Definition
ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) - better known as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - is a neuropsychic developmental disorder in children and adolescents. As can be seen from its name, this disorder is characterized by inattention, impulsivity and hyperactivity.
ADHD occurs in children and adolescents who, in some cases, continue to show symptoms even in adulthood.
Currently, it is possible to distinguish three different clinical forms of the disorder: inattentive, overactive and combined. Patients with ADHD, in the course of their life, can manifest in succession all the aforementioned clinical forms.
Causes
The exact triggering cause of ADHD is unfortunately not yet known. However, several studies have shown that children with ADHD have functional alterations in specific areas of the central nervous system, at the level of which the mechanisms underlying inhibition and self-control are regulated.
However, in the development of ADHD there is also the influence of a certain genetic component, which is associated with exogenous risk factors (such as, for example, any complications during childbirth, the consumption of alcohol or tobacco by the mother during pregnancy, etc.).
Symptoms
The main symptoms of ADHD are the same with which it is usual to characterize the disorder, ie inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity. Patients with ADHD, in fact, are easily distracted, have poor concentration, are impulsive, make decisions without thinking, they are hyperactive and struggle to stay still.
It should be emphasized that this symptomatology is not due to any type of mental retardation, but to an objective difficulty in self-control.
The information on ADHD Medication - Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Deficit is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking ADHD Medication - Attention deficit and hyperactivity.
Medicines
The drugs for the treatment of ADHD currently used are essentially two: methylphenidate (a psychostimulant) and atomoxetine (a non-psychostimulating active ingredient). The first of these active ingredients, however, appears to be the first choice in the treatment of the disorder.
In addition to drug therapy, ADHD patients can also undergo psycho-behavioral supportive therapies, or combination therapies (ie, drug therapies in combination with psycho-behavioral therapies).
In any case, psycho-behavioral therapy is usually undertaken before resorting to pharmacological treatment. In the event that this does not produce the desired effects, the doctor may decide to subject the patient to pharmacological treatment.

The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity. of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment.
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate (Ritalin®) is the drug of choice for the treatment of ADHD in children and adolescents aged between 6 and 18. It is a molecule with psychostimulating and nootropic activity, capable of improving attention and concentration, while reducing the impulsive behaviors of patients with this syndrome.
Methylphenidate is available for oral administration in the form of modified-release hard tablets and capsules.
The dose of drug to be taken must be determined by the physician on an individual basis. However, it is necessary not to exceed the maximum dose of 60 mg of methylphenidate per day.
Depending on the pharmaceutical form used, the drug can be taken in a single dose, or in divided doses throughout the day.
Finally, it is important to remember that methylphenidate should not be used for the treatment of ADHD in adults and children under six years of age.
Atomoxetine
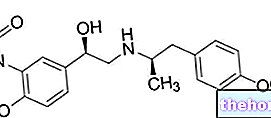
Atomoxetine (Strattera®) is another active ingredient indicated in the treatment of ADHD, which can be used in pediatric patients over six years of age, in adolescents and in adult patients.
Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, capable of improving attention and reducing impulsivity and hyperactivity in ADHD patients. However, the exact mechanism by which this occurs is still not entirely clear.
However, atomoxetine is available for oral administration in the form of capsules or oral solution.
The dose usually used in children and adolescents with a body weight up to 70 kg is 0.5-1.2 mg / kg per day. In adolescents with a body weight greater than 70 kg, on the other hand, the dose usually used is 40-80 mg per day.
Finally, the dose of atomoxetine usually used in adults is 80-100 mg per day.
Modafinil
Modafinil (Provigil®) is actually a nootropic drug used in the treatment of narcolepsy. However, in some cases, it has been used as an off-label drug for the treatment of ADHD, allowing satisfactory results to be obtained in controlling the symptoms of the disease. In particular, modafinil appears to be able to increase the cognitive functions of patients. suffering from this syndrome.
However, its use in the treatment of ADHD has not been officially approved and is at the discretion of the treating physician.