Generality
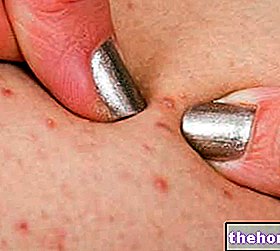
Acne is an inflammation of the pilosebaceous glands with papules (solid lesions, detected from the skin surface), pustules (more serious and disfiguring acne lesions, are due to the action of germs and arise on previous papules), comedones (or white spots and blacks), superficial, suppurated cysts (filled with pus) and, in severe cases, fistulizations (when the cysts join in the depth of the skin).

Each hair has an attached gland that produces sebum, that is the fat that makes the skin elastic and protects it.
If our skin produces excess sebum, it accumulates in the gland. At around 10 - 12 years of age, sebum production is highest, and it is also the time when acne breaks out.

All About Acne
How it forms
How does acne occur?
The "pore" from which the hair comes out becomes clogged and filled with sebum and small fragments of dead epithelial cells.
A white spot (closed blackhead) appears on the outside of the pore. The plug can open under the pressure of the sebum and a black spot (open blackhead) can form. Although ugly, it is less fearful, in fact it does not cause inflammation. If, on the other hand, the plug resists, the sebum accumulates in the canal where the hair is, until it tears the sheath that covers it and creates an inflammation.
If the epidermis ruptures, the classic "boil" (pustule) appears, or a papule appears.
If the inflammation cannot find a way out, cysts or nodules form.
Adolescent acne mainly affects the forehead and nose area; adult acne, on the other hand, affects the lower part of the face, neck and shoulders, or in any case all areas where there are more sebaceous glands.
Classification
To learn more: Acne Symptoms
It is useful to classify acne according to its characteristics; this will help both the patient and the doctor a lot.
In this regard, we can distinguish different types of acne:
- Mild comedonic: There are few blackheads on the forehead or nose.
- Severe Comedonic: The entire face and back are filled with blackheads.
- Papulus - Comedonica: there are comedones and more painful and red swellings.
- Papulus - Pustular: there are papules and also pustules.
- Pustular: It is characterized by widespread inflammation and almost all papules have turned into pustules.
- Pustule - Cystic: characterized by cysts, or hard nodules containing sebum and keratin.
- Cystic: cysts are much more numerous than pustules.
- Conglobata: Comedones aggregate and create deep lesions that will leave scars.
These types of acne are distinguished from another skin disease, called acne rosacea; it is a dermatosis caused by a parasitic mite, it is more common in women and is observed with redness of the face (cheeks, nose), papules, pustules and a severe itching The skin is seborrheic and very prone to redness.
Causes
The causes that provoke the appearance of acne can be of different origin and nature. Among these we find:
- Hormonal imbalances: the sebaceous gland, in response to male hormones (testosterone), present in both male and female, produces an excess of sebum. This does not mean that there is a hormonal imbalance, but simply the sebaceous gland "works" in excess.
- Bacterial Causes: Acne is favored by a bacterium called Propionibacterium Acnes which normally lives on the skin in physiological conditions. If skin pores become blocked, it multiplies and causes inflammation.
- Genetic predisposition: if we belong to a family where you have suffered from acne, we can prevent it.
Treatment
To learn more, read: Remedies for "acne"
There are several treatments that can be undertaken to defeat acne. Depending on the severity of the disorder and the cause that caused it, there are different approaches that can be taken: from natural or homeopathic remedies, up to real and your own pharmacological treatments that must be prescribed by your doctor or dermatologist.
To remedy the consequences of acne such as scars and various imperfections, however, you can resort to various types of aesthetic medicine techniques, always on the advice of your doctor or dermatologist.
In any case, for more detailed information about all possible acne treatments, please refer to the dedicated articles on this site.
Other articles on "Acne"
- Acne: causes and medications
- Acne: acne medications and treatments
- Acne - Acne treatment drugs
- Acne: natural remedies
- Acne homeopathy
- Diet and acne
- Acne: causes and medications