What is Folliculitis
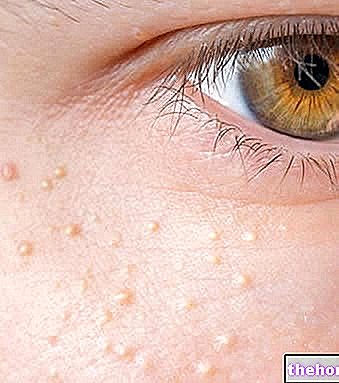
With the term folliculitis s "means a generic inflammation of the hair follicles. Fortunately, a minor disorder, superficial folliculitis begins with raised spots, filled with pus, which resemble small pimples. Generally, folliculitis manifests itself rather lightly; therefore , the skin lesions resolve spontaneously over a short period. Other types of folliculitis, on the other hand, are more severe, causing damage such as to require the use of antibiotic and / or cortisone creams.
In general, folliculitis can have an "infectious origin - therefore be caused by bacterial, viral or fungal infections - or non-infectious, therefore induced by other causes.

Infectious folliculitis
There are different forms of infectious folliculitis, which differ mainly on the basis of the etiological (causal) agent:
- Bacterial folliculitis (the most frequent form): typical infection that occurs immediately after epilating treatments (eg laser) and depilatory treatments (simple shaving), or after mechanical injuries or chemical trauma to the skin responsible for the deformation of the hair shaft
- Fungal folliculitis, is almost always caused by direct contact with objects or surfaces infected with fungi, such as common showers and changing rooms
- Viral folliculitis, typical of the area surrounding the lips
Based on the triggering pathogen and the characteristic symptoms, each type of infectious folliculitis is divided into several sub-categories. Let's see the main features, shown in the following table.
Non-infectious folliculitis
Not all types of folliculitis are caused by infections; there are, in fact, some variants that have nothing to do with infectious insults. Immunocompromised patients, suffering from obesity or dermatosis, and who have evident skin lesions are actually more at risk of folliculitis than healthy people.

Clump Folliculitis
Wispy folliculitis - also known as doll hair folliculitis - is a variety of descaling folliculitis, therefore typical of the scalp. It is characterized by the formation of pustules and inflamed areas within which there are tufts of hair that emerge from the same follicular ostium (hence the name of tufted folliculitis). Unfortunately, the course of this form of folliculitis is chronic-relapsing and tends to evolve into a sort of cicatricial alopecia.
Indeed, inserting tuft folliculitis between non-infectious folliculitis would not be entirely correct, since, in most cases, it appears to be secondary to a "staphylococcal infection. However, it has been observed that tuft folliculitis is not exclusively related to staphylococcal infections, but can also represent the consequence of other inflammatory diseases of the scalp which then lead to scarring alopecia.
Given the uncertainty of the triggering cause, the treatment of this form of folliculitis is rather difficult and often disappointing. Staphylococcus aureus in progress, the therapy that is usually undertaken is the same as described for transferring folliculitis.
Cheloid Folliculitis
Keloid folliculitis - also known as keloid nape acne - is a form of folliculitis typical of curly-haired males. It is characterized by the formation of papules, pustules and crusts behind the neck (nape) which then lead to the formation of keloid scars (from which the disorder takes its name).
Unfortunately, currently available therapies are not able to completely solve the problem. In some cases, laser therapy or liquid nitrogen cryotherapy may be helpful, but these types of treatments may not be suitable for all patients. For this reason, the doctor will have to decide on a strictly individual basis which therapeutic strategy to adopt.
Eosinophilic Folliculitis
Eosinophilic folliculitis is a type of folliculitis characteristic of severely immunocompromised patients, such as those with AIDS. This form of folliculitis is manifested by the formation of pus-rich lesions, particularly itchy, which appear mainly on the face, shoulders and forearm.
Eosinophilic folliculitis is characterized by the fact that it occurs in association with eosinophilia, that is, in association with an increase in the number of eosinophils in the peripheral blood.
However, it should be remembered that - although it has been observed with a higher incidence in AIDS patients - eosinophilic folliculitis can also occur in infants, newborns and healthy adults. In this regard, it is therefore possible to distinguish three different forms: eosinophilic folliculitis in the course of AIDS, eosinophilic folliculitis of the infant and eosinophilic folliculitis of adults (in health).
Pseudofolliculitis
As you can easily guess from its name, in this case it is not a real folliculitis, since the pimples that are formed do not contain pus. In reality, pseudofolliculitis is nothing more than the consequence of ingrown hair. This type of folliculitis, typical of people with curly hair and African Americans, can also cause scarring on the skin. One of the most well-known forms, surely, is the one that occurs in men at the level of the beard and which is commonly referred to as beard pseudofolliculitis, or irritative shaving folliculitis.














.jpg)











