elasticity - following intrauterine exposure to cigarette smoke.
Clearly, crowded places are also possible risk factors, as the probability of contagion increases considerably. Furthermore, lung diseases, heart diseases, prematurity of childbirth and artificial breastfeeding represent further factors that increase the risk of contracting bronchiolitis.
Other articles on "Bronchiolitis"
- Bronchiolitis: symptoms, diagnosis, therapy
- Bronchiolitis in brief: summary on bronchiolitis
- Medicines to Treat Bronchiolitis