Through botany, chemistry, toxicology and biology in general, pharmacognosy implements a recognition and evaluation of the quality of a drug, on the basis of macro and microscopic criteria, operating phytochemical evaluations (active principles and extraction methods most suitable for extracting them ), biological and toxicological.
When it comes to toxicity, it refers to the type of use that particular product must have; the toxicity of a herbal preparation is different from that of a drug, in which the dosage and the limits between drug and poison are very clear. A herbal preparation has a different health projection and does not determine a particular definition of toxicity, because the concentrations and methods of use are different. In the pharmaceutical product c "is the active principle while in the herbal product c" is the phytocomplex.
Pharmacognosy, therefore, is a discipline that deals with the recognition and identification of drugs, together with the evaluation of their qualities. It is an increasingly topical discipline because there is always a greater appeal towards the natural, towards everything that is nature, both for its real effectiveness and simply for an advertising promotion (such as phytocosmetic products, whose functionality is extremely poor if not nothing and recall the natural as a market strategy).
Pharmacognosy is important not only because it must recognize the drug from the point of view of quality, but also because the phytochemical knowledge can be transferred to the formulation of the product, determining its real effectiveness.
Pharmacognosy is important because all known active principles derive from plants and all plants can determine a drug; just think that many plant sources are not known at all or in a very limited way. Even today, for example, articles are published on "Echinacea, Ginger, Horse Chestnut, Oregano, very well-known plants - used as spices in the kitchen or as herbal products and health sources - but which still have a lot to teach us because they don't they know each other thoroughly. Lavender, for example, has always been used for its essential oil, while today its antioxidant properties are particularly known and appreciated; drugs are continually studied and re-evaluated because techniques are being refined more and more. of investigation.
More articles on "What" is and what pharmacognosy studies "
- Pharmacognosy as a multidisciplinary science
- Pharmacognosy
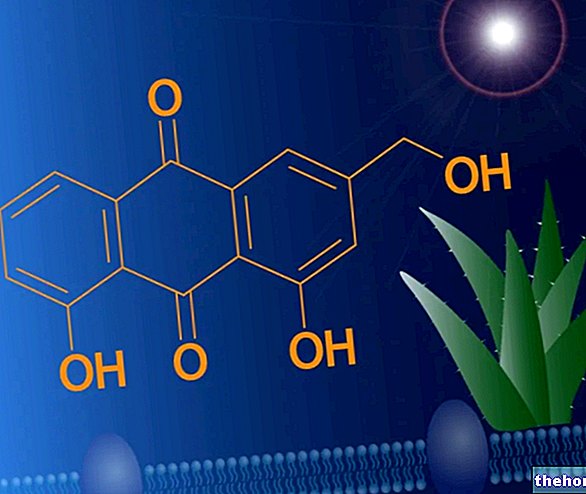
- Bitter orange, mint and aloe vera