In most cases, hard stools are caused by an inadequate diet, in particular by a low consumption of fiber, by the habit of drinking little and by being in a hurry at the table. This manifestation can also represent a consequence of sedentary lifestyle, stress or the tendency to postpone the urge to go to the bathroom.
Hard stools can also be related to certain medications and diseases, such as diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or diverticulosis. If the problem recurs frequently or does not resolve itself within a few days, it can signal the presence of more severe disorders in the gastrointestinal system, which must be investigated with a careful medical evaluation.
(or constipation), as the persistence of fecal material in the "intestine subjects" the latter to the risk of dehydration.
Hard stools can also form as a result of the occasional evacuation, but can also represent an indication of pathological conditions, affecting the gastrointestinal system, such as irritable bowel syndrome or colitis, or other systems of the " body.
When hard stools occur sporadically and resolve in a few days, they should not be a cause for concern and, often, it is not necessary to resort to special care: better eating habits are usually enough to solve the problem.
In some cases, however, hard stools can become a recurring condition and, if associated with other pathologies, require targeted treatments for their solution.
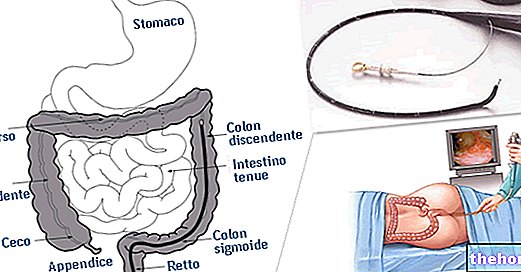
. Their consistency basically depends on the eating habits and the functionality of the subject's gastrointestinal system. Learn more about Stool Consistency and ShapeHard stools are difficult to pass, often get stuck in the intestinal tract, and can lead to constipation. This symptom is mostly attributable to a lack of fluids in the enteric canal or to a decrease in bowel movements. The factors that can contribute to this problem can, however, be many and varied.