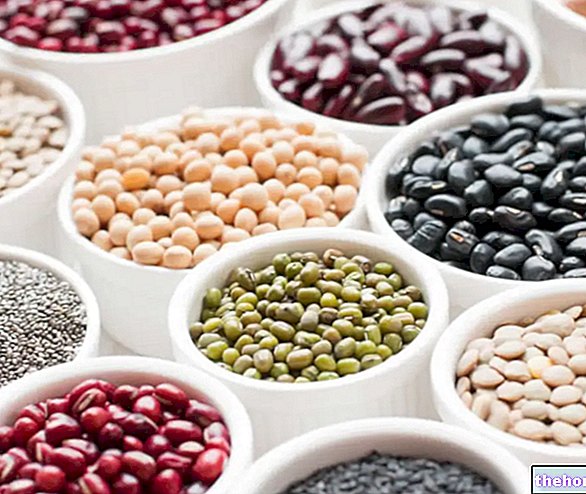
They are legumes: beans, peas, broad beans, chickpeas, lentils, soybeans, lupins, peanuts, cicerchie, caiani, carob etc.
Legumes are foods that boast an "extreme ductility; they can be used as a first course, as a side dish, as a second course (if combined with cereals) and some of their flours can be used in the food additives sector (thickeners - such as seed meal. of carob E410) or as a cutting substrate (for example chickpea flour) to reduce the amount of wheat in food products.
supercharge; in other words, teaching to use legumes as a substitute for refined grains (in people who tend to overindulge) leads to a significant reduction in excess calories, an increase in dietary fiber (with moderation of the global glycemic index and absorption of fats), a reduction in cholesterol by lecithin) and circulating triglycerides, and an increase in the intake of vitamins and mineral salts.
Compared to refined cereals and related starchy derivatives, legumes provide:
- More protein
- Less carbohydrates
- Less calories
- More dietary fiber
- More potassium (K)
- More iron (Fe)
- More calcium (Ca)
- More phosphorus (P)
- More thiamine (B1)
- More riboflavin (B2)
- More niacin (PP)
Furthermore, they do not contain gluten.
(average VB) and are made from a minimum of 18% (some chickpeas) to a maximum of 44.3% (dried lupins). The biological value is a qualitative evaluation parameter of food proteins that is based on the analysis of the essential amino acids contained in them; more precisely, the VB is given by the similarity in composition between the protein examined and the human one. It is expressed with a value numerical in turn referred to the protein nitrogen actually absorbed and used by the body, therefore net of urinary, fecal, skin losses, etc. (see the article: "Protein quality"). The reference protein for calculating the biological value is that of the egg, which has a VB = 100 (it is estimated that on 100 g of amino acids 32,256 g of essential aa and 67,744 g of non-essential aa are identified).
Note: the biological value shown in the tables refers to raw foods; they, after firing, have a considerably reduced VB. It follows that: almost all dietary proteins (including legume proteins), compared to those of human tissues or raw eggs, are deficient in one or more essential amino acids. The level of specific deficiency can be evaluated as a percentage with a parameter known as index or chemical score (IC), that is: if the "amino acid" X "is present in the human protein in quantity 10, while in the analyzed protein there are only 5 ... it is possible to define that the analyzed protein is deficient in the "amino acid" X "for 50% (IPC = 50%).