
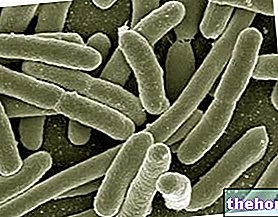
Potentially lethal, bacterial meningitis can be due to bacteria, such as: meningococcus, pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae type B, Listeria monocytogenes, group B beta hemolytic streptococcus ed Escherichia coli.
Bacterial meningitis most frequently affects individuals under the age of 5 (especially infants) and individuals in a state of immunosuppression.
Characterized by a wide variety of symptoms (eg: fever, neck stiffness, drowsiness, photophobia, etc.), bacterial meningitis can lead to serious complications, such as sepsis, encephalitis and myelitis.
In general, for the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis, a thorough physical examination, a blood culture and a lumbar puncture are essential.
Bacterial meningitis requires immediate hospitalization of the patient and requires appropriate antibiotic treatment.
For further information: Viral Meningitis: What it is, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
In addition to bacterial meningitis and viral meningitis, there is also fungal meningitis, which is meningitis due to fungi.










.jpg)











