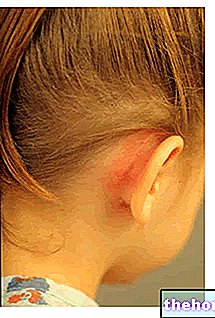
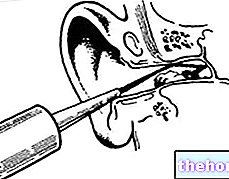
The cone shape of the ear allows it to collect sounds and direct them to the eardrum which begins to vibrate; these vibrations are transferred to the snail by means of three small bones (hammer, anvil and stirrup) which amplify the vibrations twenty times.
The snail is a spiral channel whose membrane - which covers the internal surface - is made up of filiform sensory cells (there are 24,000); when the sound wave reaches this part of the ear, it stimulates, depending on the height of the sound, different cells: the high sounds stimulate the more rigid and thin cells placed at the mouth of the spiral, while the lower sounds stimulate the largest and most flexible cells placed in the center of the canal.
The stimulation of each cell produces an electrical impulse that reaches the brain through the fibers of the acoustic nerve.
At this point, the brain "decodes" the sounds and interprets them.
The neurons of the acoustic nerve can be compared to a very small battery that is discharged with each stimulus, but recharges very quickly thanks to its own metabolism.
Did you know that ...
The organism is able not only to pick up the sound, but also to decipher its origin; in fact, the sound first reaches the ear closest to the source of this sound because the nerve impulses reach the brain in a different way. This difference, thanks to the cerebral cortex, allows the brain to decipher the origin of the sound.
minimum acoustics required to stimulate the neurons of the acoustic nerve known as the "hearing threshold". The raising of the hearing threshold reaches its maximum peak in the arc of about two minutes from the exposure to noise and then decreases slowly thereafter.
All this not only affects the activities of the individual (such as driving a vehicle) but causes damage to the hearing.
After a night at the disco, the ears have a higher hearing threshold than normal, this can even cause temporary deafness; this must be taken into account when driving a vehicle.