Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
Edited by Doctor Alessio Dini
it is caused by a sudden narrowing or complete occlusion of the coronary vessels that carry oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the heart cells.
The sudden interruption of blood flow leads in a few minutes to cellular distress and consequently to the death of the vascularized tissue from these arteries.
The infarcted zone can vary in size and, depending on its extent, residual cardiac function will be better or worse.
Early recognition of symptoms and early treatment reduce myocardial damage and mortality.
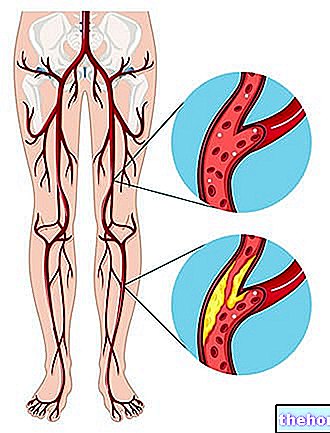
Thrombosis is a natural consequence of atherosclerosis (formation of atheromatous plaques on the internal surface of the vessels), a long-lasting process favored by incorrect life habits and behaviors, which are added to familiarity and more or less known pathologies.
At this point we list the main risk factors:
- Cigarette smoke
- Dyslipidemia (hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia)
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Overweight and obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Male sex
- Age (man> 50 years, woman> 60)
In fact, the time factor in this situation becomes the most important element and the probability of defibrillation success decreases rapidly with each minute.
In the event that the symptoms are milder, the time factor is still important. The person must arrive quickly to the emergency room where the doctor, diagnosed with the heart attack, will proceed to unblock the occluded coronary artery.
Basically, the earlier one intervenes, the higher the success rates are, since the amount of heart tissue saved is proportional to the precocity of reperfusion.
![]()
This pain has certain characteristics:
- variable intensity, usually intense and sometimes unbearable;
- it is described as constricting, overwhelming, oppressive (typically "like a weight" or "a grip" in the center of the chest);
- it is typically located behind the breastbone, but also above the stomach (sometimes the pain is mistaken for heartburn associated with indigestion)
- it can radiate to the whole chest, especially the left side, to the left arm up to the wrist and fingers, but also to the shoulder, neck, jaw and between the shoulder blades;
- it can be accompanied by cold sweats, nausea, vomiting, weakness and dizziness.
Another manifestation may be fainting (in about one case out of 10, this is the only symptom of a heart attack) and in a percentage of cases, 15-20%, the heart attack can be painless (higher incidence in subjects diabetics).
In a small percentage, acute myocardial infarction may present with the characteristics of "sudden death".
Insights
Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction Symptoms of Heart Attack in Women
![]()