What is Squalene?
Squalene is a triterpene, an organic substance widely found in nature. Particularly abundant in shark liver, from which it takes its name, it is an intermediate compound in the biosynthesis of sterols, very important substances in the physiology of animals and plants.

Functions
In the human body, squalene is one of the most important constituents of serum, an oily substance that keeps the most superficial layer of the epidermis hydrated by slowing down the evaporation of water. The sebum also protects the skin from insults of various kinds (detergents, products chemicals, microorganisms, solar radiation, etc.).
Some research also attributes to squalene a "protective action against skin cancer, thanks to its ability to fight free radicals and absorb harmful solar radiation.
Synthesis
In the human organism squalene is produced starting from the vinegar-CoA derived from the metabolism of varinutrients (carbohydrates, proteins and in particular fats) and is rapidly converted into cholesterol. At the level of the sebaceous glands, however, there is a lack of the enzymes necessary to carry out this conversion and it is for this reason that squalene is particularly abundant in the sebum.
Employments
Squalene is used in various fields, from the medical-pharmaceutical one, up to the field of cosmetics.
Medical-pharmaceutical field
Squalene is used in the production of vaccines, to enhance their activity thanks to its immunostimulating action (for more information:
Dangers of Squalene Contained in Vaccines).
Cosmetics
As mentioned, squalene is naturally part of the composition of the sebum, thus contributing to the maintenance of the hydro-lipid film that covers the epidermis.
It is thanks to the maintenance of the integrity of the hydro-lipid film that squalene is able to exert a "moisturizing action (preventing the" water contained in the deeper skin layers from evaporating) and a "protective action, protecting the skin and" organism from the aggression of pathogens.
The introduction of squalene in the cosmetic field is relatively recent and is justified by the properties attributed to it as well as those listed above and among which we also find:
- Soothing and emollient properties;
- Antioxidant properties, since squalene has been shown to be able to counteract the harmful action of free radicals and UV rays;
- Anti-aging properties (or anti-aging if you prefer).
Once applied, squalene is quickly absorbed without leaving the skin greasy, making it quite comfortable to use.
Anti-aging action
In the cosmetic field, the anti-aging activity is certainly one of the most appreciated properties of squalene.
Since the skin's sebaceous production decreases over the years, the use of ad hoc supplements and topical applications based on squalene can help reduce the signs of aging.
Furthermore, given its antioxidant and protective properties for the skin against UV rays, it can also be useful for combating and preventing photo-aging. Not surprisingly, free radicals and UV rays are among the main causes of premature aging of the skin, with the consequent appearance of the signs of aging such as wrinkles and skin spots.
At the same time, even the precious emollient and nourishing activities of which squalene is endowed can contribute to the anti-aging effect, preventing skin dryness, one of the predisposing factors for the onset of wrinkles.
Perhaps it was no coincidence, therefore, that the anti-wrinkle cream used by Cleopatra (69-30 BC) was based on olive oil (rich in squalene), milk, incense and juniper berries.
Side effects
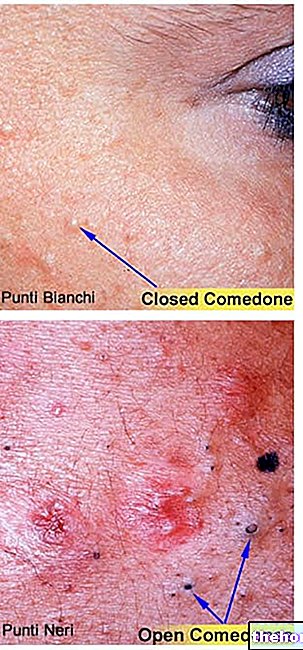
Normally, squalene used in cosmetics (therefore used topically) is well tolerated and does not cause side effects. However, in some cases, it has been shown to have comedogenic activity, therefore, its use in people with impure, combination or oily skin should be done with caution, preferably under medical supervision.
Furthermore, as with any other substance, squalene can also trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Background: Dangers of Squalene Contained in Vaccines
Squalane
Lo squalano (in English "squalane") is a derivative of squalene, obtained by hydrogenation of squalene, it represents the saturated form of this substance. The elimination of the double bonds decreases the susceptibility to oxidation and increases the shelf life of the product.

In a certain sense, squalane can therefore be defined as the "stable substitute" of squalene, precisely because it lacks oxidizable double bonds. However, squalane possesses properties similar to those of squalene. Therefore, it exerts a protective, moisturizing and emollient action on the skin.
Thanks to these characteristics and its particular stability, squalane is widely used in numerous skin care products and, in particular, in products for sensitive skin such as those of children (for more detailed information: Squalane in cosmetics).
Insights: Squalane in cosmetics