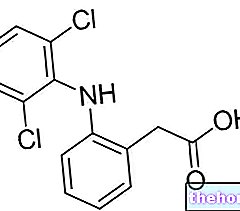
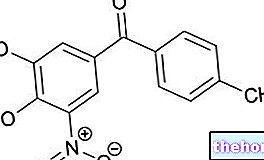
What is lidocaine?

Lidocaine can be applied directly to the skin surface, inoculated under the skin, injected intravenously or infiltrated into the joint:
- Distributed on the skin, lidocaine is used to relieve itching, burning or pain associated with inflammation of the skin.
- In the form of an injection under the skin, lidocaine is used in various fields, ranging from dental to minor surgery (aesthetic and otherwise). More generally, lidocaine injections are performed to induce local analgesia in a large number of areas of medicine.
- Injected intravenously, lidocaine is widely used in the treatment of cardiac disorders (eg ventricular arrhythmias) and in the prevention of cardiovascular events such as heart attack.
- Injected into soft tissues (eg intrasynovial injection), the drug is used in the treatment of joint disorders.
Did you know that ...
According to the classification of the FDA (Food And Drug Administration), lidocaine is considered the most suitable local anesthetic drug for pregnant women and for women who are breastfeeding.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Being an aminoamide, lidocaine differs from other common local analgesics (aminoesters) such as procaine and chlorprocaine. Compared to the latter, lidocaine is considerably more beneficial due to its very rapid and long-lasting action.
On average, the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is reached 20 minutes after administration.
Lidocaine performs its function by inhibiting the voltage-dependent sodium channels of the neurons: by doing so, the drug prevents the nerve fiber from conducting the painful stimulus, both in the skin and deep down. 50% of the circulating lidocaine is metabolized within 90-120 minutes of administration; subsequently, the drug is eliminated in the kidney, then excreted in the urine in the form of metabolites (monoethylglycinxilidide and glycinxilidide).
The half-life of lidocaine may be prolonged in the presence of impaired liver function or congestive heart failure.
Topical application
As mentioned, lidocaine is an active ingredient with a wide field of application. Applied directly to the skin, the drug proves to be an excellent solution to alleviate - albeit temporarily - the sensation of tingling, burning and pain that accompanies a good part of the skin inflammations. Lidocaine is a drug often recommended in the treatment of St. Anthony's Fire.
Lidocaine is also indicated in the treatment of jellyfish stings.
The drug can also be spread on the mucous membranes: lidocaine is in fact a good therapeutic aid to alleviate the fierce burning that accompanies vaginal candidiasis, vaginal itching, anal fissures and hemorrhoids.
It should be emphasized that in these cases lidocaine acts exclusively on the symptom, without however interacting in any way on the triggering cause.
Lidocaine can be administered transdermally before proceeding with invasive diagnostic / therapeutic interventions, such as, for example, rachicentesis; in this case the aim is to reduce the perception of pain during the introduction of the lumbar puncture needle.
Injection under the skin / deep
Lidocaine injections are used to numb a certain area of the body and thus reduce the pain and discomfort caused by medical procedures such as surgery, catheter insertions or needle insertions.
The injectable lidocaine under the skin is used in different areas. Let's see them in detail:
- In dentistry, lidocaine is used at a concentration of 2%, often in association with adrenaline (powerful vasoconstrictor). The combination of lidocaine (2%) + adrenaline (dilution 1: 80,000) is an effective and safe preparation for obtaining a excellent analgesic effect before dental interventions such as fillings, root canals, apicoectomy, dental extraction or whatever.
- In aesthetic medicine, lidocaine is injected under the skin to anesthetize the area to be treated before administering specific medications to treat skin blemishes such as wrinkles, crow's feet, scar lesions, etc. (eg hyaluronic acid filler, polylactic acid, collagen).
- Lidocaine can also be injected epidurally: in this case, the drug is used to reduce the discomfort induced by contractions during labor.
Intravenous injection
Administered intravenously, lidocaine is widely used for the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. In particular, the active ingredient is used in the treatment of arrhythmias related to acute myocardial infarction, digitalis poisoning and cardiac catheterization. Despite what has been stated, it is good to point out that, today, the routine administration for the prophylaxis of arrhythmias for myocardial infarction does not fully convince the experts; therefore it is not always recommended.
Curiosity
Lidocaine is considered the prototype of class I antiarrhythmic drugs with greater selectivity: in simple words, the active ingredient has a good local analgesic capacity, but does not have a similar atropine effect (anticholinergic activity). In these cases, lidocaine acts directly on the heart cells.
Intra-articular injection (lidocaine infiltration)
Often, lidocaine is formulated in combination with other active ingredients (eg corticosteroids) for intraarticular injection.Lidocaine and corticosteroids, with clearly different mechanisms of action, are combined to encourage the overcoming of morbid / painful conditions on an inflammatory basis. An example is the medicinal specialty Depo-Medrol + Lidocaine: the drug is injected into the soft tissues, intrasynovially (directly in the synovial fluid) and intralesional, for the treatment of synovitis, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Other uses of lidocaine
The drug can also be used as a temporary tinnitus remedy, useful for reducing the terrible ringing in the ears.
Lidocaine is often used for the control of seizures.
Inhaled in the form of a spray / aerosol, lidocaine can be used as an antitussive in the treatment of chronic cough.
Pharmaceutical forms
Lidocaine is available in a large number of pharmaceutical forms. The most common are listed below:
- Patch (for topical application)
- Gel for topical application, often combined with soothing substances such as aloe vera
- Gel / liquid for oral use
- Intravenous injection, possibly combined with adrenaline
- Intravenous infusion
- Injection under the skin as a local anesthetic in combination with adrenaline (useful for reducing or limiting bleeding)
- Self-injectable lidocaine *
- Nasal instillation or spray: in this case, lidocaine is usually combined with phenylephrine
- Preparation for inhalation
- Sterile injectable aqueous suspension, possibly associated with other active ingredients, such as corticosteroids
Self-injectable lidocaine *
Some people who show obvious heart rhythm irregularities are sometimes prescribed a special lidocaine preparation. The drug, known as LidoPen, is an automatic pre-filled self-injection device, to be used only in an emergency. The drug is injected into the upper part of the thigh or into the deltoid muscle of the arm, never in the buttocks or near a However, before self-inoculating lidocaine, medical advice is strongly recommended.
Lidocaine: contraindication and side effects "