Symptoms of ischemia depend on the organ and tissue involved; this means, for example, that a "cardiac ischemia presents with a symptomatological picture different from a" cerebral ischemia.
Survival and functional recovery after an episode of ischemia basically depend on the timeliness of treatment.
.
Oxygen and nutrients are fundamental elements for the survival of the cells making up the human organism; in fact, their prolonged absence (due for example to a lack of therapeutic intervention) triggers an irreversible process that leads to the death (or necrosis) of the organs and / or tissues involved.
Ischemia is a vascular disease, which mainly affects the arteries.
Ischemia: What are the most affected organs?
Any part of the body can suffer from ischemia.
However, there are organs that are more at risk than others and which, once affected, can have serious consequences; the bodies in question are:
- The heart, which can develop the condition known as ischemic heart disease, myocardial ischaemia, or cardiac ischemia;
- The brain, which can be a victim of cerebral ischemia;
- The intestine, which can develop intestinal ischemia;
- The extremities of the upper or lower limbs, which can undergo the so-called peripheral ischemia.
Given the higher frequency of ischemic phenomena in the aforementioned anatomical areas, in the next chapters, the article will tend to refer to the aforementioned types of ischemia.
and the consequent interruption of the blood supply to the organs and tissues guaranteed by the aforementioned arteries.In most cases, the obstructive events of an "ischemia are the consequence of an" embolism, a thrombosis and traumatic events.
Classically, embolism and thrombosis are associated with myocardial ischemia, cerebral ischemia and intestinal ischemia; traumatic events, on the other hand, are related to the appearance of peripheral ischemia in the fingers or toes.
Thrombosis and Embolism: What are they in brief?
The term "thrombosis" indicates the presence of a blood clot, called a thrombus, on the inner wall of an arterial or venous blood vessel.
The word "embolism", on the other hand, identifies the presence, in the blood (therefore in the vessels), of a mobile body of blood or non-blood origin, which takes the specific name of embolus.
If large, thrombi, as well as emboli, can clog blood vessels.
Ischemia: Risk Factors

Many conditions favor the phenomena of ischemia.
Among the numerous risk factors of this serious medical condition, they definitely deserve a mention:
- Atrial fibrillation. It is an "arrhythmia, that is, an" alteration of the heart rhythm.
- Cardiomyopathies. They are pathologists of the heart muscle (or myocardium), in the presence of which the heart functions inadequately.
- Coronary heart disease. They are diseases of the coronary arteries, ie the arterial vessels that nourish and oxygenate the myocardium.
- Diseases of the mitral valve. The mitral valve is the heart valve that regulates the passage of blood between the atrium and the left ventricle.
- Diabetes. It is a metabolic disease, which in the absence of treatment is at the origin of many complications.
- Hypertension. It is the chronic increase in blood pressure to pathological levels.
- Hypotension due to septic shock or heart failure.
- Arteriosclerosis. It is the hardening and thickening of the artery wall.
- Atherosclerosis. It is a particular form of atherosclerosis, due to the presence of atheromas (plaques of lipid, protein and fibrous material).
- Hypercholesterolemia (elevated blood cholesterol) or hypertriglyceridemia (elevated blood triglycerides).
- Hypoglycemia is a chronic reduction in blood glucose levels to pathological levels.
- The advanced age.
- Overweight and obesity.
- The sedentary lifestyle.
- Cigarette smoke.
- Venous thromboembolism. Indicates the venous formation of emboli which, once they reach the heart, can then spread to the arterial system, creating dangerous obstructions.
- Peripheral arterial disease. It is the obstruction of the arteries that supply the limbs, trunk or head.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- The thoracic outlet syndrome. It is the set of symptoms and signs deriving from the compression of the blood vessels and / or the nerves passing through the thoracic outlet.
- The compression of blood vessels caused by the presence of tumors (tumor mass effect).
- The exposure of the limbs to excessive cold or the improper use of cryotherapy combined with the application of elastic bandages.
- The severe rupture of numerous blood vessels.
- The rupture of an aneurysm.
Acute Ischemia and Chronic Ischemia
An ischemia can present itself in an acute or chronic form.
What distinguishes the acute form from the chronic form is the fact that, in the former, the reduction in blood flow is sudden and sudden, while, in the latter, the same process occurs gradually.
For the speed with which it begins and with which it gives rise to complications, acute ischemia represents a medical emergency to be treated as quickly as possible.
This means that a "cardiac ischemia will present a symptomatological picture different from that of a cerebral ischemia or a" peripheral ischemia.
In the human body, there are organs and tissues that suffer most from a reduction in the blood supply to their cells. Heart, brain and kidneys, for example, are organs particularly sensitive to the lack of oxygen and nutrients: already after 3- 4 minutes, in fact, they develop irreversible damage (necrosis).
On the other hand, it should be noted that all tissues and organs that have a slow metabolism show the first irreversible consequences after a period of about 20 minutes.
Unfortunately, some cases of ischemia are asymptomatic, meaning they lack symptoms. These situations can be very dangerous, as those who are victims of them do not realize what is happening to them and do not turn to help promptly.
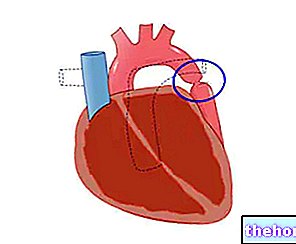
Cardiac Ischemia: What it is and Symptoms
The term "cardiac ischemia" encompasses two very common pathological conditions, known as angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, in which, following the occlusion of one or more coronary arteries, a discrepancy between consumption and supply of oxygen to the myocardium occurs .
In angina pectoris, the ischemic process is temporary / reversible and does not cause permanent damage (coronary occlusion is temporary).
On the contrary, in myocardial infarction - also known as heart attack - ischemia is protracted and involves a more or less extensive necrosis of the myocardium (in this case, the coronary occlusion is lasting over time).
Clearly, from the point of view of severity, there is a substantial difference between the two conditions: angina pectoris is the sign of less heart disease compared to myocardial infarction.
The symptoms of angina pectoris and heart attack are very similar, almost overlapping; what changes is their duration.
The typical symptoms of these two conditions include:
- Pain or pressure in the chest
- Pain which, from the chest, can radiate to the back, arm, shoulder, neck, jaw or stomach;
- Dyspnea, i.e. shortness of breath;
- Nausea with or without vomiting;
- Limitations of physical ability. For example, the patient feels tired after any effort, even minimal;
- Palpitations or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias);
- Profuse sweating.
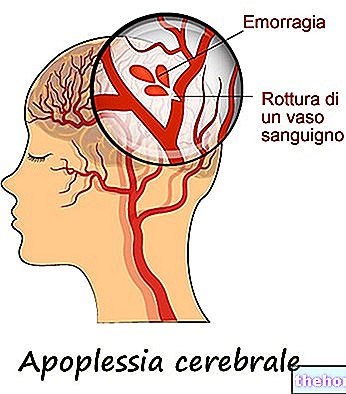
Cerebral Ischemia: What it is and Symptoms

Cerebral ischemia is the pathological process that characterizes two conditions that are certainly known to most: transient ischemic attack (or TIA) and ischemic stroke.
A TIA (also known as a mini stroke) is a "temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, symptoms lasting less than 24 hours, with no permanent consequences.
An ischemic stroke, on the other hand, is a "prolonged interruption of cerebral blood flow, which causes symptoms lasting more than 24 hours and a series of irreversible brain damage.
Although TIA and ischemic stroke are different in severity, they have a very similar symptom picture, which can include:
- Paralysis and numbness of the face and limbs;
- Difficulty walking, balance problems, coordination deficits and a tendency to fall;
- Difficulty speaking and understanding
- Visual difficulties (double vision, blurred vision, sudden blindness etc.);
- Abnormal size of the pupil and lack of responsiveness of the latter to variations in light;
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Confusion;
- Memory deficit
- Nausea with or without vomiting;
- Weakness;
- Alterations of the state of consciousness.
The succession of many mini-strokes and some particular ischemic strokes can lead to a form of dementia, known as vascular dementia.
Intestinal Ischemia: What it is and Symptoms
Intestinal ischemia consists in a reduction / interruption of the blood supply to the intestine, consequent to an arterial obstruction.
Intestinal ischemia can cause violent abdominal pain, vomiting and / or diarrhea (often with blood).
When the damage of intestinal ischemia is permanent and necrosis of the bowel section has occurred, doctors speak more properly of intestinal infarction.
For further information: Intestinal Ischemia: What it is, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentPeripheral Ischemia: What it is and Symptoms

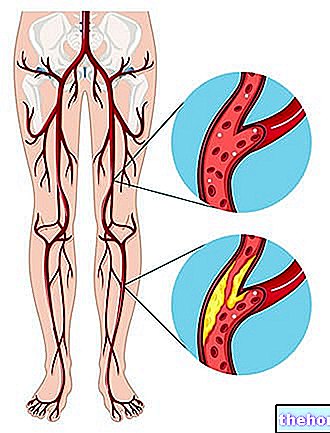
"Peripheral ischemia" is the medical term that indicates an insufficient blood supply to the upper or lower limbs, due to the obstruction of an arterial vessel.
Peripheral ischemia is generally an acute phenomenon; as such, it takes the second name of acute limb ischemia (or acute limb ischemia).
Typical symptoms of "acute limb ischemia" are: pain, paleness, paraesthesia, paralysis and loss of normal thermoregulation (poikilothermia).
Ischemia: When to Contact the Doctor?
The most severe forms of ischemia require immediate medical intervention, as the patient's survival is at risk.
Doctors believe that some symptoms are more indicative of "severe ischemia. For example, they consider a sign of extreme danger:
- Vomiting or bloody diarrhea;
- Unbearable abdominal pain;
- Paralysis of the limbs;
- Dyspnea at rest;
- Obvious changes in vision skills;
- Severe pain in the chest, as well as a strong sense of pressure;
- The inability to speak or understand;
- Alterations of the state of consciousness.
If these checks are found to be insufficient or if there is a need to investigate the situation further, he could also prescribe an echocardiogram, a chest X-ray and a "coronary angiography."
. It is a procedure that allows you to eliminate possible narrowings within a blood vessel.The technique typically used for this type of intervention is lo stenting.
The best-known arterial bypass surgery is coronary artery bypass grafting, but it is important to remind readers that lower limb artery bypasses also exist.
There are various techniques with which to perform the aforementioned operations, some more invasive than others.
Ischemia: Symptomatic Therapies
Certain episodes of ischemia also lend themselves to some symptomatic treatments, i.e. those treatments aimed at improving the symptomatological picture.
Examples of symptomatic treatments are: pain relievers (to control pain), vasodilator drugs (to increase the caliber of blood vessels), drugs to reduce the workload of the heart (calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, nitrates and beta-blockers) and oxygen therapy.
Ischemia: Preventive Therapies
Patients with ischemia following embolism or thrombosis are often subjects predisposed to relapses.
To reduce this predisposition, doctors prescribe long-term anticoagulant therapy to patients, based on the administration of drugs such as warfarin or heparin, and antiplatelet therapy, which involves the use of antiplatelet agents such as aspirin.
Ischemia and Invasive Treatments: Amputation
Severe forms of peripheral ischaemia require drastic surgery with permanent consequences, such as amputation of the affected limb.
In such situations, the amputation is motivated by a process of dry or wet gangrene, induced by the ischemic process.
In medicine, the term gangrene (or gangrene) indicates a pathological condition characterized by the massive putrefaction of one or more tissues of the body.
Gangrene requires immediate medical intervention to prevent its spread to adjacent healthy tissues; this explains the reason for the "amputation: the latter, in fact, represents the only way to stop the process of spreading the gangrene itself."
Cardiac Ischemia: the Cures

As a rule, the treatment of myocardial ischemia is based on an adjustment (obviously for the better) of the lifestyle and, depending on whether the coronary occlusion is mild or severe, on drug therapy or surgical treatment.
Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiac Ischemia
Among the drugs used in the treatment of cardiac ischemia, the following are noted:
- Anticoagulants (eg heparin) and antiplatelet agents (eg aspirin).
- Nitroglycerin.
- Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists.
- Statins.
Cardiac Ischemia Surgery
As regards surgical procedures, these include:
- The aforementioned coronary artery bypass graft;
- L "angioplasty with stenting coronary.
To learn more about "the treatment of" cardiac ischemia ", we recommend reading the dedicated article here.
Cerebral Ischemia: the Cures
The treatment of cerebral ischemia certainly includes a pharmacological treatment and, sometimes, a surgical therapy; moreover, once the blood flow is restored, it also provides a rehabilitation path for the recovery of all those motor and cognitive faculties compromised due to the " vascular event.
Medicines for the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemia
Medicines for the treatment of cerebral ischemia include:
- Antithrombotics (or thrombolytics) such as aspirin or recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA).
- Anticoagulants such as, for example, heparin, Warfarin, Clopidogrel or dipyridamole.
Cerebral Ischemia Surgery
The main surgical procedures that can be adopted in the presence of cerebral ischemia are:
- The administration of the TPA directly in situ, via catheter.
- Embolectomy or thrombectomy.
- Carotid endarterectomy. It should be noted that this therapeutic option is used when the impediment to the blood supply towards the brain is found at the level of the carotids.
- L "angioplasty with stenting.
To learn more about "the treatment of" cerebral ischemia ", we recommend reading the dedicated article here.
regular and a healthy and balanced diet, and which obviously excludes bad habits, such as cigarette smoking or alcohol abuse.