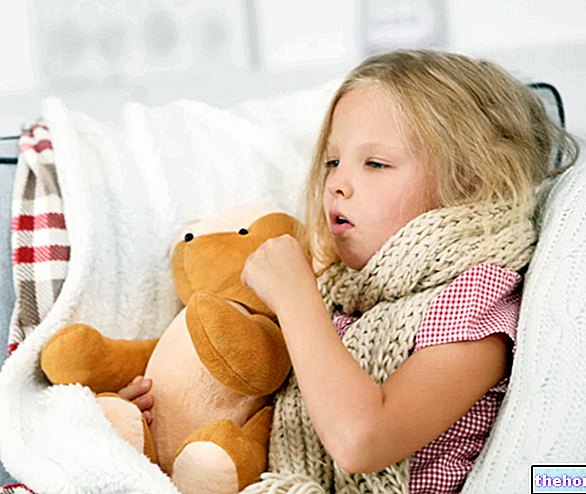
Cough is a defense mechanism of the organism, characterized by the rapid and energetic expulsion of air from the lungs; this act has the purpose of freeing the airways from any obstructions, caused for example by foreign particles, mucus, liquids, etc.
Cough in children - as well as that which occurs in adult patients - can be of two types:
- Fat cough, accompanied by the emission of mucus or phlegm (sputum);
- Dry or non-productive cough, which is a cough without any type of sputum.
In some cases, moreover, the cough can also be mixed, ie the child alternates between phases of fat cough and dry cough during the day.
, tracheitis, etc.);Depending on the triggering cause, the cough can be acute (lasting less than three weeks) or chronic (lasting more than three weeks). However, the most common type of cough in children is acute.
, insomnia, agitation and chest pain due to the constant coughing.
Furthermore, the cough is often associated with the symptoms of the pathology that caused it. For example, in the event that the cough in children is caused by a cold or flu, it can be accompanied by:
- Fever;
- Headache;
- Sore throat;
- Nausea;
- Diarrhea;
- Hoarseness;
- Articolar pains;
- Loss of appetite;
- Diarrhea.
A disease of the airways typical of young children - the so-called croup - gives rise to a form of cough known as a barking cough, due to the similarity of the cough to the barking emitted by the dog.
, the pediatrician will prescribe antibiotic drugs, such as amoxicillin or cefixime. If the cause is inflammatory, however, the doctor may opt for the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen.
In addition to this, if the doctor deems it appropriate, he may decide to start a pharmacological treatment aimed exclusively at contrasting the cough symptom.
Indeed, the pharmacological treatment of cough in children is a rather controversial issue, as there are no clinical studies performed on pediatric patients able to confirm the real efficacy and effective safety of use of antitussive drugs in this category of patients.
In any case, basically two types of drugs can be used for the treatment of cough in children:
- Cough suppressants - such as dextromethorphan and levodropropizina - whose use is carried out in case of dry cough;
- The fluidifiers or mucolytics - such as N-acetylcysteine or ambroxol - whose task is to fluidify, therefore to favor the expulsion, of the secretions that characterize a fatty cough.
In any case, the decision to administer or not medicines for the treatment of cough in children, as well as the choice of the active ingredient, the dose of drug to be taken and the duration of therapy are the sole and exclusive responsibility of the pediatrician who is treating the child. .
Therefore, it is essential not to do your own thing and avoid giving the child (especially if very young) drugs at any time - not even those without a prescription - without first asking the doctor's advice. In fact, the improper administration of Cough medicines could sometimes be counterproductive, if not harmful or potentially dangerous for the baby.
and / or increased respiratory rate, as these could be symptoms of a "possible underlying asthma disease;"