Gentian: Gentiana lutea, Genzianaceae family. Perennial herbaceous plant up to 2 m tall; which must be cultivated above 1500 m in height, otherwise the concentration of the active ingredients declines by 50%. The drug is represented by the underground parts, in particular by the roots accompanied by parts of the rhizome.
Two subspecies of officinal interest are distinguished, also on the basis of active principles: the lutea and the symphyandra. Gentian is considered a bitter drug with marked eupeptic properties; it is therefore used in both herbal and liqueur fields.
In case it is addressed to the liquor industry, the gentian is not immediately dried, but left to ferment for a short period. The digestive properties are mainly due to gentiopicrin, a glucosidic secoiridoide and to amarogentina, the "qualitatively most important iridoid for the" high bitter index.
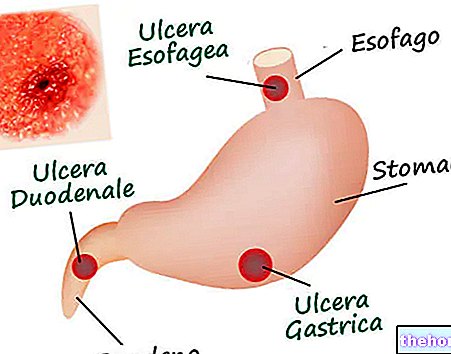
In ancient times, gentian was used as an antipyretic in association with cinchona. Gentian appears contraindicated in the presence of duodenal and gastric ulcers, as well as in cases of hypertension. In cosmetics, the infusion of the root is used for the lightening action of freckles on the skin and for the care of oily skin.
Other articles on "Genziana"
- Valerian and its sedative properties
- Pharmacognosy
- Harpagophyte or devil's claw