The Chioggia radicchio is a red vegetable, with a closed ball shape, bitter taste and characteristic flavor. Other types of red radicchio are: radicchio di Treviso and radicchio di Verona.

It is one of the many varieties of the botanical species intybus X endivia - Family Asteraceae (Compositae), Subfamily Cichorioideae and Genus Cichorium. It is differentiated into early types, harvested from April to mid-May, and late, harvested from September to March.
The radicchio di Chioggia enjoys the recognition of IGP - Protected Geographical Indication.The cultivation area of the late one is bounded by the provinces of Venice, Rovigo and Padua; the precocious one, on the other hand, is grown between the municipalities of Chioggia and Rosolina.
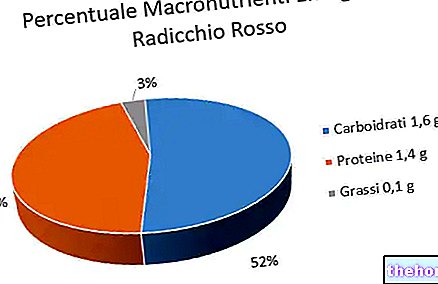
Chioggia radicchio contains significant quantities of both vitamin A, or rather equivalent retinol (especially carotenoids), and vitamin C (ascorbic acid); therefore it is inserted in both the last fundamental groups of foods - VI and VII. The radicchio di Chioggia also contains a lot of water, dietary fibers, minerals - especially potassium and magnesium - and polyphenols - with particular reference to anthocyanins.
Chioggia radicchio can be eaten raw and cooked; raw especially in salads, cooked sautéed, stewed, baked, etc.
rich in vitamin C and vitamin A or RAE.It has a very low calorie intake, as all three energetic macronutrients are present in modest quantities. Carbohydrates tend to be soluble, simple - made up of fructose. The fatty acids should be largely unsaturated and the proteins of low biological value.
The radicchio di Chioggia contains dietary fibers, most of which are soluble. There are plant steroid molecules, called phytosterols, with metabolic action opposite to cholesterol. These plant sterols belong to the broadest set of polyphenols, many others of which - especially anthocyanins - are also well present in the Chioggia radicchio. It does not contain lactose, gluten and histamine. The purine intake is very low.
Chioggia radicchio has an "excellent concentration of vitamin C or ascorbic acid and equivalent retinol (RAE), in particular beta carotene. The average contributions of potassium and magnesium are notable."
Edible part
Like all vegetables, Chioggia radicchio is not a good source of high biological value proteins. The quantity of essential amino acids and their proportion is in fact very different compared to the human protein model. Fatty acids, although mainly unsaturated, being present in small quantities do not have a significant impact on metabolism.
The abundance of fibers gives the Chioggia radicchio many beneficial properties for the body. Associated with the right amount of water, they increase the sense of satiety - increasing the volume of the meal in the stomach - a very useful feature in the slimming diet. Especially the soluble ones, they create a gel that modulates nutritional absorption through two mechanisms: they reduce the absorption rate of carbohydrates, by decreasing the insulin glycemic index of the meal, hinder the absorption and reabsorption of fats, especially cholesterol and bile juices - rich in endogenous cholesterol. Chioggia radicchio is suitable for dietary therapy against hypercholesterolemia - to which polyphenols contribute - type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertriglyceridemia. The fibers contained in it improve intestinal transit, preventing / treating constipation and related disorders such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, the tendency to anal prolapse etc; at the same time, by optimizing the expulsion of toxins and other waste, they act as a protective factor against some cancers of the colon. The fibers also nourish the intestinal flora - acting as a prebiotic - which also contributes to maintaining the health of the colon. intestine.
The radicchio di Chioggia has no contraindications for the diet of lactose intolerant, celiac and histamine intolerant. The low presence of purines makes it suitable for the nutritional regimen against hyperuricemia and gout.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, as well as a precursor to collagen, an essential element of the immune system, etc. In addition to having an antioxidant function, carotenoids can also be recombined in the organism to form vitamin A, which is necessary for visual function, for cell differentiation, to maintain reproductive function, etc. Polyphenols are the third antioxidant agent of Chioggia radicchio. The high concentration of molecules endowed with this function makes this vegetable suitable to fight the oxidative stress of the organism, acting preventively against tumors and hindering the onset of metabolic pathologies.
The richness of water and potassium is considered a preventive aspect of primary arterial hypertension, especially sodium-sensitive - potassium acts metabolically in contrast to sodium and water increases diuresis, favoring the elimination of the unwanted ion. Furthermore, these are two nutritional factors largely eliminated with sweating, greater in hot climates and in sports. Potassium and magnesium are alkalizing minerals which, when deficient in the body, can cause muscle cramps. The nutritional action of the iron and calcium contained in the Chioggia radicchio is marginal.
We remind you that, in the pregnant woman's diet, raw Chioggia radicchio must be washed carefully and possibly in solution with disinfectants, to reduce the risk of infection or infestation by bacteria or parasites that are dangerous for the success of pregnancy.
. This ingredient is also used in the preparation of a "wide variety of sauces - for example the bechamel flavored with Chioggia radicchio. Chioggia radicchio sautéed with oil, salt, lemon / wine / balsamic vinegar and garlic is famous and widespread; many enrich it with bacon or speck or diced lard or strips.