
About AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
Food supplement based on Arginine α-ketoglutarate
FORMAT
Bottle of 100 cps
COMPOSITION
Arginineα-ketoglutarate
Stabilizer: microcrystalline cellulose
Anti-caking agents: Magnesium stearate
One serving (3 capsules) contains: Arginine α-ketoglutarate 1600 mg
Product features AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
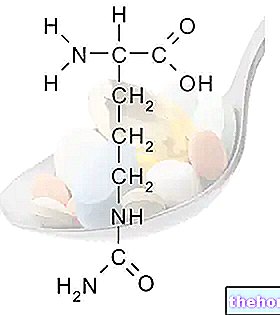
Arginine α-ketoglutarate 1600 mg - this product comes in the form of arginine salt, in which two molecules of arginine are associated with one of alpha keto glutarate. Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid for man; in fact the organism is able to synthesize it endogenously in case of deficiency. However, intense physical activity seems to increase the need for this amino acid, which can still be integrated simply with a healthy diet, since it is easily found in products of animal origin, and in some vegetables such as peanuts. A balanced diet. , in fact, it is able to bring from 4 to 6 grams per day of arginine, a quantity that is satisfactory for most individuals. Arginine is essential in numerous biological reactions; in fact it is part of the urea cycle (facilitating the elimination of waste products that derive from amino acid oxidation), it is a glucogenic amino acid (therefore it is able to supply the body with glucose in case of energy deficiency), has a plastic function (it is part of protein synthesis), and participates in the metabolism of endothelial-derived nitric oxide.

L "alpha ketoglutarate, is a very important ketoacid from a metabolic point of view, as it represents a crossroads between catabolic and anabolic reactions. This molecule is part of the krebs cycle, thus favoring the production of energy, but it is also part of the gluconeogenic process, allowing the synthesis of glucose starting from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids; finally it also falls within the synthesis of some amino acids such as glutamate (hence glutamine), proline and arginine. However, there are numerous studies that are testing the potential of this keto acid, with important results relating to the possibility of preserving the protein component in patients suffering from kidney disease, reducing the urinary secretion of nitrogen, as well as improving the conditions of patients suffering from intestinal diseases and the synthesis of collagen in elderly patients, with consequent prevention against certain pathologies such as osteoporosis, atherosclerosis and arthritis. We are still investigating its direct ability to inhibit cell proliferation and to act in the regulation of cellular function in a similar to a hormone.
Uses in sports AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
For some time now, several sportsmen have been using arginine alpha-ketoglutarate in the hope of obtaining the following results:
- Increased release of growth hormone;
- Increase in lean mass;
- Best sports performance;
- Increase of resistive capacities and maximum force.
These objectives are underpinned by the observed biological effect and in particular by the involvement of this amino acid in the synthesis of nitric oxide.
This powerful biological mediator, in fact, promoting vasodilation, should facilitate the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, allowing to sustain longer and more intensely athletic performance. Furthermore, nitric oxide also seems to be involved in numerous pathways. of intracellular communication, which could lead to the release of a number of hormones.
The metabolic effects of arginine and alpha ketoglutarate could also be useful in energetically supporting the cell, and in improving the muscle recovery phase by preserving from proteolysis and increasing protein synthesis.
Rationale for "use: what is" proven - AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
Although, in theoretical terms, this "ergogenic action could be conceivable, the data present in the scientific literature are somewhat discordant and conflicting, feeding false hopes.
- Release of GH : the literature seems to agree on the inducing effect of GH release by arginine in individuals with secretory deficiencies or following massive intravenous administration.
On the other hand, the studies on the effects of arginine taken orally taken as a secretagogue for GH are rather discordant. Some, in fact, believe it can increase GH levels, while others argue it can even reduce the potential release that would be obtained following the physical performance only.
From the various studies, therefore, a great individual variability in response emerges, which certainly takes charge of one's genetic heritage.
- Metabolic / energetic effect: numerous studies seem to agree that oral supplementation with arginine and alpha-ketoglutarate can support athletic performance, highlighting a delay in the onset of anaerobic metabolism, an increase in the peak of maximum strength and greater resistance to physical exercise .
- Body composition change: Almost all studies agree that oral arginine supplementation does not affect the change in body composition in men. The opposite is instead supported by a study carried out on obese rats.
Method of use recommended by the company
Swallow 3 capsules a day with water or other liquid of your choice, 20-30 minutes before meals or at bedtime, on an empty stomach.
Method of use in sports practice - AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
In studies in which positive results have been obtained in improving athletic performance, the administration of arginine generally varies between 2 and 8 grams per day.
A study, on the other hand, carried out on arginine alpha-ketoglutarate, suggests a dosage of 12g per day divided into 3 dosages for 8 weeks (dosage at which side effects can occur).
However, administration on an empty stomach remains valid, to avoid competitive effects in absorption.
The administration of arginine before going to bed is justified by ONLY one study that shows that the oral intake of 250 mg / kg of arginine aspartate before bedtime can increase GH levels by 60%.
How to optimize its activity - AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
Studies show how the simultaneous administration of creatine and arginine can lead to a better ergogenic boost, with a relative improvement in muscle endurance and maximum peak strength.
At the same time, the intake of arginine and antioxidants seems to increase the anaerobic threshold by 16%, delaying the sensation of fatigue.
Another possible association is that with branched chain amino acids; in fact, a study shows how the supplementation of 2 g of BCAA with 0.5 g of Arginine can reduce proteolysis following intense muscle exercise.
Side Effects AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
The most common side effects, recorded at large doses, are vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal cramps at doses above 9 grams per day.
Massive doses, generally greater than 30 g, can cause nephrotoxicity, hypotension and headaches.
Precautions for use AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate
The product is contraindicated in cases of renal or hepatic pathology, cardiovascular disease and / or hypertension, during pregnancy, during lactation and under the age of 12 and adolescents not yet formed.
This article, elaborated on the critical rereading of scientific articles, university texts and common practice, is for information purposes only and therefore has no medical prescription value. It is therefore always required to consult your doctor, nutritionist or pharmacist before undertaking the use of any supplement.. Learn more about the critical analysis of AAKG - Scitec Nutrition - Arginine α-ketoglutarate.
Pharmacokinetics, safety, and effects on exercise performance of L-arginine alpha-ketoglutarate in trained adult men.
Campbell B, Roberts M, Kerksick C, Wilborn C, Marcello B, Taylor L, Nassar E, Leutholtz B, Bowden R, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Kreider R.
Nutrition. 2006 Sep; 22: 872-81.
J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug; 59 Suppl 1: 91-106.
Biological effects of 2-oxoglutarate with particular emphasis on the regulation of protein, mineral and lipid absorption / metabolism, muscle performance, kidney function, bone formation and cancerogenesis, all viewed from a healthy aging perspective state of the art - review article.Harrison AP, Pierzynowski SG.
Amino Acids. 2009 May; 37: 153-68. Epub 2008 Nov 23.
Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease.
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Marc Rhoads J, Carey Satterfield M, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Yin Y.
Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008 Jan; 11: 50-4.
Growth hormone, arginine and exercise.
Kanaley JA.
Ann Pharmacother. 2001 Jun; 35: 755-64.
L-arginine in the management of cardiovascular diseases.
Cheng JW, Baldwin SN.
Risk assessment for the amino acids taurine, L-glutamine and L-arginine.
Shao A, Hathcock JN.
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008 Apr; 50: 376-99. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Review.
J Nutr. 2007 Jun; 137 (6 Suppl 2): 1681S-1686S.
Arginine and immunity.
Popovic PJ, Zeh HJ 3rd, Ochoa JB.
Chronic but not acute oral L-arginine supplementation delays the ventilatory threshold during exercise in heart failure patients.
Doutreleau S, Mettauer B, Piquard F, Schaefer A, Lonsdorfer E, Richard R, Geny B.
Can J Appl Physiol. 2005 Aug; 30: 419-32.
Use of amino acids as growth hormone-releasing agents by athletes.
Chromiak JA, Antonio J.
Nutrition. 2002 Jul-Aug; 18 (7-8): 657-61. Review.
Arginine and ornithine supplementation increases growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 serum levels after heavy-resistance exercise in strength-trained athletes.
Zajac A, Poprzecki S, Zebrowska A, Chalimoniuk M, Langfort J.
J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Apr; 24: 1082-90.
Arginine and antioxidant supplement on performance in elderly male cyclists: a randomized controlled trial.
Chen S, Kim W, Henning SM, Carpenter CL, Li Z.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Mar 23; 7: 13. [Epub ahead of print]
Creatine, arginine alpha-ketoglutarate, amino acids, and medium-chain triglycerides and endurance and performance.
Little JP, Forbes SC, Candow DG, Cornish SM, Chilibeck PD.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2008 Oct; 18: 493-508.
No effect of short-term arginine supplementation on nitric oxide production, metabolism and performance in intermittent exercise in athletes.
Liu TH, Wu CL, Chiang CW, Lo YW, Tseng HF, Chang CK.
J Nutr Biochem. 2009 Jun; 20: 462-8. Epub 2008 Aug 15.
Int J Sport Nutr. 1993 Sep; 3: 298-305.
Failure of commercial oral amino acid supplements to increase serum growth hormone concentrations in male body-builders.Lambert MI, Hefer JA, Millar RP, Macfarlane PW
. [Effect of L-arginine supplementation on secretion of human growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor in adults]
Fayh AP, Friedman R, Sapata KB, Oliveira AR.
Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2007 Jun; 51: 587-92. Portuguese.
Oral arginine attenuates the growth hormone response to resistance exercise.
Collier SR, Collins E, Kanaley JA.
J Appl Physiol. 2006 Sep; 101: 848-52. Epub 2006 Jun 1.
Adverse gastrointestinal effects of arginine and related amino acids.
Grimble GK.
J Nutr. 2007 Jun; 137 (6 Suppl 2): 1693S-1701S. Review.
Oral arginine does not stimulate basal or augment exercise-induced GH secretion in either young or old adults.
Marcell TJ, Taaffe DR, Hawkins SA, Tarpenning KM, Pyka G, Kohlmeier L, Wiswell RA, Marcus R.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999 Aug; 54: M395-9.
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1999 Mar; 47: 261-6.
Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral L-arginine in normal volunteers.Tangphao O, Grossmann M, Chalon S, Hoffman BB, Blaschke TF.
Branched-chain amino acids and arginine supplementation attenuates skeletal muscle proteolysis induced by moderate exercise in young individuals.
Matsumoto K, Mizuno M, Mizuno T, Dilling-Hansen B, Lahoz A, Bertelsen V, Münster H, Jordening H, Hamada K, Doi T.
Int J Sports Med. 2007 Jun; 28: 531-8. Epub 2007 May 11. Erratum in: Int J Sports Med. 2007 Jul; 28: 63
Effects of Arginine-Based Supplements on the Physical Working Capacity at the Fatigue Threshold.
Camic CL, Housh TJ, Zuniga JM, Hendrix RC, Mielke M, Johnson GO, Schmidt RJ.
J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Apr 9.


.jpg)











.jpg)











