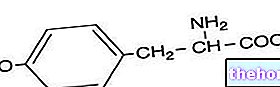
Catecholamines: what they are
Adrenaline and noradrenaline are two hormones secreted by the medullary layer of the adrenal gland and some nerve endings (noradrenaline).
These two hormones are involved in the adrenergic reaction called "FIGHT OR FLIGHT", or fight or run. As can be understood from its name, this reaction has the purpose of preparing the body for an important psychophysical effort in a very short time:
- facilitating the use of muscle energy substrates
- removing catabolites (increases renal flow)
- increasing the energy supply to vital organs
- facilitating the reconstruction of energy reserves
Adrenaline
Functions:
- increases cardiac output
- increases systolic blood pressure
- decreases diastolic blood pressure
- increases muscle blood flow
- increases renal and cutaneous blood flow
- increased glycogenolysis and lipolysis
- peripheral vasoconstriction
- splanchnic vasoconstriction
- vasodilation in the hepatic and muscular districts
- increased metabolism
- bronchiolar dilation
- increased alertness

Adrenaline is secreted in response to very low intensity stimuli and peaks around 60% of VO2 max.
Freddo
Ache
Trauma
Physical efforts
Fear
Hypercapnia
Intense pleasure
Hunger
During a static muscle exercise the secretion of adrenaline prevails over the secretion of norepinephrine.
Noradrenaline
Functions:
- increases cardiac output
- increases the total peripheral resistances
- blood pressure increases
- increases coronary flow
Norepinephrine, on the other hand, is secreted in response to high intensity stimuli and its secretion is proportional to the intensity of the exercise. Around 70-75% of VO2max there is a peak in norepinephrine secretion.
.


Adrenergic activation
The increased secretion of catecholamines prepares the body for a high psychophysical stress:
- increasing bronchodilation
- increasing the number of breaths (tachypnea)
- increasing glycogenolysis
- increasing gluconeogenesis
- increasing lipolysis
- inhibiting glycogen synthesis
- decreasing insulin
- increasing the secretion of glucagon
- increasing glycolysis
THE ADRENERGIC REACTION IN RESPONSE TO "EXERCISE IS ALSO AFFECTED BY:
- DURATION OF EXERCISE (increases with duration of exercise)
- WORKOUT (decreases with training)
- FASTING (increases in fasting states in response to hypoglycemia)
- TEMPERATURE (increases with decreasing temperature)











.jpg)











