Generality
Beans, intended as food, are the seeds produced by some herbaceous plants with an annual cycle, belonging to the Fabaceae family (Leguminosae). The binomial nomenclature of the bean plant is Phaseolus vulgaris; to tell the truth, however, the term beans could indicate many more Species, also belonging to different Genres and Sub-Genres; let's see why.

On the other hand, the Old Continent, as well as Africa and Asia, already presented its own edible legumes, even before they were imported from the Americas; for example, a large part of the Vigna genus is native to the Old World, too. belonging to the Fabaceae family. Some known species of the vineyard are: angularis (aduki bean), milk (black Indian bean), radiata (green Indian bean), ungulculata (cowpea) etc. Ultimately, the term "beans" is a completely generic noun, attributable to the seeds of leguminous plants which, roughly, resemble each other in physical and (hypothetically) taste characteristics.
NB. some varieties of beans boast an edible portion that is not limited to the seed, but also extends to the pod (similarly to the jackdaws for peas).
From a nutritional point of view, beans are legumes and as such belong to the 4th group of foods. These are particularly nutritious foods, which are consumed for their content in starch, fiber, mineral salts and B vitamins. Furthermore, beans contain numerous phytotherapeutic molecules very useful for metabolic balance (eg. Lecithins, phytosterols and antioxidants).
Bean flour
Bean flour is a powder obtained from the pulverization of dry and raw seeds; in Italy it is available at retail above all that obtained from the seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris (Borlotto variety), but there are also different products, which tend to be exotic, such as the well-known "Egyptian bean" flour (Dolichos lablabb).
Bean flour is mainly obtained through "cryomacination". This system involves the" use of "liquid nitrogen for breaking up seeds in mills"rungs"; these, very similar to stone mills, instead of having grinders, are equipped with steel discs that rotate quickly. Cryomacination is necessary to prevent the typical consistency of beans (soft and tough) from negatively interfering with more traditional systems. (stone cylinders).
Raw bean flour is a food rich in anti-nutritional elements such as "antitrypsin". This glycoprotein - although it is an essential component for the human organism (it is produced by the liver and immune cells and is therefore present in many tissues) - if it is introduced into the intestine with food, it is responsible for the inhibition of many protease (lytic enzymes) that will no longer be able to carry out their digestive function on peptides. To annihilate its anti-cryptic efficacy, most companies distribute already cooked bean flour (about 90 ° C for 180 "); on the market, it is however also available raw, which however must necessarily be treated with heat at home.
Bean flour is widely used in naturist-type diets. E "GLUTEN FREE, an aspect that makes it extremely suitable for celiac nutrition (gluten-free). Being rich in proteins, it is also used by vegans with the aim of increasing the amount of total amino acids and the biological value of foods based on it. of cereals. In bread making, the raw one is used in a ratio of 1 to 4 with that of wheat (prevalent), to the advantage of the flavor of the dough, but to the detriment of the overall strength. The cooked bean flour, on the other hand, can be used for the preparation of soups, soups and post-weaning porridges alternating with baby food (on the advice of the pediatrician). chickpea flour).
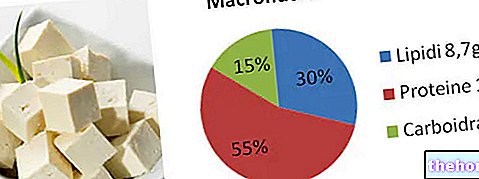
From a nutritional point of view, bean flour provides a considerable amount of energy, however lower than that of cereals proper. Calories are mainly provided by complex carbohydrates (starch), to a lesser extent by proteins (of Medium Biological Value) and only marginally by lipids (mainly unsaturated). The supply of fiber is excellent and makes it a suitable product for the diet of the person suffering from constipation.
As far as vitamins are concerned, RAW bean flour is rich in B vitamins (thiamin and niacin), while the cooked one suffers at least partial loss. With regard to mineral salts, bean flour is known for the content of potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc and selenium, essential and very important elements. Also for these characteristics (especially for iron and calcium, as well as for proteins), bean flour is extremely useful in the vegan diet. There are also useful molecules such as phytosterols, lecithins and antioxidants.
The nutritional complex of bean flour makes it a very interesting product. It has a moderate glycemic index, an essential feature in the diet of the diabetic, hypertriglyceridemic and obese. Thanks to the presence of phytotherapeutic molecules such as viscous fibers, phytosterols, lecithins and antioxidants, bean flour is also extremely useful in the hypercholesterolemic diet. Furthermore, as anticipated, for the high fiber content (which promote intestinal peristalsis and feed the bacterial flora), bean flour is also very useful in the treatment of constipation and / or as a preventive food against bowel cancer.
In addition to antitrypsin, bean flour also contains a fair amount of phytates. If the former is able to hinder protein digestion but degrades with heat, the latter tend to chelate certain mineral salts, worsening intestinal absorption. The phytates are usually eliminated from dry beans by soaking and discarding the residual water; on the other hand, this passage does not occur in bean flour, which is why it is conceivable that the relative content is significantly higher.
The average portion of bean flour is about 70-100g, to be consumed only once a day if alternating with wheat or 2-3 times as a complete replacement for the latter.
Raw bean meal is NOT a cheap product; the retail price is around 5 € / kg.
Beans all "Uccelletto"
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to the Video Recipes Section
- Watch the video on youtube
Other Foods - Legumes Peanuts Chickpeas and Chickpea Flour Cicerchie Beans Azuki Beans Green Beans Broad Beans Falafel Chickpea Flour Bean Flour Bean Flour Lentil Flour Pea Flour Soy Flour Legumes Lentils Lupins Peas Soy Jackdaws Tempeh Tofu Yogurt ARTICLES Soy OTHER Categories Alcoholics Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and derivatives Legumes Oils and fats Fish and fishery products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Second courses Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice creams and sorbets Syrups, Liqueurs and grappas Basic Preparations ---- In the Kitchen with Leftovers Carnival Recipes Christmas Recipes Diet Recipes Light Recipes Women's Day, Mum, Dad Functional Recipes International Recipes Easter Recipes Recipes for Celiacs Recipes for Diabetics Recipes for Holidays Recipes for San Valentino Recipes for Vegetarians Recipes p roteiche Regional Recipes Vegan Recipes