Generality

- Some antimetabolite agents are able to inhibit the enzymes involved in the synthesis of nucleotides (the fundamental units that make up DNA); in this way - if the nucleotide intermediates are not synthesized - the synthesis of DNA is interrupted and there is an arrest of tumor growth.
-
DNA is made up of two strands joined around each other to form a double helix. DNA is made up of many monomers, called nucleotides. There are 4 types of nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T), which combine with unique AT (adenine-thymine) and CG (cytosine-guanine) pairs held together by hydrogen bonds . The sequence of bases present along the DNA molecule carries the genetic information. Other antimetabolites, on the other hand, have a structure very similar to that of endogenous nucleotides (nucleotides normally present in the cell) and can replace them during the synthesis of the new DNA strand, thus hindering its correct formation and blocking cell replication.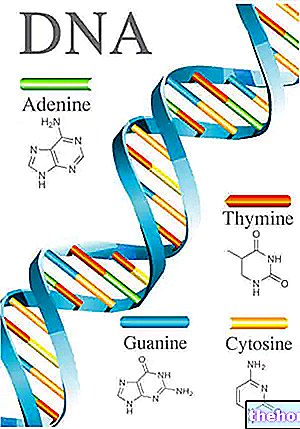
Types of antimetabolite agents
DNA is made up of four nucleotides that establish bonds between them to form the classic double helix structure that characterizes it. These nucleotides are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine, and are otherwise referred to as "nitrogenous bases'.
The nitrogenous bases - depending on the structure they possess - are divided into purines, which include adenine and guanine, and in pyrimidines, which includes cytosine and thymine.
Purine and pyrimidine inhibitors
Antimetabolite agents can be classified according to the type of nitrogen base they are able to inhibit:
- Purine inhibitors: as the name implies, these antimetabolites are able to inhibit the synthesis of purine nitrogenous bases. This class includes the mercaptopurine, used in the treatment of acute lymphatic leukemia and myeloblastic leukemia, and its derivative, the "azathioprine, with immunosuppressive activity and used in the treatment of various diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, thrombocytopenia, autoimmune hepatitis, pemphigus vulgaris, sarcoidosis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. The thioguanine, administered orally in the treatment of non-lymphocytic leukemias.
- Pyrimidine inhibitors: these antimetabolites inhibit the synthesis of pyrimidine bases. Among these we find the 5-fluorouracil, used in the treatment of colon, breast, stomach and pancreatic cancer; there floxuridine, used in the palliative treatment of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma which has metastases in the liver and which cannot be surgically removed. capecitabine, used alone or in association with a docetaxel for the treatment of breast cancer, colorectal cancer and advanced gastric cancer.
DNA polymerase inhibitors
Another class of antimetabolite drugs is constituted by DNA polymerase inhibitors, one of the enzymes involved in the synthesis of the double strand of DNA. Among these drugs we find cytarabine And gemcitabine.
Cytarabine is used for the treatment of breast, pancreatic, non-small cell lung cancer and for the treatment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin leukemia and lymphomas.
Gemcitabine can be administered subcutaneously, intrathecally (in the spinal fluid) and intravenously; it is used for the treatment of various types of leukemia.
FOLIC ACID inhibitors
Folic acid inhibitors are also considered antimetabolic agents. Folic acid, in fact, is fundamental in some steps of DNA synthesis.
As soon as the importance of the role of folic acid in the synthesis of new DNA was discovered, researchers realized the importance of its inhibitors as potential drugs for the treatment of tumors. For this reason, folic acid inhibitors have been and they are still the subject of studies and research.
They are part of this class l "aminopterin and the methotrexate, the latter is used in the treatment of breast, head, neck and some types of lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.