Generality
Topiramate is a drug with anticonvulsant activity, which is why it is used in the treatment of epilepsy, as well as in the prophylaxis of migraine attacks. the addiction to smoking.

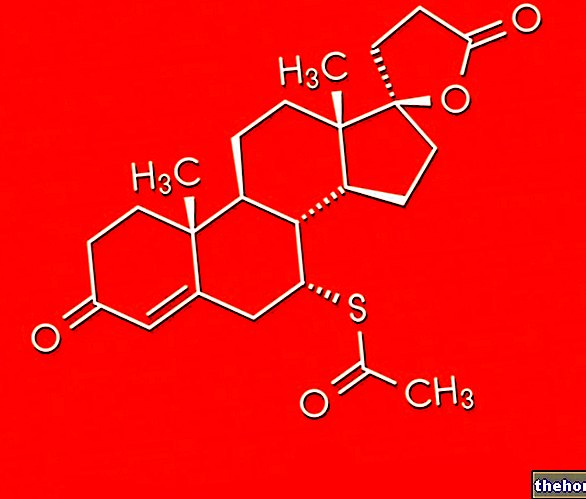
Topiramate - Chemical Structure
However, when it comes to the treatment of smoking, topiramate remains a second choice drug.
Mechanism of action
Chemically, topiramate is a monosaccharide derivative of fructose that also contains a sulfamate group. The mechanism of action by which topiramate carries out its activity has not yet been fully clarified, but it seems that it is able to activate some types of GABA receptors (or γ-aminobutyric acid, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter present in our organism) and to antagonize the receptors for glutamate (one of the major excitatory neurotransmitters in our body).
It is believed that the aforementioned activities are in some way involved in controlling the mechanisms underlying nicotine addiction and are therefore capable of decreasing the pleasure and gratification deriving from smoking.
In reality, the studies conducted on the use of topiramate in the treatment of smoking, although they have given positive results, are still too few and, most likely, further investigations will be needed.
Side effects
Not much data is available regarding the possible side effects that can occur during smoking cessation therapy with topiramate.
However, the main side effects that topiramate can cause include:
- Depression;
- Seizures
- Anxiety;
- Irritability;
- Changes in mood;
- Confusion and disorientation;
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory loss;
- Slowness of thinking;
- Increased frequency of urination.
Additionally, topiramate can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. These reactions can manifest themselves with symptoms such as skin reactions, hives, itching, edema and redness.
Dosage
Generally, topiramate is available for oral administration in the form of hard capsules or tablets.
The posology should be determined by the physician on an individual basis for each patient.
Use in pregnancy and during lactation
Due to the potential risks that may exist for the fetus or baby, the use of topiramate by pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers is not recommended and, in any case, it is always good to ask for the first. doctor's advice.
Contraindications
The use of topiramate is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to topiramate itself. In addition, topiramate is generally contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Finally, it should be remembered that topiramate can interfere with the activity of other types of drugs and can give rise to very dangerous drug interactions. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to inform your doctor if you are taking - or have recently taken - drugs. any type, including non-prescription medicines and herbal products.