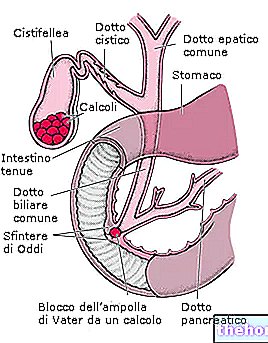
THE gallstones (lithiasis or gallbladder stones) are solid aggregations (almost always cholesterol) that form in the gallbladder.
Also called the gallbladder, the gallbladder it is the organ necessary for the storage of bile (digestive liquid secreted by the liver).

When the equilibrium of this suspension is compromised, some components precipitate, aggregate and contribute to the formation of stones.
Gallstones can cause: biliary colic, acute cholecystitis (inflammation), chronic (with thickening of the tissues, fluid, etc.) and other serious complications.
Gallstones affect 10-15% of the population, but are often asymptomatic (60-80%).
There biliary colic manifests itself with: severe pain in the upper abdomen radiating under the shoulder blade, nausea and vomiting.
N.B. Biliary colic and cholecystitis are not synonymous. In fact, in some cases (<5%) the cholecystitis are alitiasic (independent of the calculations).
The material published is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Gallbladder Stones; such indications must in no way replace the opinion of the treating physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
What to do
- Preventive action on behavioral risk factors:
- Maintain a normal weight;
- Respect the nutritional balance;
- Avoiding or treating predisposing metabolic diseases; eg:
- Hypercholesterolemia;
- Hypertriglyceridemia;
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- Avoid, whenever possible, the birth control pill;
- If you have any noticeable symptoms, you need to see a doctor or specialist for one diagnosis specific;
- Generally, an abdominal ultrasound is sufficient; if it is negative and the symptoms remain, we proceed with other tests such as:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography;
- Percutaneous cholangioscopy;
- MRI-cholangiography;
- Follow the eventual pharmacological therapy prescribed by the doctor;
- In the event that the gallstones cause serious disorders or reach annoying dimensions, the "only solution is"surgical removal of the gallbladder.
What NOT to do
- Become and remain obese for a long time;
- Coping with long periods of fasting or undernutrition also avoid losing weight too quickly;
- Follow an unbalanced and low-fat diet;
- Drink little water, eat dry foods and stay dehydrated (alcohol abuse contributes to this);
- Keep the parameters of: cholesterol, triglyceridemia and glycaemia high;
- Irregularly take the prescribed medication for gallstones.
These precautions must be avoided especially in the presence of one or more risk factors Which:
- Familiarity;
- Age> 40 years;
- Female sex;
- Multiple pregnancies;
- Scandinavian or Native American population;
- Suffering from haemolytic anemia;
- Suffering from chronic bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, Ulcerative Rectum-Colitis).
What to eat
As anticipated, diet is a determining factor; it is advisable to prefer:
- Foods of animal origin with low cholesterol and a medium-low quantity of fatty acids: fish, lean meats, partially skimmed or skimmed milk, lean ricotta, fresh lean cheeses, egg whites;
- Vegetable oil-based condiments, preferably cold pressed (rich in phytosterols and vitamin E), even in good quantities. They improve digestion, do not affect the expulsion of bile and are beneficial for the metabolism;
- Foods rich in polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats: omega 3, omega 6 and omega 9 reduce the levels of cholesterolemia, triglyceridemia and moderate the complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. They are rich in: oily fish, algae, seeds or oily fruits and related oils extraction;
- Products rich in fiber, with a low or moderate glycemic index: they reduce the absorption / reabsorption of dietary cholesterol and bile; in addition, they keep blood sugar at normal levels. Whole grains, low calorie and not very sweet fruit, legumes, vegetables and seeds oily;
- Hydrated foods; it is recommended to drink a lot of water;
What NOT to Eat
- Fried, creamy desserts, condiments of animal origin or hydrogenated: poor in good lipids, phytosterols, fat-soluble vitamins and rich in bad fatty acids;
- Foods rich in hydrogenated and trans fats: they do not have a direct effect on gallstones but negatively affect cholesterol and cardiovascular risk; moreover, their consumption implies a reduction of good fats (if we want to maintain the principle of nutritional balance with 25-30% of lipids in the diet). They are mainly contained in salty snacks and industrial sweets;
- Foods of animal origin too rich in cholesterol and fats, especially saturated: cream, butter, fatty and / or seasoned cheeses, fatty cuts of meat (bacon, lard, coppone, ribs, etc.), fatty cold cuts and especially sausages, offal, egg yolk "egg (controversial), crustaceans and certain molluscs;
- Refined, sweetened products, low in fiber and high glycemic index: white bread, desserts, etc .;
- Lots of alcoholic drinks;
Natural Cures and Remedies
It is believed that some natural products can exert a preventive effect on the formation of gallstones.
Certain herbs and foods act:
- By increasing the production of bile;
- Improving the peristaltic contractions of the gallbladder and favoring its emptying (preventing deposition);
- By reducing the absorption / reabsorption of cholesterol and bile in the intestine;
Some of these medicinal plants are:
- Milk thistle;
- Artichoke;
- Elecampane;
- Fennel;
- Aubergine;
- Borage;
- Peppermint;
- Absinthe;
- Oats;
- Cherry;
- Onion;
- Strawberry;
- Lemon;
- Grape;
- Rhubarb;
- Boldo;
- Aloe;
- Chicory;
- Rosemary;
- Dandelion (controversial);
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological remedies for gallstones are of two types:
- Against some responsible risk factors;
- Pain relievers and relaxants for the gallbladder;
- Specific to rebalance the composition of bile by stabilizing it:
- Ursodeoxycholic acid or ursodiol (eg Ursobil HT, Ursodes AGE Acid, Litursol): they tend to dissolve small and transparent stones;
- Terpenes: make bile more soluble;
- Chenodeoxycholic acid: tends to dissolve stones;
- Thiazide diuretics (eg. Hydrochlorothiazide: eg. Moduretic, Esidrex): useful against calcium aggregations.
Prevention
Prevention of gallstones requires:
- Awareness of independent risk factors (family history, sex, age, ethnicity, other diseases, etc.);
- Reduction of risk factors that depend on lifestyle and diet (overweight, metabolic diseases, fasting, nutritional imbalance, birth control pills, etc.);
- Taking prescribed drug therapy.
Medical treatments
Surgery to treat gallstones can be done in two ways:
- Traditional cholecystectomy: invasive; it involves a major surgical cut but has a very high success rate;
- Videolaparosurgery: minimally invasive; the cuts are small but it is limited when the gallbladder is hidden. In this case, the traditional method is used.












.jpg)











