What is that
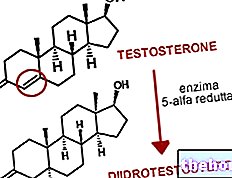
5-alpha reductase is the name of an enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone. The latter is the most powerful androgen hormone in the body and its activity is 4-5 times higher than that of testosterone.

As anticipated, it is produced thanks to the action of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme that makes the double bond existing between carbon 4 and carbon 5 simple. This small modification considerably increases the affinity of dihydrotestosterone for androgen receptors, enhancing its consequently, the business.
Functions of Dihydrotestosterone
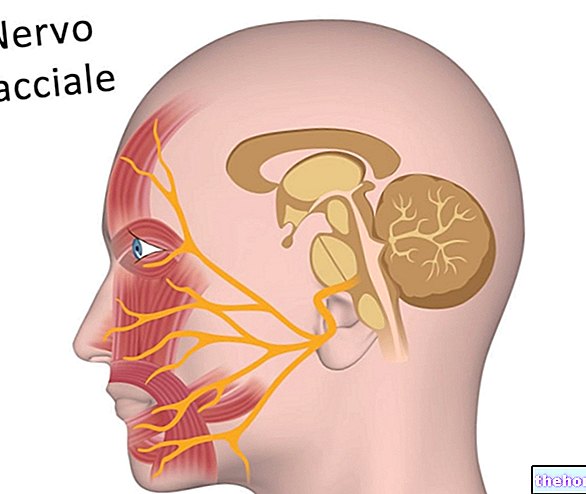
The 5-alpha reductase enzyme is expressed mainly in the prostate, testicles, hair follicles and adrenal glands. Its action is very important already during uterine life, when dihydrotestosterone determines the development of the male external genitalia. a recessive genetic defect the isoform 5-alpha reductase type II is deficient, there is an abnormal development of the external genitalia in the fetus, which results in sexual identity disorders and infertility in adulthood.
From puberty onwards, dihydrotestosterone supports the development of so-called secondary sexual characteristics, such as lowering of the voice, growth of facial and body hair, receding hairline and sebaceous secretion. Dihydrotestosterone is also important for the development of the masses. muscle and, on a psychological level, due to the appearance of sexual stimulation. An excess of it is implicated in the onset of prostatic hypertrophy, acne, seborrhea, androgenic baldness and hirsutism. A dihydrotestosterone deficiency is implicated in the onset of gynecomastia.
Isoforms
In the human body there are two isoforms of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, encoded by two different chromosomes and with different sensitivity to regulatory factors, respectively called 5-alpha reductase type I and 5-alpha reductase type II.
- The type I isoform is concentrated mainly in the skin, sebaceous glands, central nervous system and liver.
- The type II isoform is mainly expressed in the prostate and in the hair follicles.
Medicines
Two drugs have been developed to inhibit the activity of these enzymes. The first, called Finasteride, Proscar or Propecia, is a selective type II isoform inhibitor. The second, called Dutasteride or Avodart, inhibits both isoforms. These medicines are used in the treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy; finasteride is also widely used to combat hair loss. of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, a more marked action is expected, but also more evident side effects; studies are currently underway to establish this).
The side effects of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, although rare, mainly affect the sexual sphere and can cause erectile dysfunction, decreased libido and ejaculate volume.