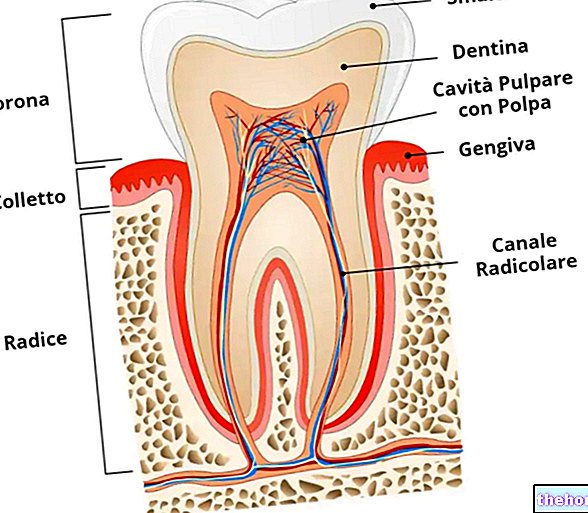
Already during pregnancy ...
The best way to take care of baby teeth is prevention.

Curiosity
When taken by the pregnant woman for long periods, some drugs - such as tetracyclines - can alter the natural tooth pigmentation (yellow teeth) and weaken the enamel in the baby's future milk teeth. In the long term, these drugs can therefore indirectly favor the formation of caries in milk teeth.
During the neonatal age ...
When the first baby teeth appear, the child is still too young to brush his teeth himself: it is therefore necessary for parents to start taking care of their child's teeth. Clearly, in this delicate phase of growth, baby teeth cannot be brushed with a toothbrush and toothpaste. The cleaning of milk teeth cannot therefore be performed in the same way as the adult's teeth are brushed: the child would run the risk of "swallowing the toothpaste or traumatizing the gums with the toothbrush, facing a series of even serious problems (eg fluorosis, in case of ingestion of large quantities of fluoride toothpaste).
Cleaning of the oral cavity should begin when the first baby tooth appears: in such circumstances, it is sufficient to gently rub a gauze soaked in physiological solution on the tooth and gums. The cleaning of the teeth, especially when performed before the night's rest, minimizes the risk of so-called "bottle caries".
During the neonatal age, the baby should be breastfed to prevent the formation of cavities in the milk teeth. The mother's milk, in fact, strengthens the teeth by promoting mineralization with calcium and phosphorus and - unlike the cow's milk (cow's milk). ) - helps protect the enamel of milk teeth.
During childhood ...
A correct diet, abundant in vegetables, balanced in terms of proteins (meat and fish), and low in refined sugars, sweets and junk food can only have a positive effect on the health of milk teeth: a "diet so set up not only it prevents the typical ailments of the modern age (first of all overweight, childhood obesity and related metabolic diseases), but also encourages the correct development of teeth.
Children are attracted to sweets, snacks, sugary snacks, gummy candies, caramelized fruit and so on. Although objectively greedy, these "foods" pose a real threat to the teeth: excessive consumption of sugars alters the natural bacterial balance of the oral cavity, thus predisposing the child to dental infections, first of all caries. It is therefore important to make the child understand which are the "good" foods to prefer and the "bad" foods to avoid or in any case to eat sporadically (then immediately running to brush his teeth).
Do not think, however, that tooth decay can be prevented simply by following a correct diet: teeth require toothpaste and a toothbrush to remove food and plaque residues that inevitably stick to the teeth after each meal.
As soon as the child is able to use the toothbrush alone, it is a good idea to educate him in the correct use of dental cleaning tools. Clearly, at this age, it is not necessary (indeed, it is contraindicated) the use of dental floss or brush, since it could hurt or damage the gums.
The choice of toothbrush is important: it must have a small head enough to be able to brush milk teeth, and the bristles that compose it should be soft. The movements of the toothbrush must be delicate and precise, i.e. always directed from the gum towards the tooth: an opposite movement (from the tooth towards the gum) can, in the long term, favor the appearance of retracted gums.
Do not forget the chewing surface of the teeth: even in this area, in fact, caries and other dental infections can manifest themselves giving rise to terrible toothache. According to this, it is well understood how important it is to brush this area as well, insisting on the intercuspid space originating from the 4 tips of the molars: being similar to a depression, this space constitutes an "ideal area for plaque deposit, consequently it can favor caries.
Another essential point for taking care of milk teeth is the choice of toothpaste. Fluorine toothpastes for children can only be used if the fluoride concentration does not exceed 500-600 ppm (adult toothpastes contain a variable amount of fluoride from 1100 to 1500 ppm). As anticipated, the risk that a child runs using a fluoride toothpaste is to swallow it, thus absorbing excessive doses of fluoride.
To prevent cavities, however, some doctors suggest supplementing the baby's diet with fluoride supplementation: the dose of the supplement must be always established by the doctor, the only one able to establish the dosage indicated for the child.
Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
Decayed milk teeth
When the milk teeth become decayed, the only intelligent and thinkable solution is the filling. It is good, therefore, to abandon the idea of not treating decayed milk teeth because they are destined to fall. By letting them rot (literally), decayed milk teeth are destined to a pathological fall, therefore against nature. In doing so, the permanent teeth that will take their place - still included in the gum and not quite ready to erupt in the oral cavity - tend to grow poorly. In such circumstances, the child runs the risk of having crooked teeth or, even worse, of suffering a malocclusion dental: these problems should not be underestimated, as they can only be corrected by using the appliance.
Did you know that ...
In severe cases, a problematic dental malocclusion (permanent dentition) may require the extraction of the crooked tooth and its subsequent repositioning in the correct position.
Clearly, we have reported a borderline case, an extreme example, but it is good to know all the eventualities that could be encountered by letting the milk teeth fall out by themselves because they are seriously ill.
After milk teeth fall out
A valuable tip to keep in mind after the fall of the milk teeth and the subsequent eruption of the permanent teeth is the dental sealing. This very important treatment, often unfortunately underestimated, guarantees good coverage from the onset of caries in the teeth in which it is performed. For this purpose, it is advisable to seal the chewing surface of the molar teeth, more exposed to the risk of dental caries because they have deep furrows (inside which bacteria and plaque tend to anchor).
After the fall of the milk teeth, the new permanent teeth require a certain "maintenance": for this reason, regular check-ups by the dentist, at least once or twice a "year, are essential to surprise in the bud any dental disorders or infections that are still silent. .
More articles on "Caring for baby teeth"
- Milk teeth
- Teething of the newborn (or deciduous dentition)
- Caries of milk teeth
- Fall of the Milk Teeth