Definition
The term giardiasis refers to an "intestinal infection sustained by a flagellated protozoan (hence the name of the disease): it is an intestinal disorder that results in abdominal cramps, bloating, watery diarrhea and general malaise. Giardiasis is very common in the most common areas. poor of the world, where hygiene is poor and water is contaminated.
Causes
Giardiasis is a "protozoal infection caused by Giardia lamblia, a microorganism that prefers places with a temperate-tropical climate and poor hygienic conditions. Giardia infects humans by ingesting food or water contaminated by its cysts, and by direct contact (eg after handling diapers). Finally, giardiasis can also be contracted through sexual contact.
Symptoms
Giardiasis occurs asymptomatically for 2/3 of infected subjects; the remainder may manifest symptoms suddenly and violently, or worsen slowly. The most common symptoms are: abdominal cramps, watery diarrhea, flatulence, milk intolerances (never had before), nausea, weight loss, vomiting.
The information on Giardia - Medicines for the Treatment of Giardiasis is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Giardia - Medicines to Treat Giardiasis.
Medicines
Infections sustained by Giardia they tend to self-resolve in 4-6 weeks, even without treatment.However, if some parasites hide in the intestinal walls, the characteristic disorders of giardiasis can last for a long time; for this reason, it is advisable to take specific drugs, aimed at eradicating the infesting agent.
Prevention is the most effective weapon: when you go to warm and temperate places, especially if hygiene is scarce, it is essential to pay attention to small precautions, even if at first glance they seem trivial. Here are some simple precautions aimed at preventing giardiasis, to be strictly followed when traveling in environments with a warm temperate climate, and in poor areas:
- Do not drink local water: prefer bottled water
- Do not drink drinks with ice (ice is almost always made from tap water)
- Do not eat undercooked products
- Wash the vegetables thoroughly. Whenever possible, consume fruit without the peel
- Wash your hands often, especially after toileting, after contact with a sick person and after changing diapers
Pharmacological treatment is recommended for patients suffering from giardiasis with symptoms, even mild ones; some patients diagnosed with "infection with Giardia they are subjected to therapy even in the absence of symptoms, to reduce the risk of contagion. Pregnant women with Giardiasis should avoid taking medications, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy.
The drugs most used in therapy are azole derivatives; when diarrhea becomes particularly severe, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
In the event that the infected patient has had sexual intercourse with one or more partners in the days after the infection, it is recommended to also subject the partner to drug treatment, since Giardia it can also be transmitted by sexual contact.
The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against giardiasis, and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment:
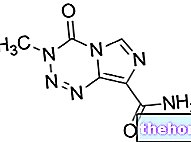
- Metronidazole (eg. Metronid, Deflamon, Flagyl): is the first-line drug for the treatment of giardiasis. It is recommended to take the drug at a dose of 250 mg, orally, every 8 hours. Continue with this dosage for 7 days, based on the nature and severity of the infection. For children with giardiasis, the indicative dose is 15 mg / kg per day, to be taken orally, dividing the load into three doses. Continue with this therapy scheme for 5-10 days.
- Tinidazole (eg Trimonase, Fasigin-N): the recommended dose for the treatment of giardiasis is 2 g, to be taken orally, once daily, with food. Affected children, older than 3 years, can take the drug at a dosage of 50 mg / kg, up to a max. of 2 g, once a day, with food.
- Nitazoxanide (eg Alinia): the drug belongs to the class of amoebioids-antiprotozoans. For the treatment of diarrhea in immunocompetent subjects suffering from giardiasis, it is recommended to take 500 mg of the drug, twice a day, with food for 3 days. For patients with giardiasis and AIDS, it is recommended to take 1 gram of the drug twice a day, with food, for 2 weeks, or until symptoms subside. For children aged 12 to 47 months, suffering from giardiasis, it is recommended to administer the drug at a dose of 100 mg (5 ml) by mouth, every 12 hours, for three days. Affected children between the ages of 4 and 11 can take up to 200 mg of the drug twice a day for three days; after the age of 12, children with giardiasis can take 500 mg of the drug, twice a day, on a full stomach, for three days.
- Paromomycin (eg. Humatin): the drug is also used in therapy for the treatment of teniasis. For the treatment of Giardia infections, it is recommended to take 25-35 mg / kg of the drug orally, divided into three doses, for 7 days. Also for children and young people suffering from giardiasis, under the age of 18, it is recommended to take the drug at a dose of 25-35 mg / kg per day, orally, dividing the load into three doses. Continue with this dosage for one week.
- Albendazole (eg Zentel): the most indicated dose for the treatment of giardiasis in adults is 400 mg, to be taken by mouth, once a day for 5 days. The drug is often used in combination with metronidazole.
A vaccine that can prevent giardiasis has not yet been devised.