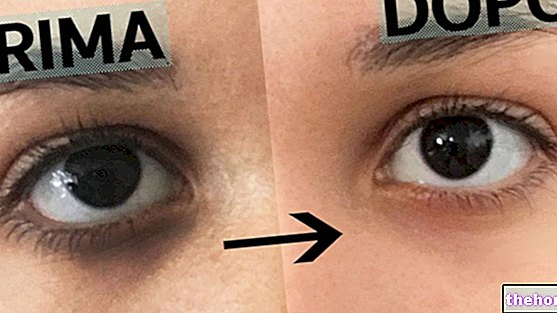
What are
The lightening creams belong to the numerous group of cosmetics designed to counteract the imperfections of time.

Data in hand, in Italy over 40% of women between the ages of 50 and 60 declare the presence of hypermelanic spots on their skin. Hence the need to use lightening creams to counteract the flowering of these dark spots, the result of an uneven distribution of melanin in the skin.
Deepening
Melanin is produced with a complex series of chemical reactions that begin with the oxidative catalysis of tyrosine by the enzyme tyrosinase.
This synthesis takes place inside the melanosomes, cellular organelles contained in the melanocytes. After that, the melanosomes move along the dendrites of the melanocytes and are transferred to the keratinocytes.Only at this point, the skin will tan, or give rise to skin spots.
Lightening substances
The lightening substances currently used to combat skin spots are different.
The most effective ingredients present in modern lightening cosmetic formulations include:
- L "ascorbic acid (or vitamin C);
- Azelaic acid is a natural substance produced by yeast Pityrosporum ovalis;
- Kojic (or kojic) acid, another natural molecule produced by fungi belonging to the genus Aspergillus;
- Arbutin, a substance naturally present in bearberry;
- Ellagic acid, a molecule with a strong antioxidant action present in numerous plants;
- Niacinamide (also known as nicotinamide, vitamin PP or vitamin B3), is a molecule produced by the body which - if applied topically - is able to exert a lightening action.
- Nonapeptide-1, a particular type of biomimetic peptide;
- Glycyrrhizin, contained within the licorice root extract.
Mechanism of action
The aforementioned lightening substances are able to carry out their activity mainly through different action mechanisms:
- By inhibiting or deactivating the tyrosinase enzyme, in order to block the biosynthesis processes of melanin from the very beginning;
- By preventing the migration of melanosomes towards keratinocytes. In this case, therefore, melanin has formed, but it does not reach the superficial layer of the skin.
- By counteracting the action of the melanotropic hormone MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone) produced by the pituitary. The task of this hormone is precisely to stimulate the synthesis of melanin by acting directly on the melanocytes present in the skin.
The table below lists the main lightening substances and their corresponding mechanism of action.
Cosmetic ingredient
Mechanism of action
Kojic acid
Deactivation of tyrosinase by chelation of the copper ion present in the enzyme.
Ascorbic acid
The antioxidant activity counteracts the oxidative phenomena underlying melanogenesis and accelerates skin turnover.
Azelaic acid
Inhibitory properties against tyrosinase.
Glycyrrhizine
Competitive inhibition of the tyrosinase enzyme.
Ellagic acid
Inhibits tyrosinase by copper chelation + antioxidant effect.
Arbutin
It inhibits the tyrosinase enzyme.
Niacinamide
It hinders the transfer of melanosomes from melanocytes to keratinocytes.
Nonapeptide-1
It is an antagonist of the MSH hormone and, moreover, it also exerts an inhibitory action against tyrosinase.
Effectiveness
The effectiveness of all the lightening substances described so far is now proven. However, their effect at the concentrations of use allowed in cosmetics is rather mild; it follows the need to use lightening products constantly and for prolonged periods.
Alternative methods
Much more effective in depigmenting terms, but also dangerous if used improperly, are chemical exfoliants, often used in combination with the aforementioned ingredients. These substances, among which mandelic acid and glycolic acid stand out for their notoriety, basically have the purpose of removing dead cells, rich in melanin, which tend to "cement themselves" on the surface. By acting in this way, exfoliants free the underlying epidermal layers, which are clearer and brighter, and promote epidermal turnover by stimulating the formation of new cells. These products, although potentially very effective, are to be absolutely avoided in case of sun exposure, during which you can still use creams with lightening cosmetic ingredients, as long as they are free of exfoliants and photosensitizing agents, and combined with a high sun protection, which prevents the synthesis of new melanin with browning of the areas predisposed to the onset of hypermelanosis.