What is Ectropion?
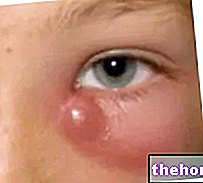
The ectropion is a condition in which the lid margin faces outwards; this involves the exposure of the conjunctiva, which is therefore subject to irritation.
The ectropion mainly affects the lower eyelid and can occur in one or both eyes. The extent of the disturbance is variable: in the most severe cases, the entire eyelid rim is affected, while when it is mild only a small segment can distance itself from the eyeball.
.jpg)
Artificial tears can help relieve symptoms temporarily, pending corrective surgery.
Symptoms
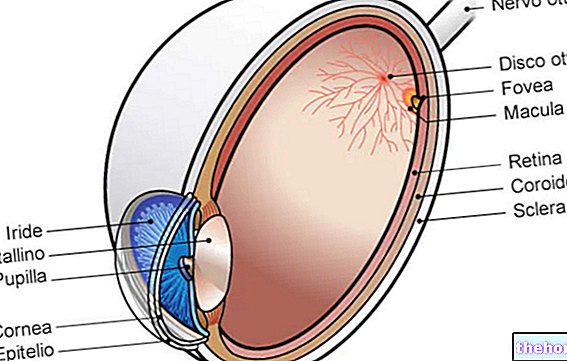
The eyelids play a fundamental role in protecting the eyes: in addition to providing a mechanical barrier, their intermittent movements distribute the tears over the entire surface of the eye, keeping it lubricated and free from dust and other particles. The tears constantly moisten the ocular surface. and flow out through a system of tear ducts, near the lower inner corner of the eyelids. Normally, the upper and lower lids close tightly, protecting the eye from damage and preventing tear evaporation.
In case of ectropion, the eyelids cannot fully perform their function. If the lid margin faces outward, the (normally moist) internal conjunctival surface is visible and exposure to air can cause chronic redness and irritation. The tear film is not evenly distributed over the ocular surface and the normal process of Drainage can stop. Also, if the tears are unable to flow properly, they make the eye vulnerable to infections, such as conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of ectropion include:
- Redness and irritation;
- Excessive tearing
- Dry eye
- Burning in the eye;
- Infection.
The patient may also have: mild eye pain, eye discharge and crusting on the eyelids. Chronic irritation, excessive dryness and exposure of the anterior surface of the eye can lead to corneal de-epithelialization (ie damage to the most superficial layer of the cornea). In the case of ectropion, reduced vision, rapid increase in pain and sensitivity to light require immediate medical attention.
Causes
In most cases, ectropion is age related. The condition is the result of muscle weakness and relaxation of the tissues associated with aging, which produce hyperlaxity of the eyelids.
Other, less common, causes of ectropion include:
- Bell's palsy (damages the nerve that controls the muscles of the face), stroke or other neurological conditions that result in facial paralysis
- Damage to the eyelids caused by trauma or burns;
- Rapid weight loss;
- Nodules and cysts that develop in the eyelid (both cancerous and benign lesions)
- Previous eyelid surgery or radiation therapy
- Scar tissue, as a result of injury or previous surgery
- Complication of a skin condition (example: contact dermatitis).

.jpg)