Generality
Cytisine is a naturally occurring alkaloid found in many plants of the Fabaceae family.
Cytisine is mainly extracted from laburnum (Laburnum anagyroides or Cytisus laburnum L.), a plant also known as "fake tobacco".

This molecule has been known and studied since the 1960s in Eastern European countries for its efficacy in the treatment of smoking cessation. However, the studies that were conducted in those years did not meet the parameters required by the Western European clinical trials legislation, for this reason, the use of cytisine in anti-smoking therapy was not taken into consideration.
In 2011, however, the New England Journal of Medicine published a study that confirmed the real efficacy of cytisine in the treatment of smoking addiction. Subsequently, numerous other researches were conducted, up to the most recent studies published in 2015 showing how cytisine-based treatment can be even more effective than classic nicotine replacement therapy.
Another point in favor of cytisine resides in the economic aspect. Cytisine, in fact, has a much lower cost than the other therapies commonly used to treat smoking. It is estimated that the costs for the cytisine-based treatment are from five to ten times lower than the costs involved in nicotine replacement therapy and varenicline therapy (a synthetic drug used in smoking therapy and with a mechanism of action similar to that of cytisine).
Cytisine is marketed in Eastern European countries under the name of Tabex®.
In Italy, however, cytisine has been available since May 2015 as a galenic preparation in pharmacies, i.e. it is produced directly in pharmacies equipped with a galenic laboratory, but only upon presentation of a medical prescription.
Mechanism of action

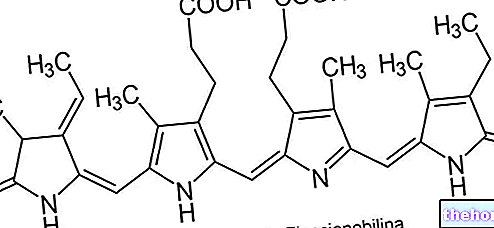
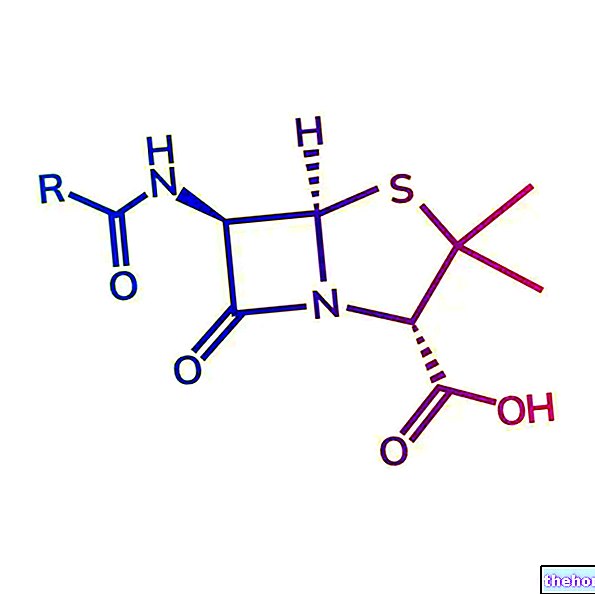
Cyisine - Chemical Structure
Cytisine is a partial agonist of the α4β2 nicotinic receptors present in the brain (the same receptors to which nicotine deriving from tobacco smoke binds) and has a "nicotine-like action.
By binding to these receptors - in addition to reducing the typical symptoms of nicotine withdrawal - cytisine is also able to reduce and, at times, completely eliminate the sensation of pleasure and gratification induced by smoking.
Unlike varenicline, cytisine causes fewer side effects and, as mentioned above, its cost is much lower.
Interactions
It is important to emphasize that the effect of cytisine can be influenced by concomitant therapy with antituberculous drugs.
In any case, it is always a good idea to tell your doctor if you are taking - or have recently taken - drugs of any kind, including non-prescription drugs and herbal products.
Warnings
Although cytisine is a well tolerated drug, it must be administered with great caution in patients suffering from certain types of diseases, such as:
- Adrenal cancer
- Schizophrenia;
- Chronic heart failure;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Cerebrovascular disorders;
- Gastroesophageal reflux;
- Peptic ulcer and / or duodenal ulcer in remission;
- Renal and / or hepatic insufficiency.
Furthermore, cytisine should also be administered with caution in patients under 18 years of age and in elderly patients over 65 years of age.
Side effects
Cytisine is usually well tolerated at therapeutic doses, but can still cause side effects, although not all patients experience them.
The main side effects that have been reported following the use of high doses of cytisine include:
- Headache;
- Stomach ache;
- Nausea;
- He retched;
- Digestive disorders;
- Dizziness;
- Muscle weakness
- Tachycardia.
Dosage
Cytisine is available for oral administration in the form of capsules.
The capsules must be taken whole, without chewing, with the help of a glass of water.
The cytisine treatment lasts for 25 days and it is necessary to stop smoking by the fifth day of therapy.
Generally, in the first three days of treatment, we start with taking 1.5 mg of the drug six times a day. Subsequently, the daily dose of drug will be gradually decreased according to a specific dosage schedule, up to the last days of therapy in which will take 1.5 mg of cytisine once or twice a day.
In any case, the doctor may decide to vary the dosage according to the patient's response to therapy. Therefore, it is essential to always follow the instructions provided by the doctor, both as regards the quantity of drug to be taken, and as regards the frequency of administration and the duration of treatment.
Use in pregnancy and during lactation
Because of the possible harm it may cause to the fetus or child, the use of cytisine by pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers is not recommended.
Contraindications
The use of cytisine is contraindicated in the following cases:
- In patients with known hypersensitivity to the same cytisine;
- In patients who have suffered from cardiovascular diseases in the past;
- In patients who have suffered from myocardial infarction;
- In patients with grade II and III hypertension;
- In patients with advanced atherosclerosis;
- In patients with unstable angina;
- In patients suffering from cardiac arrhythmias;
- In asthmatic patients;
- In patients with pulmonary edema;
- In patients with acute peptic and / or duodenal ulcer;
- Pregnant;
- While breastfeeding.