Edited by Dr. Gianfranco De Angelis
Many times we hear about training, training techniques, recovery from training, training stress, etc. But what is meant by training? And above all, what "is the right" training? First I will try to give a definition of training. apologizing in advance for any inaccuracies.

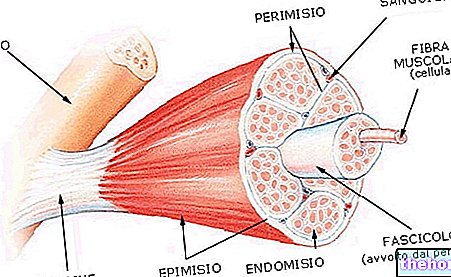
Training can be summarized in a set of physiological processes of adaptation of the organism to the repetition of a muscular work, which results in the improvement of the physical capacity of the body to perform a certain type of work.
The purpose of training is to obtain a greater capacity for mechanical work through an increase in muscle performance, muscle strength and energy availability of the muscles. It must be considered that the physiological effects of training, which increase muscle performance, consist above all in the dexterity with which a certain movement is performed, mainly using the muscles useful for the "motor act, and in the better regulation of the duration and rhythm of their contraction. In reality, this mechanism allows to eliminate the energy expenditure deriving from the" action of muscles not useful for that particular movement. The increase in muscle strength is fundamental as a training phenomenon; it is not only secondary to the increase in muscle mass due to hypertrophy, that is to the greater volume of the fibers and the filling of muscle capillaries with blood. In addition to the increase in the volume of muscle fibers and the number of blood capillaries, some biochemical processes are carried out in the trained muscle which enhance its energy possibilities, such as the greater concentration of myoglobin (a pigment similar to hemoglobin containing iron, which acts as a temporary reserve of oxygen for the muscle), some enzymes and glycogen. It is interesting to note that muscles trained in prolonged efforts are enriched with enzymes related to the best cellular transport of oxygen (aerobic condition). Those trained in intense and short efforts are enriched, on the other hand, with energetic substances of immediate use (adenosine triphosphate, phosphocreatine, etc. .); this type of biological reaction is considered as anaerobic adaptation (anaerobic condition). plastic materials; the improvement of the functional efficiency of the respiratory and cardio-circulatory systems also translates into their morphological changes, which are characteristic of subjects trained in various types of exercise. Red blood cells, and with them hemoglobin, also undergo variations in the different phases of the " training: the result is a better ability of the blood to oxygenate and tissues, which is useful for satisfying the peripheral muscle demands during the effort. The central and peripheral nervous system acquires a particular efficiency with training, especially for as regards the coordination and the speed of propagation of the stimulus, the adaptations of the endocrine glands, the functionality of all internal organs, the tone and excitability of the vegetative nervous system are also important. The set of adaptations of the organism allows the trained subject to increase his efficiency during the effort and recover quickly during the pause. The effects of training can be summarized in this combination.
In conclusion, with the training a set of positive phenomena for the human organism are realized which consist of:
- increase in muscle volume and strength, speed of contraction and muscle power;
- better neuromuscular coordination
- better cost-diaphragmatic dynamics and lung capacity
- increase in cardiac and coronary reserves; increased cardiac output; better regulation of district flows during work; better capillarization of the central and peripheral organs affected by muscle activity
- better peripheral use of oxygen during work;
- better thermoregulation during work;
- more efficient reaction stability of the organism towards environmental stimulus factors.
For all the types of benefits listed above, each individual should enthusiastically practice a healthy gymnastic-sporting activity, just enough to allow and maintain good physical efficiency. The best physical condition is obtained through a correct anaerobic (use of overloads) and aerobic (running, cycling, swimming, use of cardio-fitness machines, etc.) training program.