" first part
The MET
It is "a" unit of metabolic equivalent and is used to estimate the metabolic cost of a physical activity according to the relationship:
1 MET = 3.5 ml of oxygen consumed per kg of body weight per minute
MET, plural METS, is used by various cardio fitness equipment, including TECHNOGYM to indicate the metabolic cost of exercise.
Example: metabolic cost of exercise 8 METS
VO2 = 8 * 3.5 = 28 mlO2 / Kg
Assuming that the subject in question is a reference 29-year-old male (VO2 max = 40 mlO2 / kg), the percentage of VO2max at which he is training is:
100 * 28/40 = 70% of VO2max
Performance Index (IP)
THE PERFORMANCE INDEX (IP) was devised by Technogym (R) for a synthetic and easily comparable evaluation of the training performed.
This index refers to a rating scale ranging from 0 to 99. The higher the value, the greater the aerobic capacity.
An increase in the performance index means that, with the same HR, you are able to perform an exercise at a higher intensity.
Below are some of the simpler tests for determining maximum aerobic power, some of which can be performed independently.
Test to Measure VO2Max
Cooper test
- Drive as far as possible in 12 minutes after warming up.
- Materials needed: notes-pen, measured track
- VO2max (ml * kg-1 * min-1) = 35.97 * (miles traveled) - 11.29 (E.g .: rides 1.2 miles: VO2max = 35.97 * 1.2 -11.29 = 31.9)
- VO2 max in ml / min / kg = (Distance traveled in meters - 504.9) / 44.73
- note: Cooper's study is limited to values between 29 and 60 ml / min / kg

Simplified variant of the Cooper test:
- Materials needed: notes-pen, measured track
- Protocol: Drive as far as possible in a set time after warming up.
RESULTS
For more than 10 minutes:
VO2max = (distance in meters + (30 x time in minutes)) / (5 x time in minutes)
For less than 10 minutes:
VO2max = [(distance in meters + (30 x time in minutes)) / ((5 x time in minutes) + 5)]
Texts of the Way
2 Km Walk Test (Oja-Laukkanen)
- It is a field submaximal test
- The VO2 max value is obtained through a "sex specific predictive equation."
- Reliable, Validated and Repeatable
- Suitable for normally active subjects between the ages of 20 and 65 who do not have disabilities or pathologies such as to prevent or limit fast walking and / or who do not take drugs that alter the normal heart rate response to exercise
- Also suitable for overweight subjects who meet the same criteria
CONDITIONS THAT CONTRAINDICATE THE PERFORMANCE OF THE TEST: Myocardial infarction in the last 12 months - Uncontrolled arterial hypertension - Coronary heart disease - Pulmonary diseases Hyperthyroidism refractory to pharmacological treatments - Arrhythmia triggered by physical activity - Undiagnosed pain in the upper limbs, shoulders or chest. during physical exertion - Other severe symptoms triggered by physical exertion (headache, dizziness, dyspnoea, asthma) - Taking heart rhythm modifying drugs (eg beta blockers) - Osteo-articular pathologies in the lower limbs
- Materials needed: Measured flat route (2 Km) Heart rate monitor (optional) Stopwatch
PROTOCOL:
- General rules: Carry out the test only in adequate atmospheric conditions (mild temperature, no rain or wind). the day before, no alcohol on the day of the test and the day before, comfortable clothes and walking shoes)
- Warm-up: (a few minutes of walking at moderate speed followed by 100-200 meters at high speed to adapt to the pace that must be maintained during the execution of the test. Rest for a few minutes before performing the test)
- Carrying out the test: The subject must walk at a constant pace and at the maximum sustainable walking speed in the absence of signs of physical discomfort: "Walk as fast as you can, but do not put your health at risk". The walking speed corresponding to 80% of the theoretical maximum heart rate allows the greater precision of the predictive calculation of VO2max.
- Travel time of 2 Km (m / s)
- Heart rate (HR) recorded at the end of the test (beats / min)
- Age (years)
- BMI (ratio between weight (Kg) and height (m) squared: Kg / m). Example, the BMI of a 180 cm tall subject weighing 80 kg is equal to: 80/2 = 24.7
RESULTS:
- Men: VO2max (ml / Kg / min) 184.9 - 4.65 (time) - 0.22 (HR) - 0.26 (age) - 1.05 (BMI)
- Women: VO2max (ml / Kg / min) 116.2 - 2.98 (time) - 0.11 (HR) - 0.14 (age) - 0.39 (BMI)
CYCLE-ERGOMETER TEST
Astrand-Rhyming Test
- Materials needed: Cycle ergometer Chronometer Frequency meter (optional) Metronome
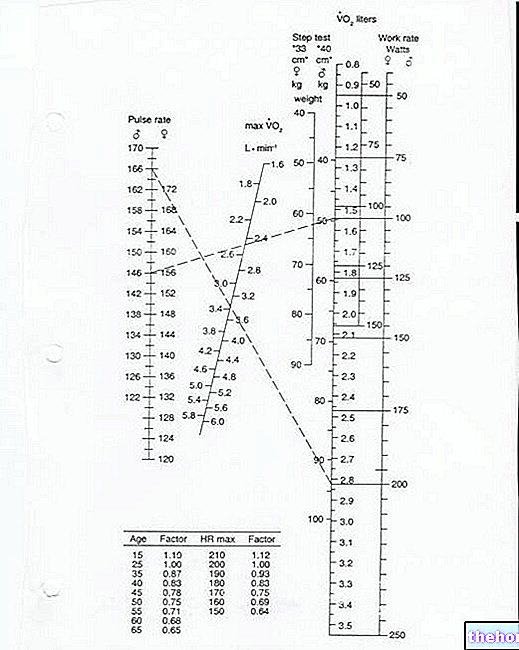
- Protocol: l Adjust the saddle height and handlebar to the right height for the subject l Pedaling speed 50 RPM l Initial load at 150, 100 or 75 W for the very, fairly and poorly trained respectively Correction factor for age, by which to multiply the Vo2 obtained from the nomogram (fig)
Test to determine aerobic power
As we have already said, direct determination of aerobic power requires expensive equipment and trained personnel. For this reason, indirect tests have been developed, which are less expensive, faster and easier to carry out. It is possible to divide these tests into two large families: MAXIMUM TESTS AND SUBMAXIMAL TESTS.
= at a level where fatigue or the appearance of symptoms prevent a further increase
= at a level of oxygen consumption that does not allow any increase (VO2max)
= at a heart rate level that does not allow for any increase (HR max)
less effort: intensity of the load does not lead to the achievement of the O2 plateau (VO2max)
The level reached can be 85% of the theoretical maximum heart rate
or the achievement of a predetermined exercise intensity
or of a certain intensity in the effort perception scale.
Warning: The arbitrarily determined target heart rate (220-age) may be maximum or near for some, and well below it for others.
EPOC: extra oxygen consumption after exercise; Dental extraction and VO2max



.jpg)