
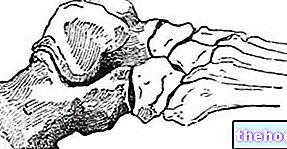
The olecranon is distinguished, in fact, by 5 surfaces: the upper surface, which fixes the terminal head of the brachial triceps muscle and the posterior elbow ligament; the posterior surface, on which the olecranon bursa is placed; the anterior surface, which constitutes the upper portion of the trochlear groove; the medial surface, on which the posterior head of the ulnar collateral carpal ligament and the initial head of the ulnar flexor carpus muscle are inserted; finally, the lateral surface, which houses the terminal head of the anconeus muscle.
The olecranon can be the subject of fractures and a condition whose correct name is olecranon bursitis, but which is better known as elbow bursitis.
The olecranon is nothing more than the palpable protrusion on the posterior surface of the elbow when the elbow is extended.
The olecranon is an example of bony apophysis, exactly like, for example, the tibial tuberosity of the tibia or the spinous and transverse processes of the vertebrae.
In anatomy, any outgrowth or protruding portion of the bones of the human body are called apophysis.


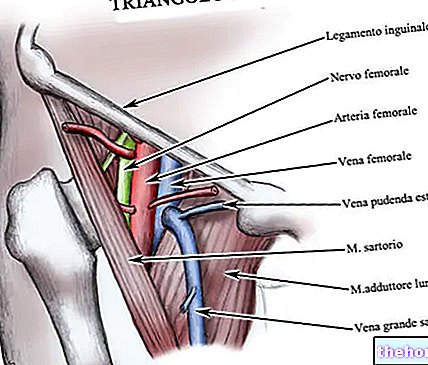









.jpg)











