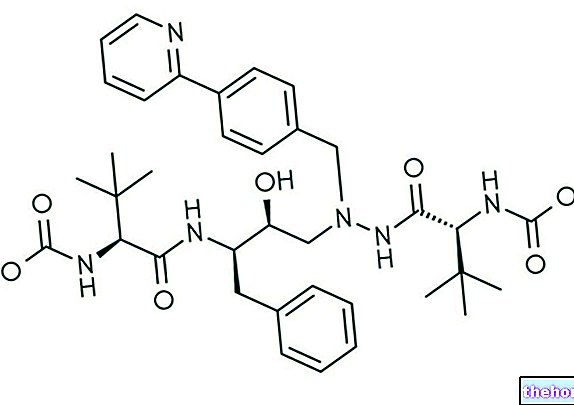
These are compounds of natural origin; more specifically, teicoplanin is produced by the actinomycete Actinoplanes teichomyceticus. To be fair, teicoplanin is not a "single molecule, but it is a compound consisting of a mixture of five different fermentation products (teicoplanin A2-1, teicoplanin A2-2, teicoplanin A2-3, teicoplanin A2-4 , teicoplanin A2-5) produced by the aforementioned bacterium, however having a common central nucleus. What differentiates the different products is one of the side chains (the variable portion is indicated by the letter "R" in the underlying chemical structure).

In order to carry out its antibiotic action, teicoplanin can be administered parenterally (by injection or infusion), or orally.
Teicoplanin-based medicines currently available on the Italian market may contain the active ingredient at different concentrations (200 mg and 400 mg). Those with a lower dosage can be dispensed upon presentation of a repeatable medical prescription (RR), but since they are classified as group A drugs - if the conditions exist (exemption for pathology) - their cost can be reimbursed by the national health system (SSN). On the contrary, medicinal products containing teicoplanin in high doses are classified as group H drugs, require the presentation of a non-repeatable limitative medical prescription (RNRL - sold to the public on prescription from hospitals or specialists) and their cost is fully borne. of the citizen.
Examples of Medicines containing Teicoplanin
- Targocid®
- Targosid®
- Teicoplanin Hikma®
- Teicoplanin Sandoz®
- Teicoplanin Zentiva®
Teicoplanin is an antibiotic used in adults and children (including infants) for the treatment of infections caused by sensitive microorganisms affecting:
- Skin and subcutaneous tissues;
- Bones and joints;
- Heart;
- Lungs;
- Urinary tract;
- Abdomen (peritonitis);
- Blood (bacteremia and septicemia caused by any of the infections listed above).
Furthermore, teicoplanin can be used to counter some intestinal infections induced by Clostridium difficile (in this case, the active ingredient is administered orally).
Did you know that ...
Teicoplanin is one of the antibiotics that can be used in the treatment of infections caused by strains Staphylococcus aureus methicillin-resistant (MRSA).
based on teicoplanin, you should tell your doctor if you have one or more of the following conditions:- If you are allergic to vancomycin (another glycopeptide with antibiotic action), since the risk of being allergic to teicoplanin is also high;
- If you have suffered from red neck syndrome;
- If you have kidney problems;
- If you have thrombocytopenia;
- If you are taking drugs that can cause hearing and / or kidney damage (ototoxic drugs and nephrotoxic drugs).
In any case, before taking any type of teicoplanin-based medicine, it is necessary to inform the doctor of one's health conditions, making him aware of the possible presence of ailments or diseases of any kind, even if not mentioned in the above list.
During treatment with teicoplanin, the doctor may decide to have the patient have regular blood tests and tests to check hearing and kidney function, especially if the treatment will last for a long time or if there are pre-existing kidney problems.
Please Note
The administration of teicoplanin may cause undesirable effects which may affect the ability to drive and / or use machines. Should this occur, such activities should be avoided.
;In any case, before starting teicoplanin therapy, you should tell your doctor if you are taking, or have recently been taking, any medications or products of any kind, including non-prescription drugs (SOP ), over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, herbal and phytotherapeutic products and homeopathic products.
experiencing undesirable effects that differ in type and intensity, or not showing them at all.Listed below are some of the side effects that may occur during teicoplanin therapy.
Serious side effects
Treatment with teicoplanin can cause serious side effects which require immediate discontinuation of administration. These effects consist of:
- Severe and sudden allergic reactions;
- Flushing in the upper body
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis;
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS).
Other serious side effects that require prompt medical attention are:
- Bronchospasm;
- Agranulocytosis;
- Decrease in all blood cells
- Alterations in kidney function;
- Seizures.
Other side effects
Other possible side effects induced by treatment with teicoplanin are:
- Rash and skin rashes;
- Itching;
- Fever;
- Ache;
- Malaise and vomiting;
- Headache;
- Dizziness
- Loss of hearing, dizziness and / or tinnitus;
- Decrease in the number of platelets;
- Increased blood levels of liver enzymes;
- Increased blood levels of creatinine;
- Abscesses;
- In case of parenteral administration, reactions at the administration site.
Overdose
Since teicoplanin medicines are normally administered in a hospital setting by doctors or healthcare professionals, overdose is unlikely, but not impossible. There are no specific antidotes, therefore, in the event of an overdose, treatment will be symptomatic and supportive.
. The target of teicoplanin is different from that of beta-lactam antibiotics; in detail, the synthesis of bacterial peptidoglycans is blocked by the specific bond with the D-alanyl-D-alanine residues.Unfortunately, it should be noted that some bacteria are able - through different mechanisms of action - to develop resistance to this active principle.
or intravenously, or by intravenous infusion (administered by a doctor or healthcare professional), as well as it can be taken orally. Dosage and method of use of medicines based on teicoplanin must be established by the doctor according to the type of infection that needs to be treated. The doses usually used in therapy will however be reported below.
For adults and children 12 years of age or older:
- Infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, lungs and urinary tract:
- Initial dose (first three doses): 400 mg every 12 hours (corresponding to 6 mg per kg of body weight) given by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
- Maintenance dose: 400 mg (corresponding to 6 mg per kg body weight) administered once daily by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
- Infections of the bones and joints and of the heart:
- Initial dose (for the first 3-5 doses): 800 mg (corresponding to 12 mg per kg of body weight), administered every 12 hours by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
- Maintenance dose: 800 mg (corresponding to 12 mg per kg of body weight), administered once daily by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
- Intestinal infections caused by Clostridium difficile:
- In these cases, teicoplanin must be taken orally. The usual dose used is 100-200 mg twice daily for 7-14 days.
For children aged 2 months to 12 years, the usual dosage is as follows:
- Initial dose (for the first 3 doses): 10 mg per kg of body weight, given every 12 hours by injection into a vein.
- Maintenance dose: 6-10 mg per kg of body weight, given once daily by injection into a vein.
For infants (from birth to 2 months of age), however, the dosages usually used are the following:
- Initial dose (on the first day): 16 mg per kg of body weight given by drip infusion into a vein.
- Maintenance dose: 8 mg per kg of body weight, given as a drip infusion into a vein once a day.
In patients with kidney problems and in patients on peritoneal dialysis the doses administered may be reduced. The doctor will decide how and how much drug to administer.
?The use of teicoplanin during pregnancy exposes the fetus to a potential risk of kidney and inner ear damage. Therefore, the active ingredient should be used during gestation only if strictly necessary and only under the strict supervision of the doctor.
Regarding breastfeeding, it is not known whether teicoplanin is excreted in breast milk. For this reason, if treatment with the active ingredient in question is necessary, the doctor will decide whether breastfeeding can be continued. or whether it should be suspended.