The saying "carrots are good for the eyes"Does it have any scientific basis? Yes, because its veracity has been proven by modern science. In fact, there is a direct connection between vitamin A, generously contained in carrots, and eye health.
A deficiency of vitamin A could cause serious consequences for vision: eye fatigue, sensitivity to light, dry eyelids, decreased immune defenses with increased susceptibility to infections, ulceration and, in cases of greater severity, irreversible blindness. It should be remembered, however, that vitamin A deficiencies are unlikely, considering that nature offers a large array of foods rich in this vitamin: in addition to carrots, pumpkin, milk, eggs, liver and animal foods in general are also sources of vitamin A. For example, half a carrot is enough to meet the body's daily requirement of vitamin A.
As we have seen, carotenoids are pigments that paint plants with the typical bright colors: among the carotenoids stand out lutein and zeaxanthin, two substances that prevent the onset of eye diseases. Lutein is known for its properties antiradical and protective of sight: it is found mainly in spinach, lettuce, peas and cabbage. Zeaxanthin is present, however, in peppers, corn, egg yolk, mango and spinach: its deficiency could cause blindness in the elderly.
Vitamin C also plays an essential role in eye health. Being the antioxidant par excellence, together with vitamin E, ascorbic acid protects the body from the attack of free radicals. For this reason, vitamin C could be a valuable aid in the prevention of some degenerative ocular diseases. Vitamin C is useful in the treatment of glaucoma and could counteract the progressive loss of vision, avoiding the "hardening" of the eye. It is also used in the prevention of corneal ulcers and is useful in the elimination of infections. It is omnipresent in vegetables, in particular it is found in lemons, citrus fruits in general, broad-leaved vegetables, strawberries, peppers, tomatoes and cauliflowers.
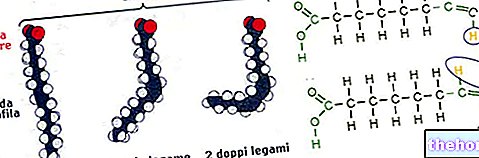
, boasts antioxidant potential: for this reason it could be useful for the prevention of ocular disorders such as cataracts and AMD (macular degeneration of adulthood). Vitamin E could decrease the severity of the acute phase of reticular fibroplasia (severe alteration of the visual structures placed behind the lens, which often leads to blindness); moreover, vitamin E has also brought positive results in strengthening the eye muscles and preventing blurred vision.Its deficiency could be a contributing cause in the detachment of the retina. Vitamin E is found in foods such as cereals, almonds, corn oil, wheat germ oil, hazelnuts.
Just as the organism benefits from a correct diet, the intake of a good quantity of vitamins is also essential for eye health: this article mainly deals with eye disorders linked to vitamin deficiencies. It should also be remembered that an "excessive intake of vitamins can cause visual disturbances of varying degrees. To give an example," an excessive supplementation of vitamin D could cause calcification of the conjunctiva and cornea.
, it is said that the eyes are the mirror of the soul: natural medicine completes the proverb, stating that the eye also represents the mirror of the body, of health and of the diseases connected to it.