How to make bread
The preparation of the bread consists of various stages.
MIXING: addition of water to the flour, then hydration of the proteins - with the formation of gluten - and of the starch granules, which become soaked and become gelatinous.
LEAVENING: yeasts transform glucose into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol, giving rise to small quantities of aromatic substances. The first nourishment of the yeast is given by the small percentage (1.5%) of dextrins and glucose contained in the flour; in the latter there are also enzymes, in particular alpha-amylases, which digest starch during leavening. , supplying the yeasts with the glucose necessary for fermentation.

FORMING: transformation of the dough into the typical forms in relation to local habits, followed by a short and further leavening period.
COOKING: generally takes place in electric ovens, regulated at a temperature of 200 - 300 ° C, which is maintained for 15 "- 60" depending on

Very important transformations take place during cooking. After baking, the temperature of the bread passes from environmental values to higher levels, rising uniformly inside and outside the product; up to 35-40 ° C the yeasts continue to proliferate and therefore an increase in the dough is noted. , exactly as it happens when you bake a cake. After 45-50 ° C, the yeasts begin to die and the leavening stops; at the same time, the water evaporates, the gluten bonds stiffen and the starch solidifies, giving the dough a greater consistency. At about 100 ° C, a crust begins to form on the surface, very important because it prevents the internal water from continuing to evaporate, maintaining the softness of the crumb. Subsequently, the external temperature continues to rise, but the internal one remains constant thanks to the insulation of the crust. On the surface, in the meantime, we witness the chambering of sugars, which leads to the browning of the crust and gives the bread the characteristic smell of cooked. . There is also a reaction between the sugars and the amino groups of the proteins (called the Maillard reaction or the non-enzymatic browning reaction), from which yellow-brown compounds originate which give the product the classic color of baked bread. This very complex reaction occurs in all cooking processes, including that of meat (especially if grilled) and leads to the formation of numerous compounds not yet fully identified.
Thanks to the intensification of fermentation and the enzymatic production of simple sugars starting from starch, which softens and plasticizes, gas expansion begins;
Inactivation and death of the microorganisms responsible for leavening (saccharomycetes);
The dough becomes rigid, the production of water vapor and the formation of the crust begin;
Homemade Rustic Bread - Alice's video recipes on MypersonaltrainerTv
Recipe to prepare a rustic bread directly at your home, explained in every detail. Follow our video recipe
My-personaltrainer rustic bread
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to the Video Recipes Section
- Watch the video on youtube
Types of bread
SPECIAL BREADS: butter, olive oil or lard can be added, in quantities not less than 4.5% of the dry matter, but also milk and milk powder, grape must, raisins, figs, olives, etc. .. .
The special bread must be kept on separate shelves from the common bread and bearing the indication of the added ingredient.
- CASSETTA OR PANCARRE BREAD ": it contains a moderate level of humidity, which is important for keeping it fresh for a long time.
- TOAST: a large part of the water content is eliminated (4-8%).
- BREADSTICKS, CRACKERS
- PROTEIN BREAD
DETERMINATION OF "HUMIDITY"
Up to 70 grams
Humidity max 29%
From 100 to 250 grams
Humidity max 31%
From 300 to 500 grams
Humidity max 34%
From 600 to 1000 grams
Humidity max 38%
Over 1000 grams
Humidity max 40%
In case of wholemeal bread + 2%
Homemade Vegetable Seed Sandwiches - Alice's video recipes
Recipe for making vegetable seed sandwiches directly at your home. Alice and My-personaltrainerTv explain to you in detail how to prepare this delicious bread enriched with unsaturated fats and vitamin E, naturally contained in vegetable seeds.
Sandwiches covered with seeds
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to the Video Recipes Section
- Watch the video on youtube
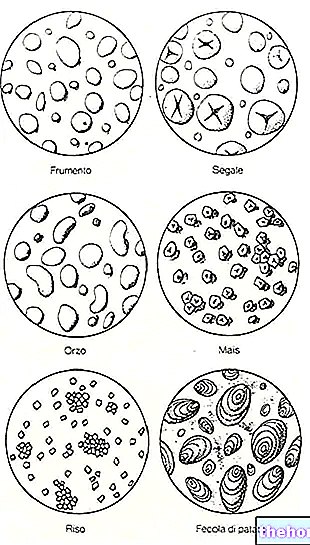
Other Cereals and Derivatives Amaranth Wheat starch Corn starch Rice starch Modified starch Oat starch Bulgur Whole grains Corn Flakes Crackers Oat bran Bran Cus cus Amaranth flour Oat flour Buratto flour Spelled flour Buckwheat flour Corn flour Corn flour Millet Barley flour Quinoa flour Small spelled flour (Enkir) Rice flour Rye flour Sorghum flour Flour and semolina Whole wheat flour Manitoba flour Pizza flour Spelled Rusks Focaccia Nuts Wheat or wheat Wheat germ Burnt wheat Buckwheat Breadsticks Oat milk Rice milk Corn Maizena Malt Millet Muesli Barley Stale bread Unleavened bread and Pita Bread Carasau bread Egg pasta Rice pasta Wholemeal pasta Piadina Small spelled Pizza Pop corn Baked goods Quinoa Rice Basmati rice Converted rice White rice Rice Wholemeal Parboiled Rice Puffed Rice Venus Rice Rye and Horned Rye Semolina Semolina Sorghum Spaghetti Spelled Teff Tigelle Triticale OTHER ARTICLES CEREALS AND DERIVATIVES Categories Food Alcoholics Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and derivatives Legumes Oils and fats Fish and fishery products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Second courses Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice creams and sorbets Syrups, liqueurs and grappas Basic Preparations ---- In the Kitchen with Leftovers Carnival Recipes Christmas Recipes Dietary Recipes Light Recipes Woman's Day, Mother's Day, Dad's Day Functional Recipes International Recipes Easter Recipes Recipes for Celiacs Recipes for Diabetics Holiday Recipes Valentine's Day Recipes Vegetarian Recipes Protein Recipes Regional Recipes Vegan Recipes















.jpg)











