
About 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
100% WHEY PRO - SCITEC NUTRITION
Concentrated and ultrafiltered whey protein food supplement
FORMAT
Pack of 900gr, 2350 gr and 5000 gr various flavors.
COMPOSITION
Concentrated and ultra-filtered whey proteins containing: lactoglobulin, lactoferrin, lactalbumin, immunoglobulin protein fraction, L-glutamine, Blend of flavors and dyes, Aspartame
Average Analysis (Cocoa Taste)
For 100 g
Per daily dose (12.5 g)
Energy value
384 Kcal / 1605 Kj
48 Kcal / 200.6 Kj
Proteins
76 g
9.5 g
Carbohydrates
5.6 g
0.7 g
Fat
8 g
1 g
Sodium
0.1 g
0 g
Potassium
0.4 g
0.1 g
Amino Acids Profile
For 100 g
Per daily dose (12.5 g)
L-Alanine
3528 mg
441 mg
L-Arginine
1692 mg
211.5 mg
L-aspartic acid
8672 mg
1084 mg
L-cysteine + L-methionine
3160 mg
395 mg
L-glutamine
13792 mg
1724 mg
L-glycine
1468 mg
183.5 mg
L-histidine
1544 mg
193 mg
L-Isoleucine
4996 mg
624.5 mg
L-Leucine
7716 mg
964.5 mg
L-Lysine
7276 mg
909.5 mg
L-Phenylalanine + L-Tyrosine
4996 mg
624.5 mg
L-proline
4924 mg
615.5 mg
L-serine
4484 mg
560.5 mg
L-threonine
5732 mg
716.5 mg
L-Tryptophan
1324 mg
165.5 mg
L-valine
4996 mg
624.5 mg
Product features 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
The proteins in question were obtained through whey concentration and ultrafiltration processes. During the production process, the whey is conveyed through a high pressure circuit to gradually lower porosity filters, which reduce the presence of any residues, guaranteeing a good quality / price ratio. Generally the products thus obtained have a protein concentration between 70 and 80% and a fat content between 4 and 6%. An important evaluation parameter, which allows to evaluate the quality of the product, is the content of sodium, which should never exceed 200 mg per 100 g of product, even if its indication on the label is not mandatory.
Whey Protein- the term whey pro generally indicates whey proteins obtained through different extraction and purification processes, distinguishing them from milk proteins particularly rich in caseins. The different amino acid profile and the different structural complexity between whey proteins and milk proteins decisively influence both the pharmacokinetic properties and the functional characteristics, guaranteeing different applications. More precisely, several studies have shown how the absorption kinetics of whey are much faster than other proteins, guaranteeing a plasma amino acid peak already 30 minutes after their ingestion; this result is essentially due to the selection of easily digestible proteins and peptides, which can be absorbed by the intestinal wall through specific transporters known as PEPT. The rapid digestion time and the high availability of amino acids that follows their intake, makes whey proteins particularly suitable in the post work-out phase, because they are ideal in favoring the recovery process. The induction of the anabolic process is one of the effects. most sought after by sportsmen and most characterized by the scientific world; this stimulus seems to be associated with different molecular and metabolic pathways, including:
- Presence of the substrate: the presence of free amino acids is necessary to start the protein synthesis process;
- Molecular action: it seems to be linked mainly to some amino acids, such as BCAAs, and more particularly to leucine and its metabolites. It has been noted, both in vitro and in vivo, how this amino acid can induce the activation of some transcription factors, such as mTor, necessary to direct the anabolism towards protein synthesis and to modulate the activity of the Akt pathway, also promoting the re-synthesis of muscle glycogen All these actions appear to be inhibited in the case of low-protein diets, where the protein content falls below half a gram per kilo of body weight.
- Hormonal action: according to what is said, the secretagogical action on beta cells by proteins is now known and unanimously recognized by the scientific world.
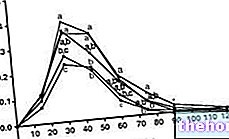
The induction of insulin secretion, which generally reaches a maximum peak around 30/50 minutes from intake, could prove to be particularly useful in supporting the anabolic phase, inducing both the resynthesis of glycogen and the protein synthesis process, already promoted by the presence of amino acids.
Although hypertrophy is the main objective sought by those who take supplements of this type, the literature has also tried to clarify other possible ergogenic capacities of whey proteins.
Although still discussed by experts in the field and less characterized than the previous characteristic, for which there also seems to be an "evident molecular basis, it is also possible to list other whey protein activities:
- Ergogenic role: several studies seem to agree on the ability of proteins to provide a greater energy boost to the athlete who uses it. In reality, the best results have been obtained by designing balanced pre-competition or pre-workout snacks and also containing a significant amount of carbohydrates.
- Protective role: still much discussed, it is partly justified by the protective action of some amino acids on muscle metabolism. More precisely, pre-competition administration should be able to save muscle proteins from catabolism and the related amino acids from oxidation. This property, observed only in some studies and denied by others, would affect the levels of creatine kinase and lactic dehydrogenase, two important markers of muscle damage.
- Immunostimulating role: recent evidence seems to suggest a protective role against the immune system. Rather evident in particular pathological conditions and in conditions of generalized stress, the enhancement of the immune defenses could be correlated on the one hand to the enhancement of the body's antioxidant capacity. And on the other to an inducing action by some amino acids such as glutamine .
How to use recommended by the company - 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
Take ½ scoop equal to 12.5 grams per day between meals, dissolved in your favorite drink.
How to use in sports practice 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
Very interesting is the rereading of the scientific articles relating to the timing and dosage of protein supplements. Of course, first of all, it is necessary to specify that it is not possible to define a recommended dosage valid for everyone, as this should be calculated and adapted to the dietary, nutritional and physiological needs of the athlete. In order for the supplementary protocol with proteins to guarantee appreciable results, it is in fact very It is important that it is perfectly coordinated with the daily dietary protein intake, which must be programmed according to body weight and the type of physical activity performed.
Once this criterion has been defined, the protein powder supplement can be used to optimize the timing of intake and reduce the problems associated with an excess of protein foods.
Most protocols define optimal - for recovery and to stimulate muscle growth - the use of whey protein intake immediately after work-out, with a ratio of 1 to 3 with carbohydrates. As it is known, in fact, the protein / CHO synergy is particularly important in restoring previously depleted glycogen reserves and in facilitating protein synthesis.
However, there are other protocols that obtain an important result in terms of hypertrophy, by dividing the protein share into several intakes at regular time intervals.
In both cases, it is recommended to take it on an empty stomach.
According to various studies, to obtain appreciable results, supplementation should be prolonged for at least 8 weeks.
Synergy - 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
Proteins + antioxidants: the association of antioxidants seems to enhance the protective effect of proteins during intense physical activity.
Proteins + CHO: seems to be the most effective combination ever. In the pre-competition, suitably combined and choosing the most suitable source, carbohydrates can support performance and improve the energy properties of the muscle; in the post-work out, however, they can optimize the recovery and growth process.
Proteins + Creatine: always combined with carbohydrates, taken in the post work out, they seem to improve the increase in lean mass, even if not all studies agree.
100% Whey Pro Side Effects - Scitec Nutrition
Known are the long-term side effects of a diet too rich in protein or amino acids; damage to the kidney, dehydration induced by increased urinary secretion, liver or kidney suffering, lipidemic alterations and related associated pathologies, tissue acidosis and bone demineralization, are just some of the consequences of an unbalanced diet over time. Among the harmful effects deriving from a diet too rich in proteins, there is certainly also the increase in adipose tissue induced by the complex metabolic crossroads responsible for the energetic-functional coordination of the organism.
Precautions for use 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition
The product is contraindicated in cases of renal or hepatic pathology, cardiovascular disease and / or hypertension, allergies and autoimmune diseases, during pregnancy, during lactation, under the age of 12 and for adolescents not yet trained.
In case of prolonged use (over 6/8 weeks) the doctor's opinion is necessary.
This article, elaborated on the critical rereading of scientific articles, university texts and common practice, is for information purposes only and therefore has no medical prescription value. It is therefore always required to consult your doctor, nutritionist or pharmacist before undertaking the use of any supplement.. Learn more about the critical analysis of 100% Whey Pro - Scitec Nutrition.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2004 Jun; 14: 255-71.
Effect of an amino acid, protein, and carbohydrate mixture on net muscle protein balance after resistance exercise.Borsheim E, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR.
Protein synthesis levels increase by associating post-workout proteins with CHOs.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2007 Jul; 23: 378-85.
Tessari P, Kiwanuka E, Cristini M, Zaramella M, Enslen M, Zurlo C, Garcia-Rodenas C.
Effects of a combined essential amino acids / carbohydrate supplementation on muscle mass, architecture and maximal strength following heavy-load training.
Vieillevoye S, Poortmans JR, Duchateau J, Carpentier A.
Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Jun 3. [Epub ahead of print]
Effects of whey protein isolate on body composition, lipids, insulin and glucose in overweight and obese individuals.
Pal S, Ellis V, Dhaliwal S.
Br J Nutr. 2010 Apr 9: 1-8. [Epub ahead of print]
Effect of protein / essential amino acids and resistance training on skeletal muscle hypertrophy: A case for whey protein.
Hulmi JJ, Lockwood CM, Stout JR.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010 Jun 17; 7: 51. [Epub ahead of print]
Timing protein intake increases energy expenditure 24 h after resistance training.
Hackney KJ, Bruenger AJ, Lemmer JT.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 May; 42: 998-1003.
Post-exercise carbohydrate plus whey protein hydrolysates supplementation increases skeletal muscle glycogen level in rats.
Morifuji M, Kanda A, Koga J, Kawanaka K, Higuchi M.
Amino Acids. 2010 Apr; 38: 1109-15. Epub 2009 Jul 11.
The effects of creatine and whey protein supplementation on body composition in men aged 48 to 72 years during resistance training.
Eliot KA, Knehans AW, Bemben DA, Witten MS, Carter J, Bemben MG.
J Nutr Health Aging. 2008 Mar; 12: 208-12.
Supplementation with a whey protein hydrolysate enhances recovery of muscle force-generating capacity following eccentric exercise.
Buckley JD, Thomson RL, Coates AM, Howe PR, DeNichilo MO, Rowney MK.
J Sci Med Sport. 2010 Jan; 13: 178-81. Epub 2008 Sep 2 ..
Effect of protein ingestion on energy expenditure and substrate utilization after exercise in middle-aged women.
Benton MJ, Swan PD.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2007 Dec; 17: 544-55.
Impact of differing protein sources and a creatine containing nutritional formula after 12 weeks of resistance training.
Kerksick CM, Rasmussen C, Lancaster S, Starks M, Smith P, Melton C, Greenwood M, Almada A, Kreider R.
Nutrition. 2007 Sep; 23: 647-56.
Effects of resistance training and protein supplementation on bone turnover in young adult women.
Mullins NM, Sinning WE.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 2005 Aug 17; 2: 19.
J Trop Pediatr. 2006 Feb; 52: 34-8. Epub 2005 Jul 13.
Moreno YF, Sgarbieri VC, da Silva MN, Toro AA, Vilela MM.
Milk whey protein decreases oxygen free radical production in a murine model of chronic iron-overload cardiomyopathy.
Bartfay WJ, Davis MT, Medves JM, Lugowski S.
Can J Cardiol. 2003 Sep; 19: 1163-8.
Effects of leucine and whey protein supplementation during eight weeks of unilateral resistance training.
Coburn JW, Housh DJ, Housh TJ, Malek MH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Johnson GO, Donlin PE.
J Strength Cond Res. 2006 May; 20: 284-91.
Systemic indices of skeletal muscle damage and recovery of muscle function after exercise: effect of combined carbohydrate-protein ingestion.
Betts JA, Toone RJ, Stokes KA, Thompson D.
Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Aug; 34: 773-84.
nt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2009 Feb; 19: 79-96.
Cornish SM, Candow DG, Jantz NT, Chilibeck PD, Little JP, Forbes S, Abeysekara S, Zello GA.
College of Kinesiology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada.
utr Res. 2008 Oct; 28: 651-8.
Katsanos CS, Chinkes DL, Paddon-Jones D, Zhang XJ, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR.
Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men.
Tang JE, Moore DR, Kujbida GW, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM.
J Appl Physiol. 2009 Sep; 107: 987-92. Epub 2009 Jul 9.
The effect of bovine whey protein on ectopic bone formation in young growing rats.
Kelly O, Cusack S, Cashman KD.
Br J Nutr. 2003 Sep; 90: 557-64.
Bovine colostrum supplementation during endurance running training improves recovery, but not performance.
Buckley JD, Abbott MJ, Brinkworth GD, Whyte PB.
J Sci Med Sport. 2002 Jun; 5: 65-79.
Effect of bovine colostrum on anaerobic exercise performance and plasma insulin-like growth factor I.
Buckley JD, Brinkworth GD, Abbott MJ.
J Sports Sci. 2003 Jul; 21: 577-88.
















.jpg)











