
Toothache - better defined as odontalgia - is a very variable symptom that essentially depends on the cause of origin. Depending on the underlying disorder, toothache can in fact take on an acute and throbbing connotation or develop pain milder which is accentuated in response to thermal / physical stimuli.
As we will see in the course of the discussion, toothache is usually due to a "dental infection or" inflammation of the gum; however, there is no shortage of cases of "psychological" or idiopathic toothache, which do not recognize an easily identifiable cause. Even chipped teeth, dental hypersensitivity and tooth growth can cause unpleasant odontalgia.
Toothache, which regresses only with a correct treatment of the causes of origin, requires a dental visit to trace the etiological factor (responsible for the pain). Only after having ascertained the cause through specialist control supported by an X-ray examination, is possible to proceed with a specific intervention.
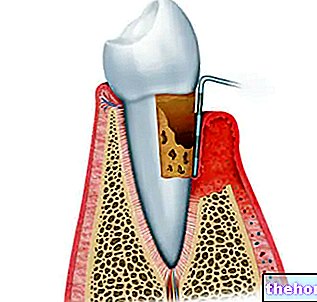
: inflammation of the alveolus (the bony cavity in which the dental roots lodge). In this case, the painful, acute and pungent perception arises when cold, hot, acidic, salty or sugary foods come into contact with the tooth.
Toothache related to dental hypersensitivity can depend on poor oral hygiene, performed for example by cleaning the teeth with toothbrushes with too hard bristles or brushing them in an inappropriate way (from the tooth to the gum). Toothache from hypersensitivity can also derive from the habit of constantly using whitening toothpastes, containing very aggressive substances that weaken the dental enamel.
Even bulimic patients (who voluntarily indulge in vomiting), those suffering from bruxism and gingival recession tend to often suffer from hypersensitivity toothaches.
In the cases just described, toothache is not directly related to dental infections or gum inflammation: in such circumstances, the pain does not require filling or devitalization operations precisely because the cause is not infectious. The only solution to treat or prevent toothache from dentinal hypersensitivity is to "constantly perform" adequate home dental cleaning (with a toothbrush, toothpaste - possibly enriched with fluoride - and dental floss), avoiding taking acidic foods or all those substances that could accentuate the pain.
it is always a source of excitement and frenzy for the little one. Toothache (if it can be considered as such) results in redness and inflammation of the gums.
When baby teeth begin to fall out and be replaced by permanent teeth, the baby tends to be agitated and constantly puts his hands in his mouth. Although it is a completely physiological phenomenon, the fall of milk teeth is not always well accepted by the child, who reacts by accusing gingival inflammation and manifesting an "evident agitation.
The loss of permanent teeth - which has nothing to do with that of milk teeth - is often explained by serious dental infections that are not adequately treated (e.g. pyorrhea): in this case, the perceived toothache is clearly very acute, excruciating and unbearable.
or dental inflammation. Often, odontalgia is a secondary symptom of conditions that have nothing to do with the teeth. Among the most noteworthy are: inflammation of the ears (otalgia), some heart problems (angina pectoris and myocardial infarction), sinusitis and trigeminal neuralgia All of these conditions can begin with a tremendous - and inexplicable - toothache.
Sometimes, toothache can be a transient phenomenon that occurs regardless of a certain cause. This is the case of stress-induced toothache: a person who is particularly stressed or tend to be depressed tends to involuntarily clench their teeth, without realizing it. Continuous grinding promotes bruxism which, in the long term, can predispose to toothache. The most effective remedy for toothache derived from bruxism is to relax, carving out some time to dedicate to yourself. Autogenic training, pilates, yoga, physical exercise certainly help to harmonize the various parts of the body. , with a positive reflex aimed at counteracting stress-related phenomena, such as bruxism toothache.
Other articles on "Toothache - Causes"
- Type of toothache
- Toothache: What to do
- Toothache remedies




.jpg)





















