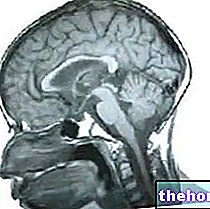
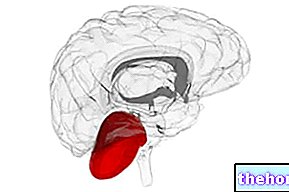
What is the Pituitary Adenoma
The pituitary adenoma is a benign tumor that develops from the cells of the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland responsible for the secretion of hormones that regulate numerous functions of the organism. The clinical picture determined by a pituitary adenoma depends on many factors. Due to its large size, a macroadenoma can cause important health effects, due to the compression of neighboring structures (pituitary hypofunction, visual symptoms and neurological signs).