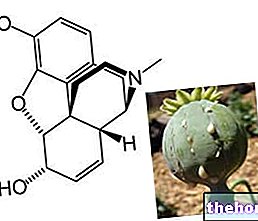
From a chemical point of view, codeine can be considered as a derivative of morphine (another natural alkaloid present in the opium poppy).
Despite its availability in nature, codeine is currently mainly produced synthetically.
This active ingredient is used in the pharmaceutical field for its analgesic properties (for this purpose it is generally used in combination with other active ingredients, such as NSAIDs and paracetamol) and antitussive (used in the form of dihydrocodeine, both alone and in combination with other ingredients active; or in the form of neutral hydrobromide of codeine dihydrate in association with ivy extracts - Hedera elix).
Codeine is available in medicines for oral use (tablets, effervescent tablets and granules, oral drops, syrup) and rectal (suppositories).
All the aforementioned medicines require a medical prescription in order to be dispensed, repeatable (RR) or non-repeatable (RNR) depending on the case. Some are classified as class A drugs, so their cost can be reimbursed by the National Health System (it may still be necessary to pay a ticket), while others are classified as class C drugs, therefore, their cost is fully borne by the citizen.