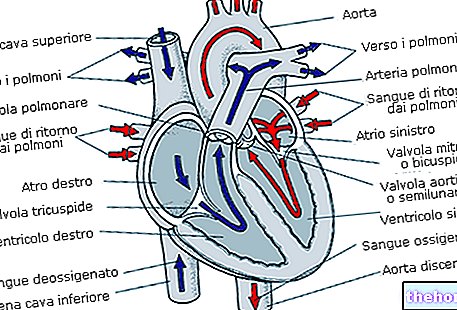
The mass of air surrounding the Earth is called the Earth's atmosphere. Air is a mixture of gas, the components of which are listed in the following table:
The main trace gases included in the composition of air are: argon, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, nitrous oxide, neon, helium, krypton and xenon. In the air there are also variable quantities of atmospheric dust, consisting of very small material particles (those which, to be clear, are seen when a ray of light passes through a door ajar) and water vapor.
Other curiosities:
breaths vary on average from 15 to 20 per minute, but can increase to 60 or more during a rather demanding effort; similarly, at rest only 10% of the air contained in the lungs is renewed with each respiratory act, while with a deep voluntary inhalation act it is possible to reach up to 80%.
The composition of the air is the same at sea level and at high ground; it is therefore not true that in the "mountain air there is less oxygen", its partial pressure is simply lower and, consequently, its availability; for this reason our physical abilities decrease by 30% on the summit of Mont Blanc, and by 80% on the summit of Everest.











.jpg)











