Generality
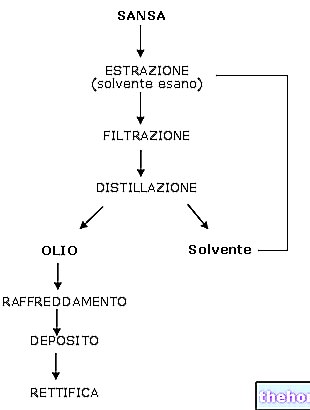
Vegetable oils are obtained by pressing or by extraction with solvents from the fruits or seeds of many plants.

The main source of vegetable oils is represented by oil seeds. Among the vegetable oils, however, there are also some obtained exclusively or mainly from the pulp of the fruits; this is the case of palm oil and olive oil. Similar products can also be obtained from palm and olive seeds, although in this case it is more correct to speak of palm kernel oil and pomace oil.
The best known vegetable oils used in the food sector are:
- Linseed oil
- Grapeseed oil
- Coconut oil
- Palm oil
- Oil and palm kernel
- Corn oil
- Sunflower oil
- Sesame seed seeds
- Wheat germ oil
- Jojoba oil
- Hemp seed oil
- Castor seed oil
- Evening primrose seed oil
- Avocado oil
- Soybean oil
- Rice oil
- Safflower oil
- Rapeseed oil
- Peanut oil
- Walnut oil
- Macadamia oil
- Argan oil.
What remains of the seed or fruit after extraction is mainly used for: fuel, fertilizer or feed (sunflower protein content; 38-40% corn and soy; 40%: peanut; 50%: cotton and grape seeds).
Types of Oil and Properties
Main vegetable oils for food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic use
FIRST NAME
SPECIES
Peanut oil
Arachys hypogaea
Behen oil
Moringa oleifera
Coconut oil
Cocos nucifera
Cotton oil
Gossypium
Jojoba oil
Simmondsia chinensis = Scalifornica = Buxuschinensis
Sunflower oil
Helianthus annuus
Linseed oil
Linum usitatissimum
Corn oil
Zea mays
Sweet almond oil
Prunus communis = P.dulcis = P.amygdalus
Palm oil
Elaeis guineensis
Olive oil
Oleum europaea
Castor oil
Ricinus communis
Sesame oil
Sesamum indicum
Soybean oil
Glycine max = Soja hispida
Composition in fatty acids of the main vegetable oils

Peanut oil
Peanut oil is an oil rich in oleic acid (35-72%) and linoleic (13-45%). Being composed mainly of monounsaturated fatty acids it is in some ways similar to olive oil and as such it is quite stable at high temperatures. Its high smoke point, which is around 180 ° C, makes it a vegetable oil particularly suitable for frying.
Vitamin E content is also good (19.1 mg / 100g)

Sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is characterized by high percentages of unsaturated fatty acids and modest saturated contents. In particular, sunflower oil is very rich in linoleic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, very useful for controlling cholesterol and triglycerides.
Thanks also to its excellent vitamin E content (68 mg / 100 g), sunflower oil is an ideal condiment to add raw to dishes.
However, its use in cooking and frying is not recommended, as the polyunsaturated fatty acids it contains would easily undergo degenerative processes, producing harmful residues for the body.

Corn seed oil
Corn oil has a composition similar to that of sunflower oil and is therefore rich in vitamin E (34.5 mg / 100g) and linoleic acid (38-52%).
Used raw to season dishes, it is an excellent ally for our health.

Soybean oil
Soybean oil contains both essential fatty acids (linoleic and linolenic). Twenty grams of unrefined soybean oil meet the daily requirement of both essential fats. Like olive oil, it should be stored in a cool, sheltered environment. from sunlight (use opaque bottles).

Coconut oil
It is composed almost exclusively of medium-chain saturated fatty acids. This particular type of fatty acid is not dangerous for our health as it does not affect the levels of bad cholesterol in the blood.
Therefore, despite its high percentage of saturated fat (84%), coconut oil is not as dangerous for our health as one might think after a brief analysis.
However, it is a vegetable oil of lower quality than traditional olive oil and other commonly used seed oils (corn, sunflower, peanut wheat germ).

Palm oil
Palm oil is extracted from the palm fruit and is quite rich in long-chain fatty acids which make it a rather harmful vegetable oil for the heart and arteries
Palm kernel oil is instead obtained from the seeds of the fruit and from a nutritional point of view it is preferable to palm oil (comparable to coconut oil as it is rich in MCT).
Both oils are particularly rich in vitamins A and E.

Rapeseed oil
Rapeseed oil is characterized by the abundant presence of erucic acid, a harmful substance for the organism. Because of the presence of this harmful fatty acid, rapeseed oil is used by law exclusively in association with other oils. , without exceeding 5% of the total. The selection of the species has however allowed to obtain varieties of rapeseed with erucic acid content close to zero; the oil extracted from these crops has characteristics similar to olive oil and has been renamed canola oil.

Grapeseed oil
Of all vegetable oils, grape seed oil is undoubtedly the richest in linoleic acid. If used for frying, like all vegetable oils rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, it easily deteriorates giving rise to an extremely toxic compound called HNE (4-hydroxy- -2-nonenal). This toxin is absorbed from food and if taken in high doses can cause severe damage to the liver, arteries (atherosclerosis) and nervous system (stroke, parkinson's, Alzheimer's)

Sesame oil
Particularly rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, sesame oil is characterized by equal quantities of oleic acid (37-49%) and linoleic acid (37-47%).
It is extracted by pressing from sesame seeds, of which it retains the typical flavor and fragrance. It has a dark, reddish color and is mainly used in oriental cuisine.
Linseed oil
Being very rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids in contact with air it easily undergoes oxidation and polymerization phenomena which transform the surface layer into a solid, compact and elastic film which constitutes the basic property of the so-called oil paints.
Wheat germ oil
Very rich in vitamin E and polyunsaturated fatty acids, it is an oil that is friendly to our health as long as it is consumed raw.
Dietary oils
Characterized by the addition of vitamins (A, D, E)
Vegetable oils ideal for frying
* Refined vegetable oils have a higher smoke point than unrefined and are therefore more suitable for frying
Other Foods - Oils and Fats Peanut Butter Cocoa Butter Butter Greaves Wheat Germ Animal Fats Margarine Vegetable Cream Tropical Oils and Fats Frying Oils Vegetable Oils Peanut Oil Borage Oil Rapeseed Oil Krill Oil Poppy Seed Oil Seed Oil Pumpkin Avocado oil Hemp oil Safflower oil Coconut oil Cod liver oil Wheat germ oil Linseed oil Macadamia oil Corn oil Almond oil Hazelnut oil Walnut oil Olive oil Palm oil fish Rapeseed oil Rice oil Pomace oil Seed oil Soybean oil Grapeseed oil Extra virgin olive oil Sesame seeds and sesame oil Lard OTHER ARTICLES OILS AND FATS Categories Food Alcoholics Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and Derivatives Legumes Oils and Fats Fish and fishery products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Seconds pi acts Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice creams and sorbets Syrups, liqueurs and grappa Basic Preparations ---- In the Kitchen with leftovers Carnival recipes Christmas recipes Light diet recipes for Celiacs Recipes for Diabetics Recipes for Holidays Recipes for Valentine's Day Recipes for Vegetarians Protein Recipes Regional Recipes Vegan Recipes