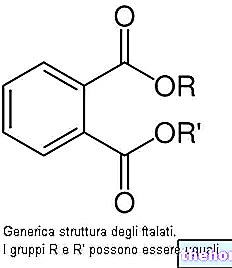
of calcium and inorganic acids, such as, for example, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Below is the chemical reaction that involves the use of this last acid:
Ca3 (PO4) 2 + 3 H2SO4 → 3 CaSO4 + 2 H3PO4
The thermal process, on the other hand, involves obtaining phosphoric anhydride starting from elemental phosphorus. Once formed, the anhydride must then be hydrated until orthophosphoric acid is obtained, as illustrated in the following reaction:
P2O5 + 3 H2O → 2 H3PO4
This latter process generally gives rise to a purer orthophosphoric acid than the wet process.
environmental, it appears as a white solid that melts at a temperature of about 42 ° C.
However, phosphoric acid is generally marketed in the form of a concentrated 85% aqueous solution. It is a colorless, odorless and non-volatile solution, but corrosive and with a rather dense, almost "syrupy" consistency.
In addition to being soluble in water, orthophosphoric acid is also soluble in ethanol. It is neither explosive nor flammable, but due to its corrosiveness to skin and mucous membranes, it must however be handled with great care.
in order to favor the adhesion of cementation materials for capsules, bridges, veneers, fillings, etc. In this context, orthophosphoric acid is generally used in 37% solutions.